ASTM D7731-11e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Dipropylene Glycol Monobutyl Ether and Ethylene Glycol Monobutyl Ether in Sea Water by Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC/MS/MS)
Standard Test Method for Determination of Dipropylene Glycol Monobutyl Ether and Ethylene Glycol Monobutyl Ether in Sea Water by Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC/MS/MS)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
DPGBE and EGBE have a variety of residential and industrial applications such as, cleaning formulations, surface coatings, inks and cosmetics. These analytes may be released into the environment at levels that may be harmful to aquatic life.
This method has been investigated for use with reagent and sea water.
SCOPE
1.1 This procedure covers the determination of Dipropylene Glycol Monobutyl Ether (DPGBE) and Ethylene Glycol Monobutyl Ether (EGBE) in sea water by direct injection using liquid chromatography (LC) and detection with tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS). This analyte is qualitatively and quantitatively determined by this method. This method adheres to selected reaction monitoring (SRM) mass spectrometry.
1.2 The Detection Verification Level (DVL) and Reporting Range for DPGBE and EGBE are listed in Table 1.
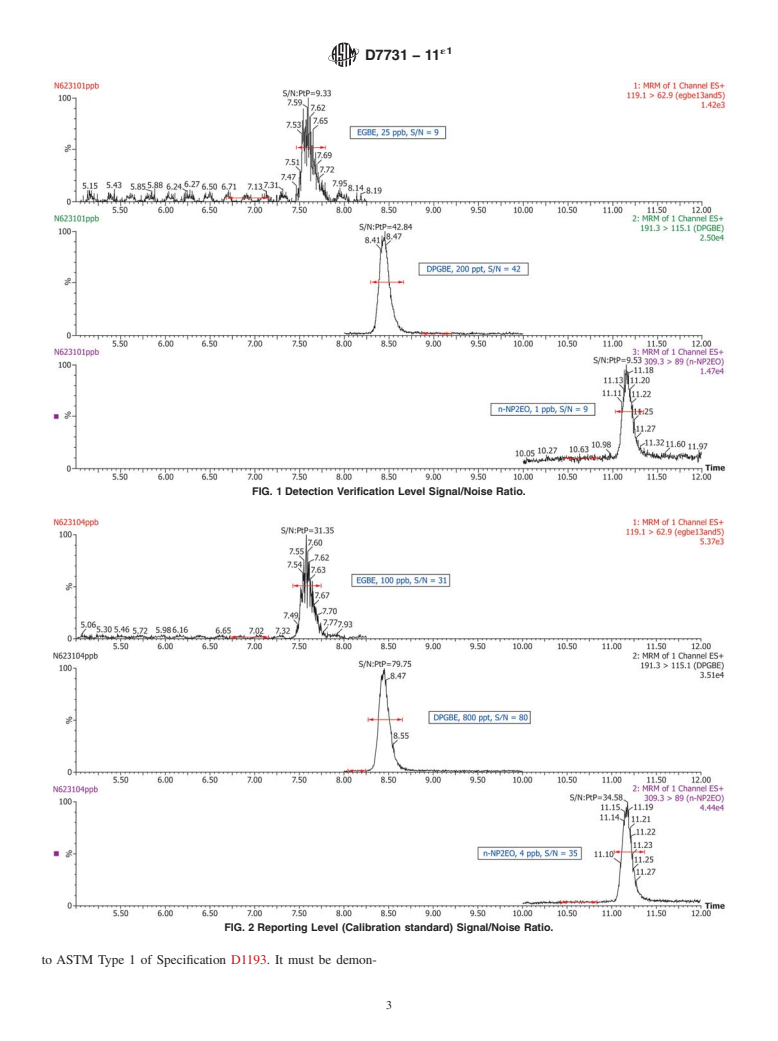
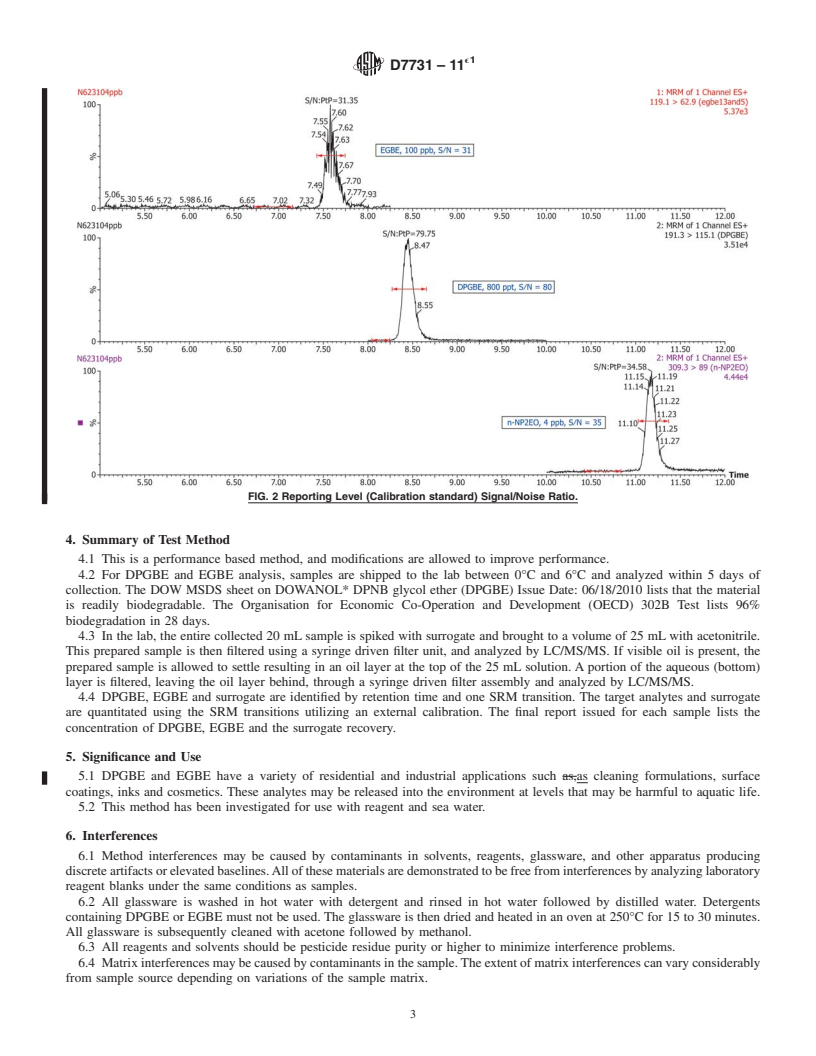
1.2.1 The DVL is required to be at a concentration at least 3 times below the Reporting Limit (RL) and have a signal/noise ratio greater than 3:1. Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 display the signal/noise ratio of the single reaction monitoring (SRM) transition.
1.2.2 The reporting limit is the concentration of the Level 1 calibration standard as shown in Table 4 for DPGBE and EGBE, taking into account the 20% sample preparation dilution factor.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
´1
Designation:D7731 −11
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Dipropylene Glycol Monobutyl Ether and
Ethylene Glycol Monobutyl Ether in Sea Water by Liquid
1
Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC/MS/MS)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7731; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—This test method was changed editorially in August 2011.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1 This procedure covers the determination of Dipropylene
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
Glycol Monobutyl Ether (DPGBE) and Ethylene Glycol
D2777 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias of
MonobutylEther(EGBE)inseawaterbydirectinjectionusing
Applicable Test Methods of Committee D19 on Water
liquid chromatography (LC) and detection with tandem mass
3
2.2 Other Standards:
spectrometry (MS/MS). These analytes are qualitatively and
EPApublication SW-846 Test Methods for Evaluating Solid
quantitativelydeterminedbythismethod.Thismethodadheres
Waste, Physical/Chemical Methods
to selected reaction monitoring (SRM) mass spectrometry.
3. Terminology
1.2 The Detection Verification Level (DVL) and Reporting
Range for DPGBE and EGBE are listed in Table 1. 3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 detection verification level, DVL, n—a concentration
1.2.1 The DVL is required to be at a concentration at least
that has a signal/noise ratio greater than 3:1 and is at least 3
3 times below the Reporting Limit (RL) and have a signal/
times below the Reporting Limit (RL).
noise ratio greater than 3:1. Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 display the
signal/noise ratio of the single reaction monitoring (SRM) 3.1.2 reporting limit, RL, n—the concentration of the
transition. lowest-level calibration standard used for quantification.
3.1.2.1 Discussion—In this test method, a 20 mL sample
1.2.2 The reporting limit is the concentration of the Level 1
aliquot is diluted to a 25 mL final volume after thoroughly
calibration standard as shown in Table 4 for DPGBE and
rinsing the collection vial with acetonitrile for quantitative
EGBE, taking into account the 20% sample preparation dilu-
transfer.Inthiscase,thelowestcalibrationlevelof100ppbfor
tion factor.
EGBE would allow for a reporting limit of 125 ppb to be
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
achieved.
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
3.2 Symbols:
standard.
3.2.1 ppb—parts per billion, µg/L
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the 3.2.2 ppt—parts per trillion, ng/L
-3
3.2.3 mM—millimolar,1x10 moles/L
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.2.4 NA—no addition
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.2.5 ND—non-detect
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D19 on Water Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
andisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeD19.06onMethodsforAnalysisfor the ASTM website.
3
Organic Substances in Water. Available from National Technical Information Service (NTIS), U.S. Depart-
Current edition approved May 1, 2011. Published June 2011. DOI: 10.1520/ ment of Commerce, 5285 Port Royal Road, Springfield, VA, 22161 or at http://
D7731-11E01. www.epa.gov/epawaste/hazard/testmethods/index.htm
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
´1
D7731−11
TABLE 1 Detection Verification Level and Reporting Range
6.4 Matrix interferences may be caused by contaminants in
Analyte DVL (µg/L) Reporting Range the sample. The extent of matrix interferences can vary
(µg/L)
considerably from sample source depending on variations of
DPGBE 0.2 1–10
the sample matrix.
EGBE 25 125–1250
7. Apparatus
7.1 LC/MS/MS System
4. Summary of Test Method
7.1.1 Liquid Chromatography System—Acomplete LC sys-
4
4.1 This is a performance based method, and modifications
tem is needed in order to analyze samples. Any system that is
are allowed to improve performance.
capable of performing at the flows, pressures, controlled
temperatures, sample volumes, and requirements of the stan-
4.2 For DPGBE and EGBE analysis, samples are shipped to
dard may be used.
the lab between 0°C and 6°C and analyzed within 5 days of
7.1.2 Analytical Column—Waters
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
ϵ1
Designation:D7731–11 Designation: D7731 – 11
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Dipropylene Glycol Monobutyl Ether and
Ethylene Glycol Monobutyl Ether in Sea Water by Liquid
1
Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC/MS/MS)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7731; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (ϵ) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ϵ NOTE—This Test Method was changed editorially in August, 2011
1. Scope
1.1 This procedure covers the determination of Dipropylene Glycol Monobutyl Ether (DPGBE) and Ethylene Glycol
Monobutyl Ether (EGBE) in sea water by direct injection using liquid chromatography (LC) and detection with tandem mass
spectrometry (MS/MS).This analyte isThese analytes are qualitatively and quantitatively determined by this method.This method
adheres to selected reaction monitoring (SRM) mass spectrometry.
1.2 The Detection Verification Level (DVL) and Reporting Range for DPGBE and EGBE are listed in Table 1.
1.2.1 The DVLis required to be at a concentration at least 3 times below the Reporting Limit (RL) and have a signal/noise ratio
greater than 3:1. Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 display the signal/noise ratio of the single reaction monitoring (SRM) transition.
1.2.2 The reporting limit is the concentration of the Level 1 calibration standard as shown in Table 4 for DPGBE and EGBE,
taking into account the 20% sample preparation dilution factor.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D2777 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias of Applicable Test Methods of Committee D19 on Water
3
2.2 Other Standards:
EPA publication SW-846 Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste, Physical/Chemical Methods
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 detection verification level, DVL, n—a concentration that has a signal/noise ratio greater than 3:1 and is at least 3 times
below the Reporting Limit (RL).
3.1.2 reporting limit, RL, n—the concentration of the lowest-level calibration standard used for quantification.
3.1.2.1 Discussion—In this test method, a 20 mLsample aliquot is diluted to a 25 mLfinal volume after thoroughly rinsing the
collectionvialwithacetonitrileforquantitativetransfer.Inthiscase,thelowestcalibrationlevelof100ppbforEGBEwouldallow
for a reporting limit of 125 ppb to be achieved.
3.2 Abbreviations:
3.2.1 ppb—parts per billion, µg/L
3.2.2 ppt—parts per trillion, ng/L
-3
3.2.3 mM—millimolar,1x10 moles/L
3.2.4 NA—no addition
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D19 on Water and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D19.06 on Methods for Analysis for
Organic Substances in Water.
Current edition approved May 1, 2011. Published May,August,, 2011. DOI: 10.1520/D7731–11E01.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from from National Technical Information Service (NTIS), U.S. Department of Commerce, 5285 Port Royal Road, Springfield, VA, 22161 or at
http://www.epa.gov/epawaste/hazard/testmethods/index.htm
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
ϵ1
D7731 – 11
TABLE 1 Detection Verification Level and Reporting Range
Analyte DVL (µg/L) Reporting Range (µg/L)
DPGBE 0.2 1–10
EGBE 25 125–1250
FIG. 1 Detection Verification Level Signal/Noise Ratio.
3.2.5 ND—non-detect
2
---------------------- Page: 2 ----------------------
ϵ1
D7731 – 11
FIG. 2 Reporting Level (Calibration standard) Signal/Noise Ratio.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 This is a performance based method, and modifications are allowed to improve performance.
4.2 For DPGBE and EGBE analysis, samples are shipped to the lab between 0°C and 6°C and
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.