ASTM C1803-20
(Guide)Standard Guide for Abrasion Resistance of Mortar Surfaces Using a Rotary Platform Abraser
Standard Guide for Abrasion Resistance of Mortar Surfaces Using a Rotary Platform Abraser
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Wear on mortar surfaces can be generated by a number of factors including skidding, scraping or sliding of objects on the surface, foot and tire traffic. This guide provides a means to quantify the abrasion resistance of treated or untreated mortars and other similar products.
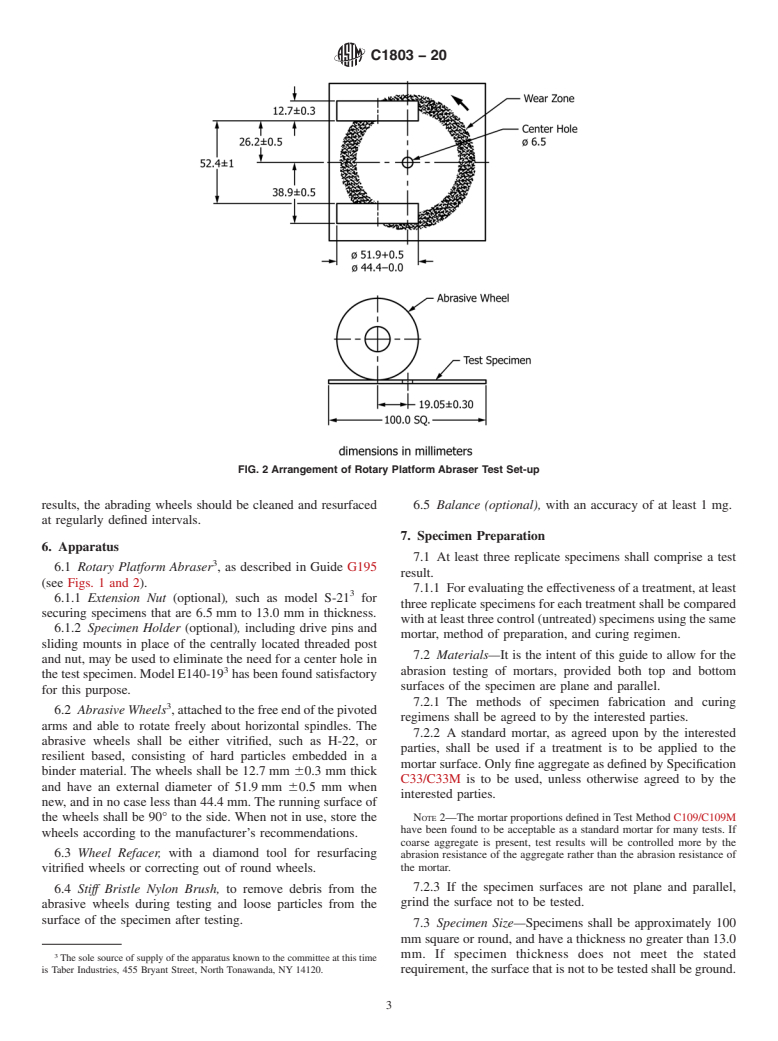
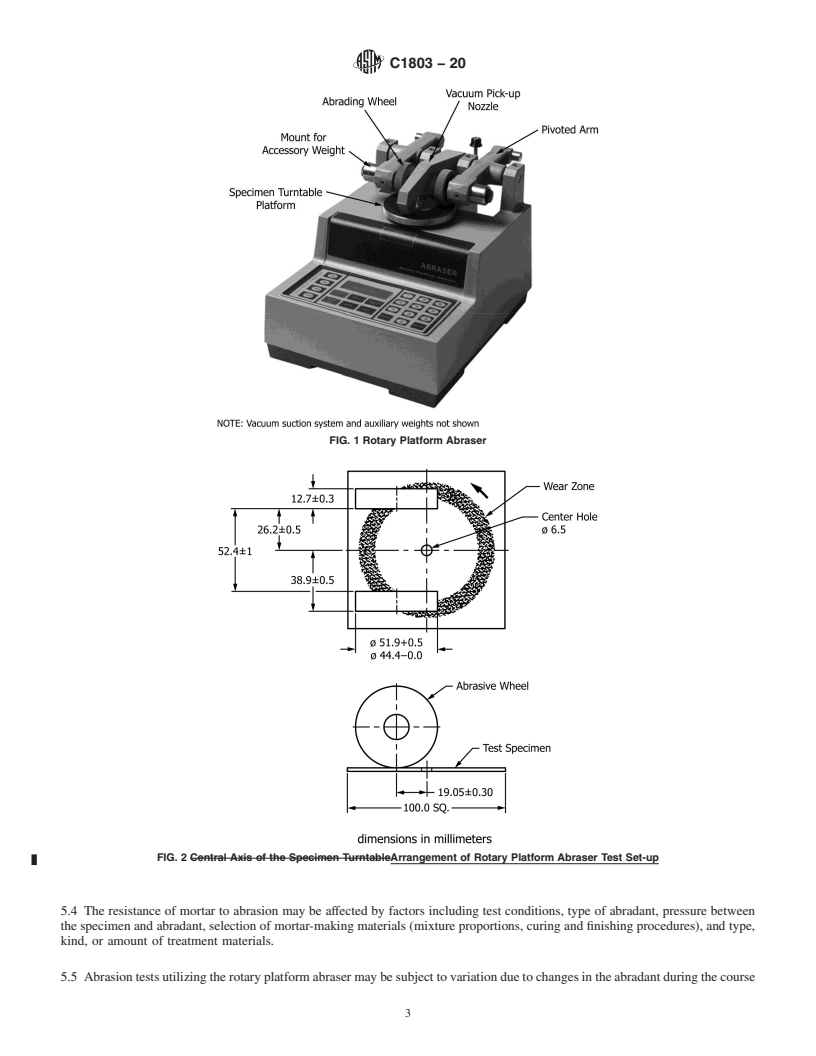
FIG. 1 Rotary Platform Abraser
FIG. 2 Arrangement of Rotary Platform Abraser Test Set-up
5.1.1 This guide can be used to determine the effectiveness of fluid applied hardeners, densifiers and sealers by comparison with untreated control specimens.
5.1.2 This guide can be used with other test methods to determine the effectiveness of surface treatments after abrasion. For example, Test Method D6532 can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of clear water repellents on hydraulic cement mortar specimens based on water absorption after water soaking, by testing the specimen prior to abrasion and after the specimen has been subjected to abrasion.
5.2 This guide may be useful for acceptance testing of a mortar surface, and it can be used to evaluate the effects of processing variables such as substrate preparation before treatment, surface texture, treatment application variables, and curing regimen.
5.3 Results may be used to correlate with in-place performance, for comparative rating of the performance of alternative materials, or for comparison among treated and untreated surfaces. The resistance of material surfaces to abrasion, as measured on a testing machine in the laboratory, is generally only one of several factors contributing to wear performance as experienced in the actual use of the material. Other factors may need to be considered in any calculation of predicted life from specific abrasion data.
5.4 The resistance of mortar to abrasion may be affected by factors including test conditions, type of abradant, pressure between the specimen and abradant, selection of mortar-making materials (mixture proportions, curing and finishing procedures), and type, kind, or amo...
SCOPE
1.1 This guide is intended to assist in establishing procedures for determining the relative abrasion resistance of treated or untreated mortar surfaces.
1.2 This guide utilizes the rotary platform abraser, which generates a combination of rolling and rubbing to cause wear to the specimen surface. Wear can be quantified as cycles to a specific end-point. Other commonly used evaluations are presented in Appendix X1 and include mass loss, wear index, or volume loss.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
Note 1: Other procedures used to measure abrasion resistance of concrete surfaces include Test Methods C418, C779/C779M, C944/C944M, and C1138M. Other methods that reference the rotary platform abraser and may be of interest include Specification C744 and Test Methods C1353, D4060 and F510.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: C1803 − 20
Standard Guide for
Abrasion Resistance of Mortar Surfaces Using a Rotary
1
Platform Abraser
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1803; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* C109/C109M Test Method for Compressive Strength of
Hydraulic Cement Mortars (Using 2-in. or [50 mm] Cube
1.1 This guide is intended to assist in establishing proce-
Specimens)
dures for determining the relative abrasion resistance of treated
C125 Terminology Relating to Concrete and Concrete Ag-
or untreated mortar surfaces.
gregates
1.2 This guide utilizes the rotary platform abraser, which
C418 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Concrete by
generates a combination of rolling and rubbing to cause wear
Sandblasting
to the specimen surface. Wear can be quantified as cycles to a
C744 Specification for Prefaced Concrete and Calcium Sili-
specific end-point. Other commonly used evaluations are
cate Masonry Units
presented in Appendix X1 and include mass loss, wear index,
C779/C779M Test Method forAbrasion Resistance of Hori-
or volume loss.
zontal Concrete Surfaces
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
C944/C944M Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Con-
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
crete or Mortar Surfaces by the Rotating-Cutter Method
standard.
C1138M Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Concrete
NOTE 1—Other procedures used to measure abrasion resistance of
(Underwater Method)
concrete surfaces include Test Methods C418, C779/C779M, C944/
C1353 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Dimension
C944M, and C1138M. Other methods that reference the rotary platform
Stone Subjected to Foot Traffic Using a Rotary Platform
abraser and may be of interest include Specification C744 and Test
Methods C1353, D4060 and F510. Abraser
D4060 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Organic
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
Coatings by the Taber Abraser
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
D6532 Test Method for Evaluation of the Effect of Clear
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
Water Repellent Treatments on Water Absorption of Hy-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. draulic Cement Mortar Specimens
F510 Test Method for Resistance to Abrasion of Resilient
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard- Floor Coverings Using an Abrader with a Grit Feed
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the Method
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
G195 Guide for Conducting Wear Tests Using a Rotary
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Platform Abraser
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
3. Terminology
2. Referenced Documents
3.1 Definitions:
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this guide, refer to
C33/C33M Specification for Concrete Aggregates
Terminology C125.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Guide:
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee C09 on Concrete and
3.2.1 abraser, n—an instrument designed to determine the
Concrete Aggregates and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C09.62 on
resistanceofsurfacestoabrasion,alsoreferredtoasanabrader.
Abrasion Testing.
Current edition approved Dec. 15, 2020. Published January 2020. Originally
3.2.1.1 Discussion—For the rotary platform abraser used in
published in 2015. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as C1803–15. DOI:
this guide, abrasion is produced by a combined action of
10.1520/C1803-20.
2
rolling and rubbing.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3.2.2 abrasion cycle, n—one complete rotation of the speci-
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. men turntable platform.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1803 − 20
3.2.3 resurface, v—the procedure of refreshing the running 5.1.2 This guide can be used with other test methods to
surface of an
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C1803 − 15 C1803 − 20
Standard Guide for
Abrasion Resistance of Mortar Surfaces Using a Rotary
1
Platform Abraser
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1803; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This guide is intended to assist in establishing procedures for determining the relative abrasion resistance of treated or
untreated mortar surfaces.
1.2 This guide utilizes the rotary platform abraser, which generates a combination of rolling and rubbing to cause wear to the
specimen surface. Wear can be quantified as cycles to a specific end-point. Other commonly used evaluations are presented in
Appendix X1 and include mass loss, wear index, or volume loss.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
NOTE 1—Other procedures used to measure abrasion resistance of concrete surfaces include Test Methods C418, C779/C779M, C944/C944M, and
C1138M. Other methods that reference the rotary platform abraser and may be of interest include Specification C744 and Test Methods C1353, D4060
and F510.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C33/C33M Specification for Concrete Aggregates
C109/C109M Test Method for Compressive Strength of Hydraulic Cement Mortars (Using 2-in. or [50 mm] Cube Specimens)
C125 Terminology Relating to Concrete and Concrete Aggregates
C418 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Concrete by Sandblasting
C744 Specification for Prefaced Concrete and Calcium Silicate Masonry Units
C779/C779M Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Horizontal Concrete Surfaces
C944/C944M Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Concrete or Mortar Surfaces by the Rotating-Cutter Method
C1138M Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Concrete (Underwater Method)
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C09 on Concrete and Concrete Aggregates and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C09.62 on Abrasion
Testing.
Current edition approved July 1, 2015Dec. 15, 2020. Published September 2015January 2020. Originally published in 2015. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as
C1803–15. DOI: 10.1520/C1803-15.10.1520/C1803-20.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1803 − 20
C1353 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Dimension Stone Subjected to Foot Traffic Using a Rotary Platform Abraser
D4060 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Organic Coatings by the Taber Abraser
D6532 Test Method for Evaluation of the Effect of Clear Water Repellent Treatments on Water Absorption of Hydraulic Cement
Mortar Specimens
F510 Test Method for Resistance to Abrasion of Resilient Floor Coverings Using an Abrader with a Grit Feed Method
G195 Guide for Conducting Wear Tests Using a Rotary Platform Abraser
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this guide, refer to Terminology C125.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Guide:
3.2.1 abraser, n—an instrument designed to determine the resistance of surfaces to abrasion, also referred to as an abrader.
3.2.1.1 Discussion—
For the rotary platform abraser used in this guide, abrasion is produced by a combined action of rolling and rubbing.
3.2.2 abrasion cycle, n—one
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.