ASTM C944-99(2005)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Concrete or Mortar Surfaces by the Rotating-Cutter Method
Standard Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Concrete or Mortar Surfaces by the Rotating-Cutter Method
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method gives an indication of the relative wear resistance of mortar and concrete based on testing of cored or fabricated specimens. This test method has been successfully used in the quality control of highway and bridge concrete subject to traffic. Primarily intended for use on the top ends of 152-mm [6-in.] diameter concrete cores, mortar specimens, or other samples of concrete of insufficient test area to permit the conduct of tests by Test Method C 418 or C 779/C 779M, this test method is also applicable on concrete surfaces in place by measuring the abrasion loss as described in Section 9, Procedure B, of Test Method C 779/C 779M.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for determining the resistance of either concrete or mortar to abrasion. This test method is similar to Procedure B of Test Method C 779/C 779M.
1.2 The values stated in SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:C944–99 (Reapproved 2005)
Standard Test Method for
Abrasion Resistance of Concrete or Mortar Surfaces by the
1
Rotating-Cutter Method
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C 944; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope other samples of concrete of insufficient test area to permit the
conduct of tests by Test Method C 418 or C 779/C 779M, this
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for determining the
test method is also applicable on concrete surfaces in place by
resistance of either concrete or mortar to abrasion. This test
measuring the abrasion loss as described in Section 9, Proce-
method is similar to Procedure B of Test Method C 779/
dure B, of Test Method C 779/C 779M.
C 779M.
1.2 The values stated in SI units or inch–pound units are to
4. Apparatus
be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each
4.1 Abrasion Device—Adrill press or similar device with a
system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system
chuck capable of holding and rotating the abrading cutter at a
shall be used independently of the other. Combining values
speed of 200 r/min and exerting a force of either a normal load
from the two systems may result in non–conformance with the
of 98 6 1 N [22 6 0.2 lbf] or a double load of 197 6 2 N [44
standard.
6 0.4 lbf] on the test specimen surface. Fig. 1 shows a
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
commercial drill press and Fig. 2 illustrates details of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
rotating cutter. The difficulty in maintaining a constant load on
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
the abrading cutter when using the lever, gear, and spring
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
system of a drill press has been eliminated by placing the
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
desired load directly upon the spindle that turns the cutter. The
2. Referenced Documents machine consists essentially of a frame that supports the drive
2
motor, stepped pulley, and spindle. A clamping device to hold
2.1 ASTM Standards:
the specimen is built into the base.
C42 Test Method for Obtaining and Testing Drilled Cores
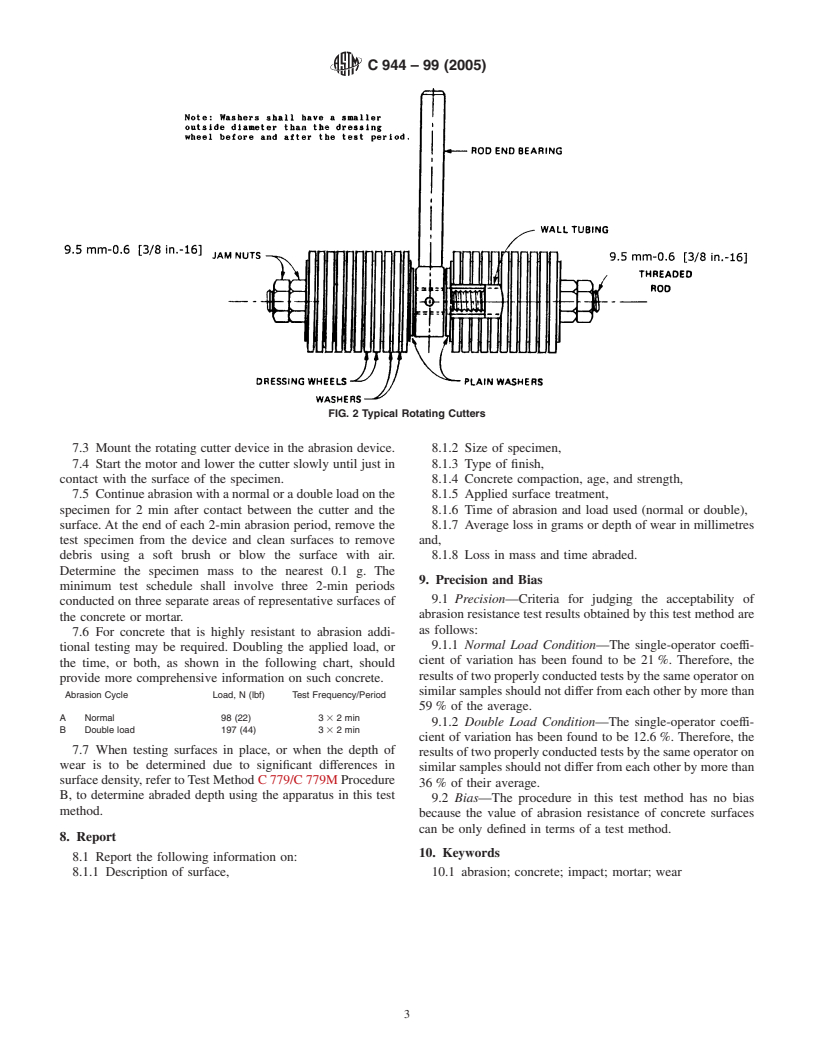
4.2 Rotating Cutter—Arotating cutter similar to that shown
and Sawed Beams of Concrete
in Fig. 2 and Fig. 3 shall be used in which 22 37.5 mm [1.5 in.]
C 418 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Concrete by
diameter dressing wheels and 24 25.4 to 31.75 mm [1 to 1.25
Sandblasting
in.] diameter washers are mounted. The washers as received
C 779/C 779M Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of
shall be stacked and locked on a bolt for the purpose of
Horizontal Concrete Surfaces
reducing their diameter to the specified range to avoid restrict-
3. Significance and Use
ing abrasion of the concrete by the washers. Cutter assembly,
including washers, shall be locked onto horizontal rods such
3.1 This test method gives an indication of the relative wear
that individual dressing wheels are free to turn independently.
resistance of mortar and concrete based on testing of cored or
The overall diameter of the cutter or the diameter of the
fabricated specimens. This test method has been successfully
1
circular area abraded is 82.5 mm [3 ⁄4 in.]. Care shall be taken
used in the quality control of highway and bridge concrete
to achieve constant contact between the rotating cutter and the
subject to traffic. Primarily intended for use on the top ends of
entire test surface of the sample. This can be better accom-
152-mm [6-in.] diameter concrete cores, mortar specimens, or
plished if the cutters have a swivel connection allowing some
vertical movement. If the dressing wheels have one rounded
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C09 on
edge, they shall be mounted with the rounded edge toward the
Concrete and ConcreteAggregates and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
vertical shaft. The individual grinding wheel dressers on the
C09.62 on Abrasion Testing of Concrete.
horizontal shaft of the cutter shall be repositioned whenever a
Current edition approved July 10, 1999. Published September 1999. Originally
approved in 1980. Last previous edition approved in 1990 as C 944 – 90a. change in the diameter of the outer cutters becomes apparent.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
This is accomplished by reversing each set of dressing wheels
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
to bring the smaller diameter cutters toward the vertic
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.