ASTM A456/A456M-99
(Specification)Standard Specification for Magnetic Particle Examination of Large Crankshaft Forgings
Standard Specification for Magnetic Particle Examination of Large Crankshaft Forgings
SCOPE
1.1 This is an acceptance specification for the magnetic particle inspection of forged steel crankshafts having main bearing journals or crankpins 4 in. [200 mm] or larger in diameter.
1.2 There are three classes, with acceptance standards of increasing severity:
1.2.1 Class 1.
1.2.2 Class 2 (originally the sole acceptance standard of Specification A456).
1.2.3 Class 3 (formerly covered in Supplementary Requirement S1 of Specification A456-64 (1970)).
1.3 This specification is not written to cover diesel locomotive crankshafts specifically, but Class 2 or 3 may be applied if manufacturer and ultimate user agree to its use. Note-Specification A668/A 688M is a product specification which may be used for crankshaft forgings.
1.4 The values stated in either inches or SI (metric) units are to be regarded separately as the standard. Within the text and figures, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification.
1.5 Unless the order specifies the applicable "M" specification designation, the material shall be furnished to the inch units.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: A 456/A 456M – 99
Standard Specification for
Magnetic Particle Examination of Large Crankshaft
Forgings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 456/A 456M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope A 983/A 983M Specification for Continuous Grain Flow
Forged Carbon and Alloy Steel Crankshafts for Medium
1.1 This is an acceptance specification for the magnetic
Speed Diesel Engines
particle inspection of forged steel crankshafts having main
E 1417 Practice for Liquid Penetrant Examination
bearing journals or crankpins 4 in. [200 mm] or larger in
diameter.
3. Classification of Indications
1.2 There are three classes, with acceptance standards of
3.1 Magnetic particle indications on the surface of the
increasing severity:
crankshaft shall be classified as follows:
1.2.1 Class 1.
3.1.1 Open cracks, flake, or pipe.
1.2.2 Class 2 (originally the sole acceptance standard of
3.1.2 Nonmetallic inclusions or stringers occurring in a
Specification A 456).
longitudinal direction.
1.2.3 Class 3 (formerly covered in Supplementary Require-
3.1.3 Twist cracks or nonmetallic inclusions usually occur-
ment S1 of Specification A 456–64 (1970)).
ring at 45 to 70° from the axis of the journal.
1.3 This specification is not intended to cover continuous
3.2 They shall also be classified as follows:
grain flow crankshafts, however, Test Method A 983/A 983M
3.2.1 Open indications are visible after removal of the
may be used for this purpose.
magnetic particles or can be detected by the use of contrast dye
NOTE 1—Specification A 668/A 688M is a product specification which
penetrant, as described in Type II of Practice E 1417.
may be used for crankshaft forgings.
3.2.1.1 Pinpoint indications are open indications ⁄16 in.
1.4 The values stated in either inches or SI (metric) units are
[1.5 mm] in maximum dimension, as detected by application of
to be regarded separately as the standard. Within the text and
Type II of Practice E 1417.
figures, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in
3.2.2 Non-open indications are indications which are not
each system are not exact equivalents; therefore each system
visually detectable as described in 3.2.1.
shall be used independently of the other. Combining values
4. Ordering Information
from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the
specification. 4.1 The inquiry and purchase agreement shall contain a
1.5 Unless the order specifies the applicable “M” specifica-
statement that the crankshaft(s) is (are) to be subject to
tion designation, the material shall be furnished to the inch acceptance according to this specification. If reference to class
units. is omitted, Class 2 shall apply.
4.2 The use of Supplementary Requirements S1 and S2
2. Referenced Documents
should be specified if required.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5. Procedure
A 275/A 275M Test Method for Magnetic Particle Exami-
nation of Steel Forgings 5.1 Magnetic particle inspection shall be conducted accord-
A 668/A 668M Specification for Steel Forgings, Carbon
ing to Test Method A 966/A 966M, except when Supplemen-
and Alloy, for General Industrial Use tary Requirement S1 is to be used. The use of prod type
A 966/A 966M Test Method for Magnetic Particle Exami-
contacts is not permitted on finished crankshafts. Magnetic
nation of Steel Forgings Using Alternating Current leeches may only be used on noncritical parts of the crankshaft
when Supplementary Requirement S2 is utilized.
6. Areas of Inspection
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A-1 on Steel,
Stainless Steel, and Related Alloys , and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
6.1 Major Critical Areas:
A01.06 on Steel Forgings and Billets.
Current edition approved Sept. 10, 1999. Published November 1999. Originally
published as A 456–64. Last previous edition A 456–95a.
2 3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.05. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.03.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
A 456/A 456M – 99
6.1.1 The critical area of any crankpin shall be that area plus over ⁄2 in., depress, and if they are not open or are worsening,
or minus 60° from the 6 o’clock position of the pin extending
accept them. Otherwise remove by dimpling to a maximum
3 5
⁄8 in. [10 mm] above the thrust collar around the fillet, and ⁄8
depth of ⁄16 in. [5 mm].
in. [16 mm] into the pin along its axis measured from
7.1.1.4 The total area of dimples shall be limited as in
approximately the blend of the pin surface and fillet, as shown
7.2.1.3.
in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2.
7.1.2 Minor Critical Areas:
6.1.2 The critical areas of any main bearing journal shall be
7.1.2.1 Open indications oriented at an angle in excess of
that area plus or minus 60° from the 12 o’clock position on top
30° to the longitudinal axis must be removed to a depth not
of the journal extending ⁄8 in. [9.5 mm] above the thrust
exceeding ⁄16 in. [5 mm], by dimpling.
collar around the fillet and ⁄8 in. [15.9 mm] into the journal
along its axis measured from approximately the blend of the
7.1.2.2 Open indications longer than 1 ⁄2 in. [35 mm]
journal surface and the fillet, as shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2.
individually or more than 3 in. [75 mm] of total length per
6.1.3 The critical area of any crankpin or main journal also
bearing journal, that are parallel to the longitudinal axis within
includes that surface area closer than ⁄4 in. [6 mm] to the
30°, must be removed by dimpling to a depth no greater than
junction of the radius blend and the journal surface of any oil
⁄16 in. [5 mm]. Intermittent open indications in a line, spaced
hole.
less than ⁄4 in. [6 mm] apart, shall be considered continuous
6.2 Minor Critical Areas—Minor critical areas include all
or as one indication.
machined fillets, thrust bearing, and bearing surfaces not
1 1
7.1.2.3 Open indications ⁄8 in. [3 mm] to 1 ⁄2 in. [35 mm]
specified as major critical areas.
long, with the exception of those referred to in 7.1.2.1, shall be
7. Acceptance Standards
depressed 0.003 to 0.010 in. [0.05 to 0.25 mm] below the
7.1 Class 1: surface but need not be removed.
7.1.1 Major Critical Areas:
7.1.2.4 Open indications less than ⁄8 in. [3 mm] long need
7.1.1.1 Open indications over ⁄4 in. [6 mm] in length shall
not be depressed, dimpled, or removed.
be removed by dimpling to a depth no greater than ⁄16 in. [5
7.1.2.5 A cluster of open indications, with the exception of
1 1
mm]. Open indications over ⁄16 to ⁄4 in. [1.5 to 6 mm] in
those referred to in 7.1.2.1, having a total length not exceeding
length shall be depressed as in 7.2.2.3.
2 ⁄2 in. [65 mm] in any 1 by 1-in. [25 by 25-mm] square area
7.1.1.2 Pinpoint indications are permissible, except in clus-
of bearing surface shall be depressed 0.003 to 0.010 in. [0.05
1 1
ters of more than 5 in any ⁄4 by ⁄4 -in. [6 by 6-mm] area, in
to 0.25 mm] below the surface but need not be removed. When
which case they must be dimpled to a depth of no more than ⁄16
the total length exceeds 2 ⁄2 in. [65 mm], the indications are
in. [5 mm]. If they do not open or increase in number they are
to be removed by dimpling to a depth no greater than ⁄16 in.
acceptable and need not be removed.
[5 mm].
7.1.1.3 Non-open indications are acceptable up to and
including ⁄2 in. [13 mm] in length. If non-open indications are 7.1.2.6 Non-open indications are acceptable.
Metric Equivalents
3 5
⁄8 in. = [10 mm] ⁄8 in. = [16 mm]
FIG. 1 Critical Surface Areas of Crankpin and Main Bearing Journal
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
A 456/A 456M – 99
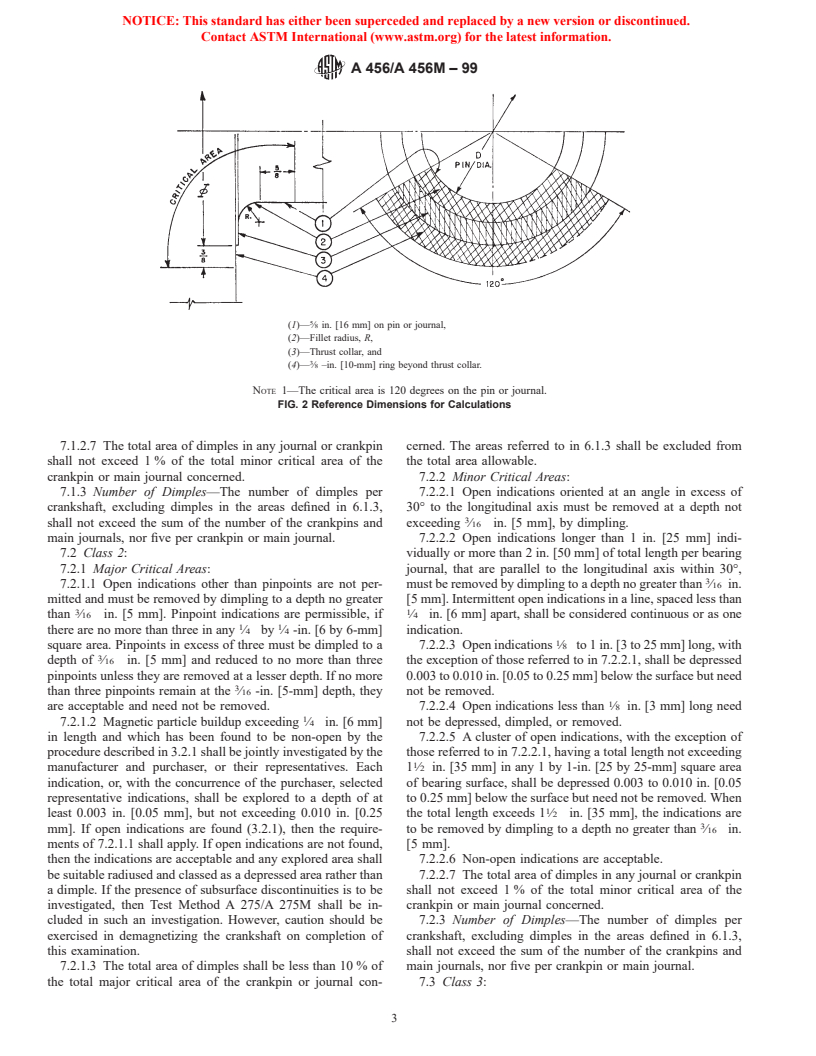
(1)— ⁄8 in. [16 mm] on pin or journal,
(2)—Fillet radius, R,
(3)—Thrust collar, and
(4)— ⁄8 –in. [10-mm] ring beyond thrust collar.
NOTE 1—The critical area is 120 degrees on the pin
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.