ASTM F510-93(2008)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Resistance to Abrasion of Resilient Floor Coverings Using an Abrader with a Grit Feed Method
Standard Test Method for Resistance to Abrasion of Resilient Floor Coverings Using an Abrader with a Grit Feed Method
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
When subjected to normal in-use traffic conditions, a flooring material is exposed to abrasion caused by the destructive action of fine hard particles. This situation occurs whenever a particle-polluted intermediate layer exists between traffic bodies (that is, shoes and a flooring surface). Under continuing exposure to an “abrasive action,” a flooring material may suffer a thickness loss sufficient to reduce its service life.
Abrasion resistance measurements of resilient floor coverings can be complicated since the resistance to abrasion is affected by many factors. One of these is the physical properties of the material in the floor covering surface, particularly its hardness and resilience. The type and degree of added substances, such as fillers and pigments, can also affect abrasion resistance. It can also be affected by conditions of the test (for example, the type and characteristics of the abradant and how it acts on the area of the specimen being abraded, including the development and dissipation of heat during the test cycle). The surface characteristics of the specimen, such as type, depth, and amount of embossing, can likewise affect the abrasion resistance of resilient floorings.
This test method is designed to simulate one kind of abrasive action and abradant that a flooring may encounter in the field. However, results should not be used as an absolute index of ultimate life because, as noted, there are too many factors and interactions to consider. Also involved are the many different types of service locations. Therefore, the data from this test method are of value chiefly in the development of materials and should not be used without qualifications as a basis for commercial comparisons.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the laboratory procedure for determining the abrasion resistance of resilient flooring using an abrader with a grit feeder.
1.2 The equipment used in this test method is a modification of the Taber abraser. The regular ceramic wheels are replaced by leather clad brass rollers. A grit-feeding device feeds 240-mesh aluminum oxide grit onto the specimen before it passes under the leather clad rollers. Using the exhaust system incorporated in the apparatus, the used grit and abraded material are continuously removed after passing under both rollers.
1.3 This test method employs a rotary, rubbing action caused by the dual abrading wheels. One wheel rubs the specimen from the center outward and the other from the outside toward the center. The wheels traverse a complete circle and have an abrasive action on the rotating specimen at all angles. It is felt that this action approaches the twisting action between shoe and floor that occurs when a person turns. The use of loose grit serves the function of an abradant and also aids in the rolling action felt to be characteristic of normal walking.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F510 − 93(Reapproved 2008)
Standard Test Method for
Resistance to Abrasion of Resilient Floor Coverings Using
1
an Abrader with a Grit Feed Method
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF510;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
4
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1 This test method covers the laboratory procedure for
D1860Test Method for Moisture and Creosote-Type Preser-
determining the abrasion resistance of resilient flooring using
5
3
vative in Wood (Withdrawn 2006)
an abrader with a grit feeder.
D792Test Methods for Density and Specific Gravity (Rela-
1.2 Theequipmentusedinthistestmethodisamodification
tive Density) of Plastics by Displacement
of the Taber abraser. The regular ceramic wheels are replaced
E122PracticeforCalculatingSampleSizetoEstimate,With
by leather clad brass rollers. A grit-feeding device feeds
Specified Precision, the Average for a Characteristic of a
240-mesh aluminum oxide grit onto the specimen before it
Lot or Process
passes under the leather clad rollers. Using the exhaust system
E171Practice for Conditioning and Testing Flexible Barrier
incorporated in the apparatus, the used grit and abraded
Packaging
material are continuously removed after passing under both 2.2 ANSI Standard:
rollers.
B74.12Checking the Size of Abrasive Grain for Grinding
6
Wheels, Polishing, and General Industrial Uses
1.3 This test method employs a rotary, rubbing action
caused by the dual abrading wheels. One wheel rubs the
3. Terminology
specimen from the center outward and the other from the
3.1 Definitions:
outside toward the center. The wheels traverse a complete
3.1.1 abrasion—of resilient floor coverings, a form of wear,
circle and have an abrasive action on the rotating specimen at
in which a gradual removing of a flooring surface is caused by
all angles. It is felt that this action approaches the twisting
the frictional action of relatively fine hard particles.
action between shoe and floor that occurs when a person turns.
3.1.2 resistance to abrasion— of resilient floor coverings,
Theuseofloosegritservesthefunctionofanabradantandalso
the ability of a material to withstand mechanical actions of
aids in the rolling action felt to be characteristic of normal
relatively fine hard particles, which by rubbing, scraping, and
walking.
eroding remove material from a floor covering surface.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4. Significance and Use
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4.1 When subjected to normal in-use traffic conditions, a
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
flooring material is exposed to abrasion caused by the destruc-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
tive action of fine hard particles. This situation occurs when-
ever a particle-polluted intermediate layer exists between
traffic bodies (that is, shoes and a flooring surface). Under
continuingexposuretoan“abrasiveaction,”aflooringmaterial
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeF06onResilient
Floor Coveringsand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F06.30 on Test may suffer a thickness loss sufficient to reduce its service life.
Methods - Performance.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2008. Published December 2008. Originally
4
approved in 1978. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as F510–93(2004). DOI: For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
10.1520/F0510-93R08. contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
2
This test method is described by W. E. Irwin in “Development of a Method to Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
MeasureWearonResilientFlooring,” Journal of Testing and Evaluation,Vol4,No. the ASTM website.
5
1, January 1976, pp. 15–20. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
3
This grit feed method is frequently referred to as the “Frick Grit Feed Method” www.astm.org.
6
becauseitisbasedonworkdonebyOttoF.V.Frickasdescribedin“StudiesofWear Available from American National Standards Institute, 25 West 43rd St., 4th
on Flooring Materials,” Wear, Vol 14, 1969, pp. 119–131. Floor, New York, NY 10036.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F510 − 93 (2008)
5.1.2 Feeder attachment, for the abraser.
7
5.1.3 Lea
...







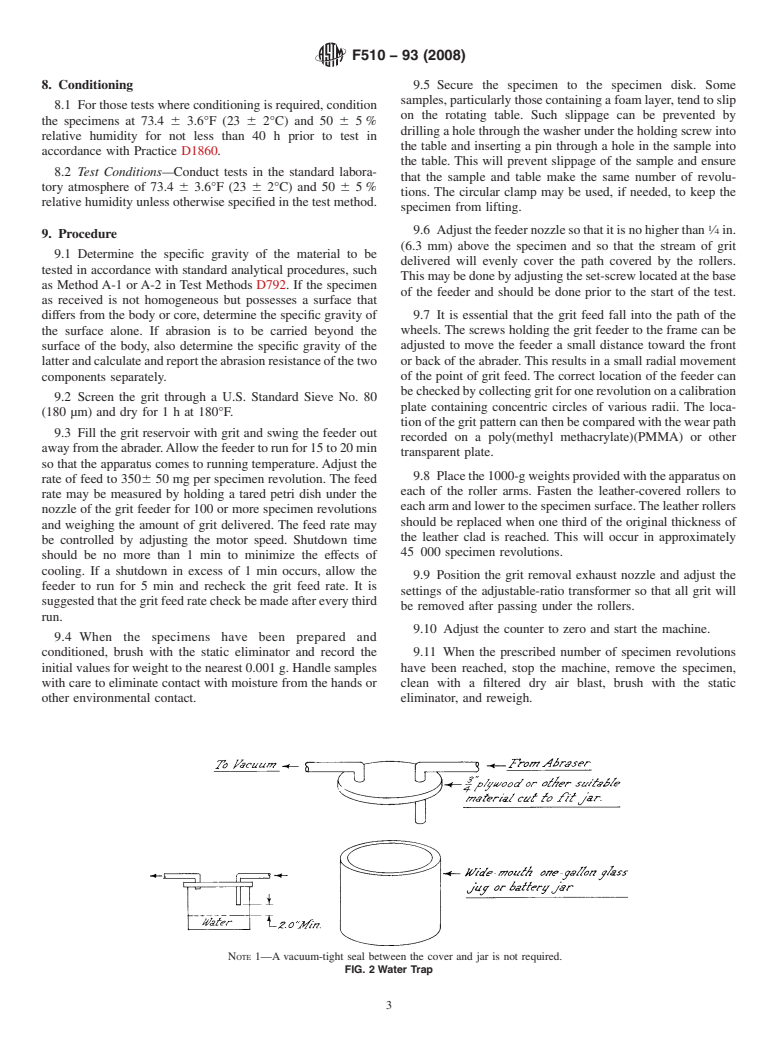
Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.