ASTM D2949-01a(2008)e1
(Specification)Standard Specification for 3.25-in. Outside Diameter Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Drain, Waste, and Vent Pipe and Fittings
Standard Specification for 3.25-in. Outside Diameter Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Drain, Waste, and Vent Pipe and Fittings
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers requirements and test methods for materials, dimensions and tolerances, deflection load, crush resistance, hydrostatic-burst resistance, flattening resistance, impact resistance, and solvent cement. A form of marking is also included. Plastic which does not meet the material requirements specified in Section 5 is excluded.
Note 1—This specification was formerly issued under the title, 3-in. Thin Wall Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Drain, Waste, and Vent Pipe and Fittings.
Note 2—Techniques for making solvent-cement joints are given in Practice D2855.
1.2 The text of this specification references notes, footnotes, and appendixes which provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of the specification.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 7, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
´1
Designation: D2949 – 01a (Reapproved 2008)
Standard Specification for
3.25-in. Outside Diameter Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic
Drain, Waste, and Vent Pipe and Fittings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2949; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
´ NOTE—6.6 was editorially corrected in March 2010.
1. Scope D1599 TestMethodforResistancetoShort-TimeHydraulic
Pressure of Plastic Pipe, Tubing, and Fittings
1.1 This specification covers requirements and test methods
D1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to
formaterials,dimensionsandtolerances,deflectionload,crush
Plastics
resistance, hydrostatic-burst resistance, flattening resistance,
D1784 Specification for Rigid Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC)
impact resistance, and solvent cement. A form of marking is
Compounds and Chlorinated Poly(Vinyl Chloride)
also included. Plastic which does not meet the material
(CPVC) Compounds
requirements specified in Section 5 is excluded.
D2122 Test Method for Determining Dimensions of Ther-
NOTE 1—This specification was formerly issued under the title, 3-in.
moplastic Pipe and Fittings
ThinWallPoly(VinylChloride)(PVC)PlasticDrain,Waste,andVentPipe
D2152 Test Method for Adequacy of Fusion of Extruded
and Fittings.
Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Pipe and Molded Fittings by
NOTE 2—Techniques for making solvent-cement joints are given in
Acetone Immersion
Practice D2855.
D2412 Test Method for Determination of External Loading
1.2 Thetextofthisspecificationreferencesnotes,footnotes,
Characteristics of Plastic Pipe by Parallel-Plate Loading
and appendixes which provide explanatory material. These
D2444 Test Method for Determination of the Impact Resis-
notesandfootnotes(excludingthoseintablesandfigures)shall
tance of Thermoplastic Pipe and Fittings by Means of a
not be considered as requirements of the specification.
Tup (Falling Weight)
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
D2564 Specification for Solvent Cements for Poly(Vinyl
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Piping Systems
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
D2855 Practice for Making Solvent-Cemented Joints with
and are not considered standard.
Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Pipe and Fittings
1.4 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the
D3311 Specification for Drain, Waste, and Vent (DWV)
test methods portion, Section 7, of this specification: This
Plastic Fittings Patterns
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
F402 Practice for Safe Handling of Solvent Cements, Prim-
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
ers, and Cleaners Used for JoiningThermoplastic Pipe and
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health
Fittings
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita-
F412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
tions prior to use.
F1498 Specification for Taper Pipe Threads 60° for Ther-
moplastic Pipe and Fittings
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3. Terminology
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
3.1 Definitions—Definitions are in accordance with Termi-
nology F412, and abbreviations are in accordance with Termi-
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F17 on Plastic nology D1600, unless otherwise specified.
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.63 on DWV.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2008. Published February 2009. Originally
4. Significance and Use
´1
approved in 1971. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as D2949–01a . DOI:
4.1 The requirements of this specification are intended to
10.1520/D2949-01AR08.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
provide pipe and fittings suitable for drainage of sewage and
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
certain other liquid wastes where toughness, resistance to
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
´1
D2949 – 01a (2008)
deterioration from water and chemicals, flattening and aging 6.2.2.4 Fittings Dimensions—The dimensions of fittings
resistance, and strong tight joints are required. coveredbythisspecificationshallmeettherequirementsgiven
4.2 When joining 3.25-in. outside diameter PVC DWV in Table 3 through Table 11.
piping to 3-in. Schedule 40 PVC DWV piping, it is necessary
NOTE 4—Additional fittings in IPS dimensions are included in Speci-
to use either reducer bushings or increasers, as shown in the
fication D3311.
tables at the end of the text, due to the differences in pipe
6.3 Deflection Load and Crush Resistance:
outside diameters.
6.3.1 Pipe—The pipe shall support a minimum load of 600
NOTE 3—Industrial waste disposal lines should be installed only with
lbf/linear ft (810 N/m) at 15% deflection of the original
the specific approval of the cognizant building code authority since
diameter (deflection load), and shall deflect 60% of the
chemicals not commonly found in drains and sewers, and temperatures in
original diameter (crush resistance) without cracking, rupture,
excess of 160°F (70°C), may be encountered.
or other visible evidence of failure when tested in accordance
5. Materials
with7.4.Theminimumpipestiffnessat5%deflectionshallbe
115 lbf/in.·in. (800 kPa).
5.1 Basic Materials—Pipe and fittings shall be made from
6.3.2 Fittings—Individual fittings unassembled shall with-
virgin poly (vinyl chloride) compounds meeting the require-
stand a minimum load of 1000 lbf/ft (1350 N/m) of centerline
mentsofClass12454,asdefinedanddescribedinSpecification
length without cracking or other visible evidence of failure
D1784.
when tested in accordance with 7.4.This requirement does not
5.2 Rework Material—The manufacturer shall use only his
apply to inline fittings.
owncleanpipeorfittingreworkmaterialandthepipeorfitting
6.4 Minimum Hydrostatic Burst Pressure—When tested at
produced shall meet all the requirements of this specification.
73°F (23°C) in accordance with 7.5, the minimum burst
5.3 Solvent Cement—The solvent cement shall meet the
pressure of pipe shall be 500 psi (3.45 MPa) and the minimum
requirements of Specification D2564.
burst pressure of fittings shall be 200 psi (1.38 MPa).
6. Requirements
NOTE 5—The minimum burst pressure for fittings are lower than that
6.1 General—The pipe and fittings shall be homogeneous for pipe because the geometry is such, particularly area and radii, that the
stresses produced in the wall of the fitting are higher than those produced
throughoutandfreeofvisiblecracks,holes,foreigninclusions,
in pipe tested at the same internal pressures. This requirement is intended
or other injurious defects. The pipe shall be as uniform as
only for the purpose of quality control to ensure that the pipe and fittings
commercially practicable in color, opacity, density, and other
have no weak areas, particularly at flow and weld lines.
physical properties.
6.5 Flattening Resistance—The average decrease in inside
6.1.1 The requirements in this section are intended only for
use as quality control tests, not as simulated service tests. diameters of pipe and fittings shall not exceed 10% when
tested in accordance with 7.6 (Note 3).
6.2 Dimensions and Tolerances—All dimensions shall be
measured in accordance with Test Method D2122. All toler- 6.6 Impact Resistance—The minimum impact resistance,
ances shall meet the requirements of Tables 1-11 unless whentestedatthetimeofmanufacture,shallbe50ft·lbf(67.79
otherwise specified. J) at 73°F (23°C) for pipe and 20 ft·lbf (27.12 J) at 73°F for
6.2.1 Pipe: fittings.TestinaccordancewithTestMethodD2444usingTup
C and Holder A for pipe and Tup A and Holder B for fittings.
6.2.1.1 Pipe Dimensions—The outside diameters and wall
thicknesses of the pipe shall meet the requirements of Table 1. Use a 12-lb (5-kg) tup for testing pipe and fittings. Test
couplings cemented to short pieces of pipe and allowed to dry
6.2.1.2 Pipe Length—The pipe shall be in either 10 or 20-ft
or 3 or 6-m lengths, unless otherwise specified with allowable for 24 h.
tolerance of + ⁄2 in., 0 in. or +13 mm, −0 mm. 6.6.1 Test 10 specimens. When 9 or 10 specimens pass,
6.2.2 Fittings: accept the lot. When 2 or more specimens fail, test 10
6.2.2.1 Fittings-Socket Dimensions—The socket dimen- additional specimens. When 17 of 20 specimens tested pass,
sions of fittings shall meet the requirements given in Table 2. accept the lot. When 4 or more of 20 specimens fail, test 20
additional specimens. When 32 of 40 specimens pass, accept
6.2.2.2 Fittings Laying Length Dimensions—The laying
lengthdimensionsoffittings,shallconformtotherequirements the lot. When 9 or more of 40 specimens fail, the lot does not
meet the requirements of this specification.
given in Table 3 through Tables 11.
6.2.2.3 Transition Adapters—The dimensions of adapters 6.6.2 Failure of the test specimen shall be shattering or any
for connecting plastic pipe to cast iron hubs shall conform to crack or break extending entirely through the pipe wall and
the dimensions given in Table 4. visible to the unaided eye.
TABLE 1 Dimensions and Tolerances for Outside Diameters and Thicknesses of PVC 3.25-in. Outside Diameter Plastic Drain, Waste,
and Vent Pipe, in. (mm)
A
Nominal Outside Diameter Wall Thickness
Pipe Size, Tolerance on Out-of-Roundness
Average Min Tolerance
in. Average (maximum minus minimum)
3.25 3.250 (82.56) 60.008 (60.20) 0.030 (0.76) 0.125 (3.18) +0.020 (+0.50)
A
Theminimumisthelowestwallthicknessofthepipeatanycrosssection.Themaximumpermittedwallthickness,atanycrosssection,istheminimumwallthickness
plus the stated tolerance.
´1
D2949 – 01a (2008)
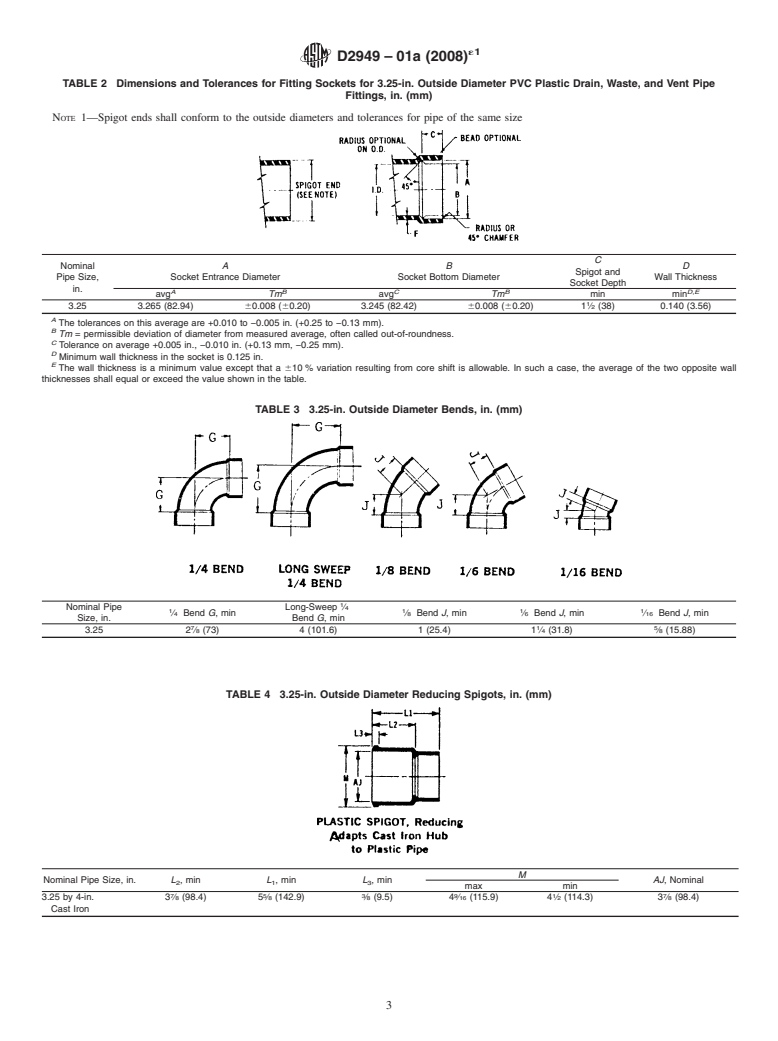
TABLE 2 Dimensions and Tolerances for Fitting Sockets for 3.25-in. Outside Diameter PVC Plastic Drain, Waste, and Vent Pipe
Fittings, in. (mm)
NOTE 1—Spigot ends shall conform to the outside diameters and tolerances for pipe of the same size
C
Nominal A B D
Spigot and
Pipe Size, Socket Entrance Diameter Socket Bottom Diameter Wall Thickness
Socket Depth
in.
A B C B D,E
avg Tm avg Tm min min
3.25 3.265 (82.94) 60.008 (60.20) 3.245 (82.42) 60.008 (60.20) 1 ⁄2 (38) 0.140 (3.56)
A
The tolerances on this average are +0.010 to −0.005 in. (+0.25 to −0.13 mm).
B
Tm = permissible deviation of diameter from measured average, often called out-of-roundness.
C
Tolerance on average +0.005 in., −0.010 in. (+0.13 mm, −0.25 mm).
D
Minimum wall thickness in the socket is 0.125 in.
E
The wall thickness is a minimum value except that a 610 % variation resulting from core shift is allowable. In such a case, the average of the two opposite wall
thicknesses shall equal or exceed the value shown in the table.
TABLE 3 3.25-in. Outside Diameter Bends, in. (mm)
Nominal Pipe Long-Sweep ⁄4
1 1 1 1
⁄4 Bend G,min ⁄8 Bend J,min ⁄6 Bend J,min ⁄16 Bend J,min
Size, in. Bend G,min
7 1 5
3.25 2 ⁄8 (73) 4 (101.6) 1 (25.4) 1 ⁄4 (31.8) ⁄8 (15.88)
TABLE 4 3.25-in. Outside Diameter Reducing Spigots, in. (mm)
M
Nominal Pipe Size, in. L,min L,min L,min AJ, Nominal
2 1 3
max min
7 5 3 9 1 7
3.25 by 4-in. 3 ⁄8 (98.4) 5 ⁄8 (142.9) ⁄8 (9.5) 4 ⁄16 (115.9) 4 ⁄2 (114.3) 3 ⁄8 (98.4)
Cast Iron
´1
D2949 – 01a (2008)
TABLE 5 3.25-in. Outside Diameter Reducing Sanitary Tee and 45° Wyes, in. (mm)
Sanitary Tee Reducing 45° Wye Reducing Single and Double
Nominal Pipe Size, in.
G,min G,min G,min G,min G,min G,min
1 2 3 1 2 3
15 3 3 3 1 17
3.25 by 3.25 by ⁄16 (23.8) 1 ⁄4 (44.5) 2 ⁄16 (55.6) ⁄8 (9.5) 3 ⁄4 (82.5) 3 ⁄32 (89.7)
1 ⁄2-in. IPS
3 1 3 1 11
3.25 by 3.25 by 2-in. IPS 1 ⁄8 (34.9) 2 (50.8) 2 ⁄4 (57.2) ⁄8 (9.5) 3 ⁄4 (82.5) 3 ⁄16 (93.6)
TABLE 6 3.25-in. Outside Diameter Bushings in. (mm)
7.3.1 For referee purposes, conduct tests in the standard
laboratory atmosphere of 73.4 6 3.6°F (23 6 2°C) and 50 6
5% relative humidity.
7.3.2 For routine quality control testing, conduct tests at the
temperature and humidity of the manufacturers testing area.
7.4 Deflection Load and Crush Resistance—Measure the
deflection load and crush resistance of pipe and fittings in
accordance with Test Method D2412. In the test for pipe note
the load when the initial inside diameter is reduced by 5%
(pipestiffness),by15%(deflectionload),andcontinuethetest
until the diameter is reduced by 60% of its original value
(crush resistance). The rate of head approach shall be 0.20 to
Nominal Pipe Style 1
Size, in. L,min CM,min R,min
0.25 in./min (5.1 to 6.4 mm/min). Each specimen shall meet
1 7 1 3
3.25 by 1 ⁄2-in. IPS 1 ⁄8 (47.6) 1 ⁄8 (28.6) ⁄8 (9.5)
the requirements of 6.3.1.
7 3
3.25 by 2-in. IPS 1 ⁄8 (47.6) 1 (25.4) ⁄8 (9.5)
3 1
3.25 by 3-in. IPS 1 ⁄4 (44.5) ⁄4 (6.4) 0 (0)
7.4.1 Fitting Test Specimens—Test three complete fittings.
Shim fittings to give full centerline contact with platens.
Fittingshavingnonuniformdiameterssuchasreducersshallbe
considered acceptable when the wall thickness at all points is
6.7 Threads—For all fittings having taper pipe threads,
equal to or greater than the wall thickness of pipe of the same
threads shall conform to Specification F1498 and be gaged in
material and diameter that meets the crush resistance require-
accordance with 7.7.
ments. Each specimen shall meet the requirements of 6.3.2.
6.8 Extrusion Quality—The pipe shall not flake or disinte-
7.4.2 Procedure—Terminate the test when the inside diam-
grate when tested in accordance with Test Method D2152.
eter of pipe test specimens is reduced to 40% of its original
7. Test Methods value or the pipe cracks or shows other visible evidence of
failure. Terminate the test on fittings when the load reaches
7.1 Sampling—Take a random sample from each lot or
1000 lbf/ft (1350 N/m) of centerline length. Observe the load
shipment of the pipe and fittings sufficient to determine
and deflection at the first evidence of cracking, if any. Record
conformancewiththisspecification.About40ft(12m)ofpipe
location and type of failure.
are required to make the tests prescribed. The number of
fittings required varies depending on the size and type of 7.4.3 Calculation—For pipe, divide the load in pounds-
force or newtons at 15% deflection (deflection load) and also
fitting.
7.2 Conditioning— at failure (crush resistance), if such occurr
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.