ASTM C1354-96
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Strength of Individual Stone Anchorages in Dimension Stone
Standard Test Method for Strength of Individual Stone Anchorages in Dimension Stone
SCOPE
1.1 This test method provides procedures for determining the ultimate strength of an assembly consisting of stone with mechanical anchor (anchorage). Load is applied, seperately, perpendicular to the surface of the panel and parallel to the surface of the panel. this test is intended to represent the interaction of the anchor with the stone panel. However, influence of the backup structure on the strength of the assemblies is not included.
1.2 this method is applicable to stone panels supported by mechanical anchors.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C 1354 – 96
Standard Test Method for
Strength of Individual Stone Anchorages in Dimension
Stone
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C 1354; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.1.2 anchorage, n—assembly consisting of a stone panel
with a mechanical anchor.
1.1 This test method provides procedures for determining
3.1.3 panel, n—cut stone with large face dimensions in
the ultimate strength of an assembly consisting of stone with
relation to its thickness, for placement in a building structure or
mechanical anchor (anchorage). Load is applied, separately,
frame assembly.
perpendicular to the surface of the panel and parallel to the
surface of the panel. This test is intended to represent the
4. Summary of Test Method
interaction of the anchor with the stone panel. However,
4.1 Test specimens consisting of a stone panel sample and a
influence of the backup structure on the strength of the
mechanical anchor are fabricated in the same manner and of
assemblies is not included.
the same materials as their intended construction uses. The
1.2 This method is applicable to stone panels supported by
mechanical anchor is connected to a test support. A test load is
mechanical anchors.
applied perpendicular or parallel to the face of the stone panel.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
The test load is applied gradually using a calibrated test
standard.
machine; load is increased until the stone or the mechanical
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
anchor fails.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4.2 The load at failure and mode of failure of each test
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
specimen is observed and recorded. The test as described above
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
is repeated five times for each combination of stone and anchor
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
to be tested and for each direction of load to be tested.
2. Referenced Documents
5. Significance and Use
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5.1 This test method is intended to provide information
C 1242 Guide for Design, Selection, and Installation of
from which applicable design data can be determined for a
Exterior Dimension Stone Anchors and Anchoring Sys-
2 given anchor used to support a dimension stone panel. The
tems
3 strength of a limited length of anchor may be related to a longer
E 4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
length of support when the flexibility of the support is properly
E 575 Practice for Reporting Data from Structural Tests of
considered by the designer. Refer to Guide C 1242.
Building Constructions, Elements, Connections, and As-
semblies
6. Testing Machine
6.1 The testing machine shall conform to the requirements
3. Terminology
of Practices E 4.
3.1 Definitions:
6.2 The load from the testing machine shall be applied
3.1.1 anchor, n—in general, a metal shape inserted into a
through appropriate devices (a lubricated ball-and-socket or a
slot or hole in the stone panel that provides for the transfer of
lubricated universal joint) to apply direct tension to the test
loads from the stone to the building structure, either directly or
specimen without bending.
through an intermediate structure.
7. Support Frame and Loading Device
7.1 The support frame (excluding the anchor to be tested)
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C-18 on
shall have sufficient strength to not yield while supporting
Dimension Stone and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C18.01.
maximum applied load. In addition, the support frame shall be
Current edition approved Oct. 10, 1996. Published December 1996.
sufficiently stiff to limit deflection to less than 1 mm (0.04 in.)
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.07.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01. at maximum test load and to limit rotation to less than 2°.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
C 1354
FIG. 1A Edge of Panel Supported by Tab Inserted into Kerf in Edge of Panel
FIG. 1B Edge of Panel Supported by Pin Installed into Hole Drilled into Edge of Panel
FIG. 1 Setup for Testing Connection in Edge of Sample—Test Procedure A
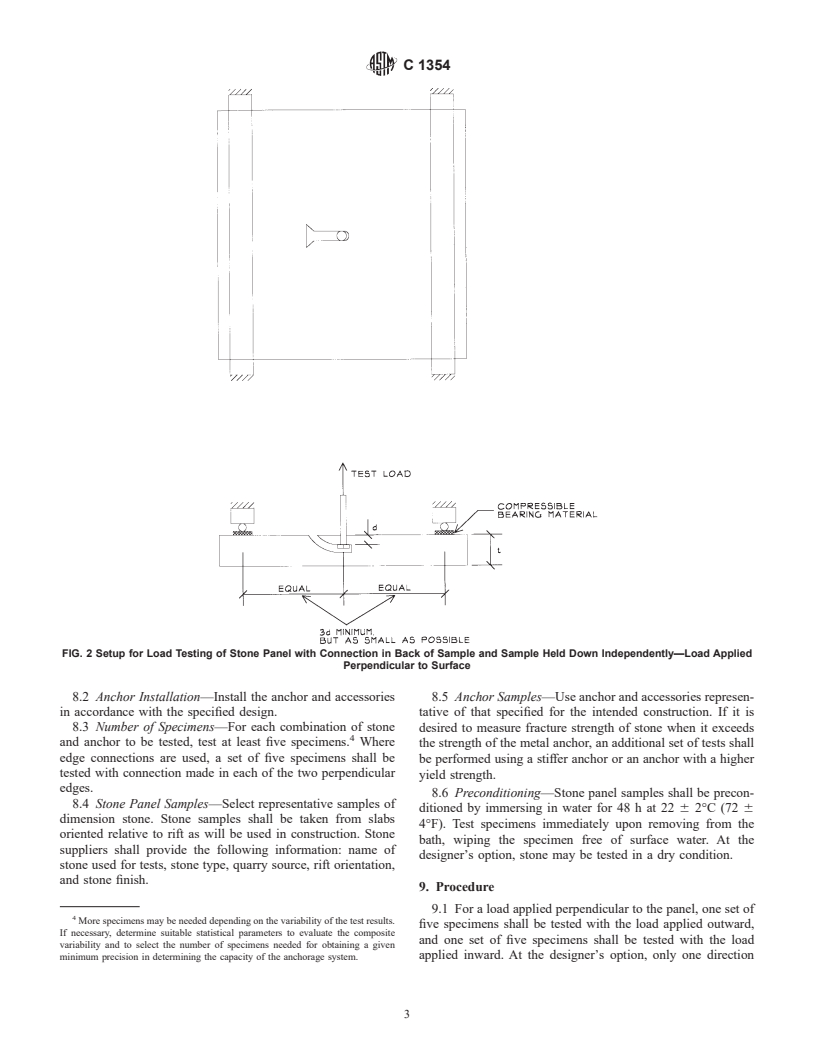
7.2 For load perpendicular to the surface of the stone panel: independent anchors as shown in Fig. 2 or by the device used
7.2.1 A rubber pad or a setting gypsum bed shall be used to apply load as shown in Fig. 3.
between the stone and the loading or restraint surface to avoid 7.3 For load parallel to the surface of the stone panel:
concentration of stress in the surface of the stone sample. 7.3.1 The stone panel sample is restrained in the plane of the
7.2.2 A frame to support a stone sample with anchor in the panel while a test load is applied parallel to the plane of the
side edge of the stone is shown in Fig. 1. Fig. 1 represents panel as shown in Fig. 4. The area beneath the anchor shall be
outward loading on a single stone panel. At the designer’s kept unsupported to prevent restraint of spalls that may
option, two stone panels can be tested on a single split anchor. artificially increase the strength. The surface between the
7.2.2.1 The test specimen is supported at one end by the loading plate and the stone panel sample shall be lubricated.
anchor. The anchor shall be attached to the support frame in the
8. Test Specimens
same way it will be attached to the backup structure in
construction. The sample of stone is supported at the opposite 8.1 Anchorage System—The anchorage system shall be
end by a 25 mm (1 in.) diameter rod. representative of the type to be used in field construction and
7.2.2.2 The load from the testing machine is applied to the shall include the anchor to be used and all accessories normally
stone sample through a 25 mm (1 in.) diameter rod, located as required to attach the anchor to the backup structure. If sealant,
close as possible to the anchor that supports the stone but at a epoxy, or other form of kerf filler is specified to be used in field
distance not less than the thickness of the panel.
construction, the bond between the sealant, epoxy, or other
7.2.3 A frame to test a stone sample with anchor in back of form of kerf filler shall be intentionally prevented in the test
the stone and the load applied
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.