ASTM A291-95(1999)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Steel Forgings, Carbon and Alloy, for Pinions, Gears and Shafts for Reduction Gears
Standard Specification for Steel Forgings, Carbon and Alloy, for Pinions, Gears and Shafts for Reduction Gears
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers normalized and tempered carbon steel and quenched and tempered alloy steel forgings for pinions, gears, and shafts.
1.2 Several classes of steel are covered as follows:
1.2.1 Class 1 is normalized and tempered carbon steel.
1.2.2 Classes 2 to 9 , incl, are liquid quenched and tempered alloy steel.
1.3 All classes are considered weldable under proper conditions. Welding technique is of fundamental importance and it is presupposed that welding procedure and inspection shall be in accordance with approved methods for the class of material used.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: A 291 – 95 (Reapproved 1999) An American National Standard
Standard Specification for
Steel Forgings, Carbon and Alloy, for Pinions, Gears and
Shafts for Reduction Gears
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 291; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 4. Heat Treatment
1.1 This specification covers normalized and tempered car- 4.1 Preliminary Heat Treatment:
bon steel and quenched and tempered alloy steel forgings for 4.1.1 The forgings shall be given such preliminary heat
pinions, gears, and shafts. treatment as is proper for the design and composition. The
1.2 Several classes of steel are covered as follows: forgings shall be heated to a suitable temperature for a
1.2.1 Class 1 is normalized and tempered carbon steel. sufficient length of time for austenitization and shall be suitably
1.2.2 Classes 2 to 9, incl, are liquid quenched and tempered cooled to bring about complete transformation.
alloy steel. 4.1.2 Forgings may be immediately treated for mechanical
1.3 All classes are considered weldable under proper con- properties after preliminary heat treatment or may be rough
ditions. Welding technique is of fundamental importance and it turned prior to treatment for mechanical properties.
is presupposed that welding procedure and inspection shall be 4.2 Heat Treatment for Mechanical Properties—The forg-
in accordance with approved methods for the class of material ing shall be reheated to a temperature above the upper critical
used. temperature and held a sufficient length of time for complete
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded austenitization. Class 1 shall be air cooled while Classes 2
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for through 8 shall be liquid quenched.
information only. 4.3 Tempering—The forgings shall be tempered to develop
the specified properties. Minimum tempering temperatures
2. Referenced Documents
shall be as follows:
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Minimum Tempering Temperature
Class °F (°C)
A 275/A 275M Test Method for Magnetic Particle Exami-
2 1 and 2 1150 (620)
nation of Steel Forgings
3, 3A, and 4 1075 (580)
A 370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
5, 6, 7 1050 (565)
8 1100 (595)
of Steel Products
9 1000 (540)
A 388/A 388M Practice for Ultrasonic Examination of
Heavy Steel Forgings The charge shall be cooled under uniform conditions in the
furnace at a maximum rate of 100°F (55°C) per h to 600°F
A 788 Specification for Steel Forgings, General Require-
ments (316°C).
4.4 Stress Relief—If the manufacturer elects to heat treat for
3. Ordering Information
mechanical properties prior to machining, the forgings shall be
3.1 Instructions for purchasing forgings to this specification stress relieved after machining (4.5) at a temperature that is 50
should be in accordance with Specification A 788. In addition,
to 100°F (28 to 55°C) below the last previous tempering
a detailed drawing, sketch, or written description of the forging temperature but in no case below 1000°F (540°C). The
should be included with the inquiry or order.
forgings shall be cooled under uniform conditions in the
3.2 Supplementary requirements are provided and shall furnace at a maximum rate of 100°F (55°C)/h to 600°F
apply only when specified in the purchase order.
(316°C).
4.5 Machining:
4.5.1 Rough machining before heat treatment for mechani-
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A-1 on Steel,
cal properties may be performed at the option of the manufac-
Stainless Steel and Related Alloys, and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.06 on Steel Forgings and Billets.
turer.
Current edition approved July 15, 1995. Published September 1995. Originally
4.5.2 If the producer elects to heat treat for mechanical
published as A291 – 46. Last previous edition A291 – 92.
2 properties prior to machining, the forgings shall be stress
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.05.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.03.
Copyright © ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
A 291
relieved after machining. full-size prolongation left on one end of each individual
4.5.3 Boring—Forgings, after being heat treated for me- forging or on both ends of the multiple forging if the forgings
chanical properties and subsequently bored, shall be stress are made in multiple. The nominal or specified outside rough-
relieved. machined diameter or thickness of the forgings, disregarding
large ends, collars and flanges, shall determine the size of
5. General Requirements
prolongations for test specimens.
5.1 Unless otherwise specified herein, the requirements of 7.1.3.3 The axis of the longitudinal tension test specimen
Specification A 788 shall apply to forgings supplied to this shall be located at any point 1 ⁄4 in. (31.75 mm) below the
specification. surface of the forging. The axis of the tangential test specimen
shall be located as near to the surface of the forging as
6. Chemical Requirements
practicable.
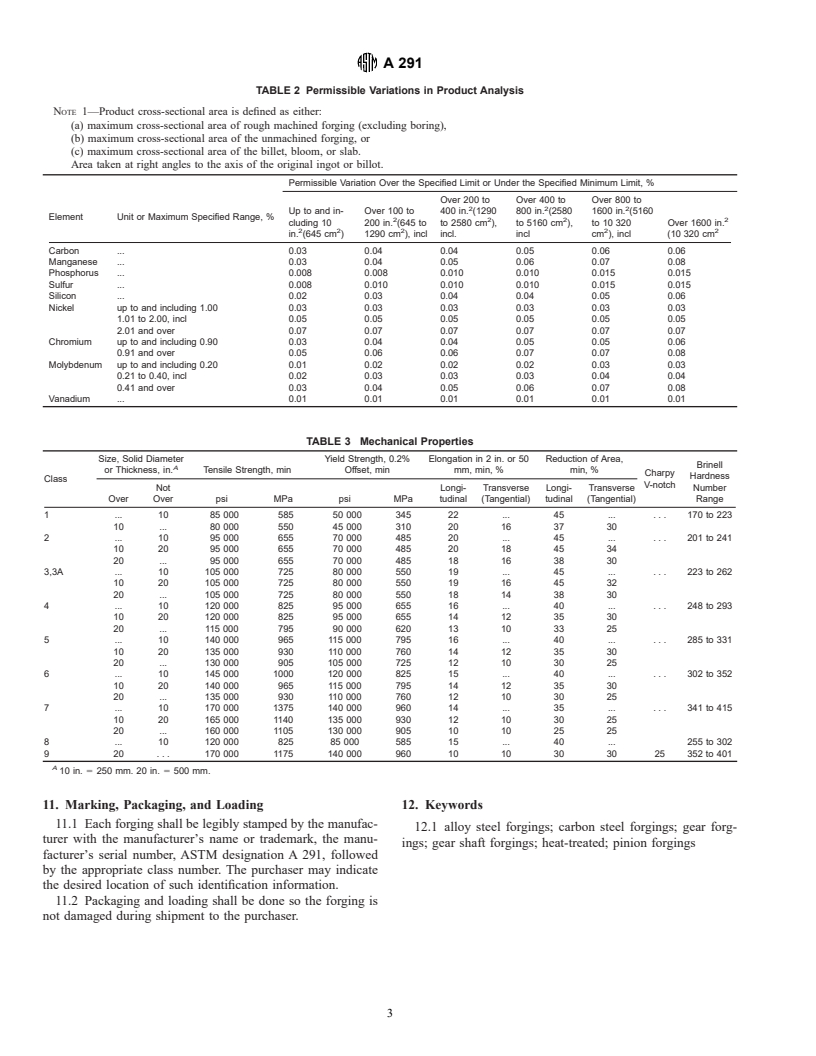
6.1 The steel shall conform to the requirements for chemical 7.2 Brinell Hardness:
composition prescribed in Table 1. 7.2.1 The material shall conform to the requirements for
6.2 The limits for elements other than carbon, manganese, hardness as prescribed in Table 3. Brinell hardness tests shall
phosphorus, sulfur, and silicon in Class 2 alloy shall be agreed be made on prepared areas on the forgings after machining to
upon between the manufacturer and purchaser. the sizes ordered by the purchaser and after stress relieving if
stress relieving is required.
7. Mechanical Requirements
7.2.2 Number and Location of Tests—On each forging 8 in.
7.1 Tensile and Impact Requirements: (203 mm) and over in diameter, four Brinell hardness tests
shall be made on the outside surface of that portion of the
7.1.1 The material shall conform to the requirements for
tensile and impact properties prescribed in Table 2 when tested forging on which teeth will be cut, two tests being made on
each helix 180° apart and the tests on the two helices shall be
in accordance with Test Methods and Definitions A 370 and
impact properties (see S2) when agreed upon between the 90° apart. On each forging under 8 in. in diameter, two Brinell
purchaser and the supplier. hardness tests shall be made, one on each helix 180° apart.
7.1.2 Classification—The nominal or specified rough- Hardness tests shall be performed at the quarter-face width of
machined diameter or thickness of solid forgings, disregarding the tooth portion diameter. On shaft forgings, two hardness
large ends, collars and flanges, or the nominal rough-machined tests shall be made on each end 180° apart.
wall thickness of bored forgings shall determine the size 7.2.3 Test Method—Tests shall be made in accordance with
classification. Test Methods and Definitions A 370.
7.1.3 Number, Location, and Orientation of Test Specimens:
8. Retreatment
7.1.3.1 At least one tension test specimen either longitudinal
8.1 If the results of the mechanical tests of any forging do
or tangential at the option of the manufacturer shall be taken
not conform to the specified requirements, the manufacturer
from each forging unless a number of forgings are forged and
may retreat the forging one or more times, but not more than
treated in multiple, in which case one tension test specimen
three additional times without approval of the purchaser.
shall be taken from each end of the multiple forging. When
impact tests are specified in accordance with Supplementary
9. Dimensions and Tolerance
Requirement S2, one set of impact tests shall also b
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.