ASTM D7290-06
(Practice)Standard Practice for Evaluating Material Property Characteristic Values for Polymeric Composites for Civil Engineering Structural Applications
Standard Practice for Evaluating Material Property Characteristic Values for Polymeric Composites for Civil Engineering Structural Applications
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This practice covers the procedures for computing material property characteristic values for polymeric composite materials intended for use in civil engineering structural applications. A characteristic value represents a statistical lower bound on the material property structural member resistance factors for civil engineering design codes for composite structures.
This practice may be used to obtain characteristic values for stiffness and strength properties of composite materials obtained from measurements using applicable test methods.
SCOPE
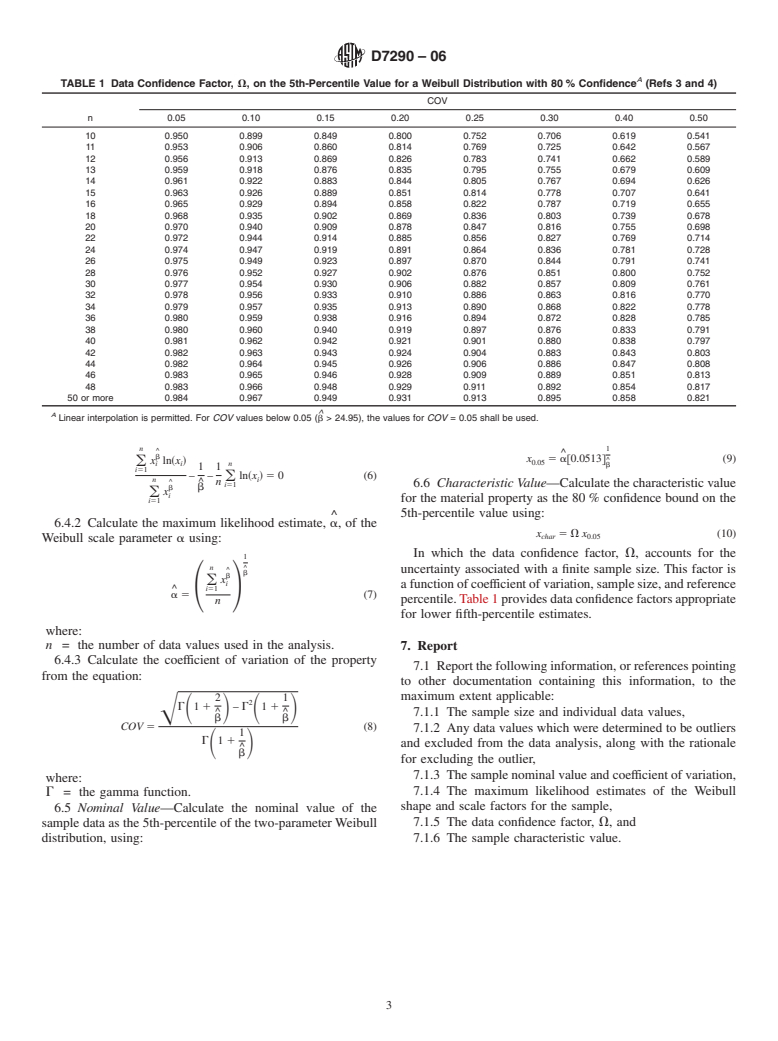
1.1 This practice covers the procedures for computing characteristic values of material properties of polymeric composite materials intended for use in civil engineering structural applications. The characteristic value is a statistically-based material property representing the 80 % lower confidence bound on the 5th-percentile value of a specified population. Characteristic values determined using this standard practice can be used to calculate structural member resistance values in design codes for composite civil engineering structures and for establishing limits upon which qualification and acceptance criteria can be based.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D7290 – 06
Standard Practice for
Evaluating Material Property Characteristic Values for
Polymeric Composites for Civil Engineering Structural
Applications
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7290; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2.2 Other Document:
MIL-Handbook-17 Polymer Matrix Composites, Volume 1,
1.1 This practice covers the procedures for computing
Revision F
characteristic values of material properties of polymeric com-
posite materials intended for use in civil engineering structural
3. Terminology
applications. The characteristic value is a statistically-based
3.1 Definitions—Terminology D3878 defines terms relating
material property representing the 80 % lower confidence
to high-modulus fibers and their composites. Terminology
bound on the 5th-percentile value of a specified population.
D883definestermsrelatingtoplastics.TerminologyE6defines
Characteristic values determined using this standard practice
termsrelatingtomechanicaltesting.TerminologyE456defines
can be used to calculate structural member resistance values in
terms relating to statistics. In the event of a conflict between
design codes for composite civil engineering structures and for
terms, Terminology D3878 shall have precedence over the
establishing limits upon which qualification and acceptance
other documents.
criteria can be based.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.2.1 characteristic value—a statistically-based material
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
property representing the 80 % lower confidence bound on the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
5th-percentile value of a specified population. The character-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
istic value accounts for statistical uncertainty due to a finite
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
sample size.
2. Referenced Documents 3.2.1.1 Discussion—The 80 % confidence bound and 5th-
percentile levels were selected so that composite material
2.1 ASTM Standards:
characteristic values will produce resistance factors for Load
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
and Resistance Factor Design similar to those for other civil
D3878 Terminology for Composite Materials
engineering materials (see Refs 1 and 2).
D5055 Specification for Establishing and Monitoring Struc-
3.2.1.2 Discussion—The term “characteristic value” is
tural Capacities of Prefabricated Wood I-Joists
analogous to the term “basis value” used in the aerospace
D5457 Specification for Computing Reference Resistance
industry where A- and B-basis values are defined as the 95 %
of Wood-Based Materials and Structural Connections for
lower confidence bound on the lower 1 % and 10 % values of
Load and Resistance Factor Design
a population, respectively.
D5574 Test Methods for Establishing Allowable Mechani-
3.2.2 data confidence factor, V—a factor that is used to
cal Properties of Wood-Bonding Adhesives for Design of
adjustthesamplenominalvalueforuncertaintyassociatedwith
Structural Joints
finite sample size.
E6 TerminologyRelatingtoMethodsofMechanicalTesting
3.2.3 nominal value—the 5th percentile value of the data
E178 Practice for Dealing With Outlying Observations
represented by a probability density function.
E456 Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
3.2.4 outlier—an outlying observation, or “outlier,” is one
that deviates significantly from other observations in the
sample in which it occurs.
This practice is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D30 on Composite
MaterialsandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeD30.05onStructuralTest
Methods.
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2006. Published October 2006. DOI: 10.1520/
D7290-06. AvailablefromU.S.GovernmentPrintingOfficeSuperintendentofDocuments,
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or 732 N. Capitol St., NW, Mail Stop: SDE, Washington, DC 20401, http://
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM www.access.gpo.gov.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on The boldface numbers in parentheses refer to the list of references at the end of
the ASTM website. this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D7290 – 06
NOTE 2—Practice E178 provides several methods for statistically
4. Significance and Use
analyzing a dataset for outliers. The MNR method is used here because it
4.1 This practice covers the procedures for computing
is a simple method that is unlikely to be miscalculated, misinterpreted or
materialpropertycharacteristicvaluesforpolymericcomposite
misapplied.
materials intended for use in civil engineering structural
NOTE 3—An outlying observation may be an extreme manifestation of
applications. A characteristic value represents a statistical
the random variability of the material property value. For such a case, the
lower bound on the material property structural member value should be retained and treated as any other observation in the
sample. However, the outlying observation may be the result of a gross
resistance factors for civil engineering design codes for com-
deviation from prescribed experimental procedure or an error in calculat-
posite structures.
ing or recording the numerical value of the data point in question. When
4.2 Thispracticemaybeusedtoobtaincharacteristicvalues
the experimentalist can document a gross deviation from the prescribed
for stiffness and strength properties of composite materials
experimental procedure, the outlying observation may be discarded,
obtained from measurements using applicable test methods.
unless the observation can be corrected in a rational manner.
6.2.1 Outlier Criteria for Single Samples—For a sample of
5. Sampling
size n, arrange the data values {x , x , x , .x } in order of
1 2 3 n
5.1 Samples selected for analysis shall be representative of
increasing magnitude with x being the largest value. Calculate
n
the material property population for which the characteristic
the MNR statistic as the maximum absolute deviation from the
values are to be calculated.
sample mean divided by the sample standard deviation:
5.2 The minimum number of samples shall be specified in
design codes that reference this standard.
x – x
i
? ?
MNR 5 maxS D (3)
s
n21
NOTE 1—Section 5.3.1 of the building code requirements for structural
concrete (ACI 318-05) requires at least 30 samples to determine the
6.2.1.1 Calculate the critical MNR value, CV, based on a
standard deviation of concrete compressive strength for a new batch plant
5 % significance level using the following approximation:
but allows a reduction to a minimum of 15 samples, provided that a
modification factor is used to increase the standard deviation if less than
CV ' 2– (4)
S D
30 samples are used (Ref 3). For wood, Specification D5457 requires a 5 n
=
minimum of 30 samples for computing the reference resistance of wood
6.2.1.2 Therearenooutliersinthesampleofobservationsif
based materials and structural connections for Load and Resistance Factor
the calculated MNR statistic is smaller than the critical value
Design, and states that extreme care must be taken during sampling to
ensure a representative sample for sample sizes less than 60. The bending CV, that is MNR# CV.Ifthe MNR statistic is found to be
capacity of wood I-joists can be determined either by analysis or
greater than the critical value, then the MNR shall be denoted
empirically by testing (Specification D5055). If the capacity is determined
a possible outlier. The possible outlier shall be inv
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.