ASTM B21/B21M-18
(Specification)Standard Specification for Naval Brass Rod, Bar, and Shapes
Standard Specification for Naval Brass Rod, Bar, and Shapes
ABSTRACT
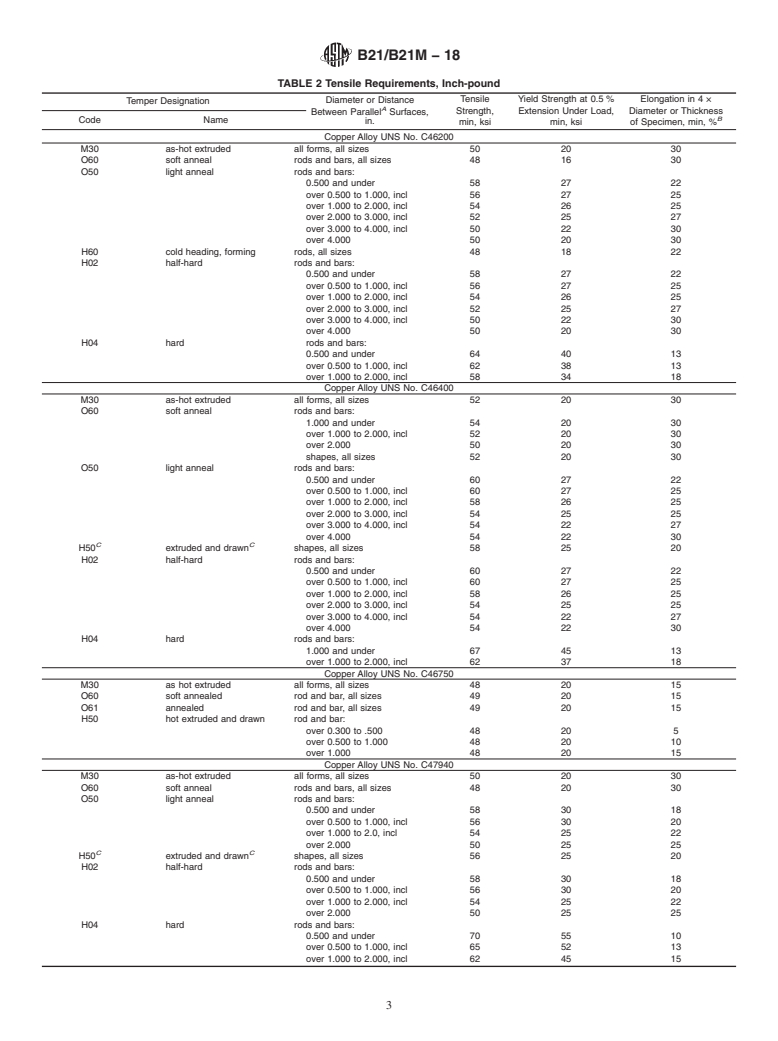
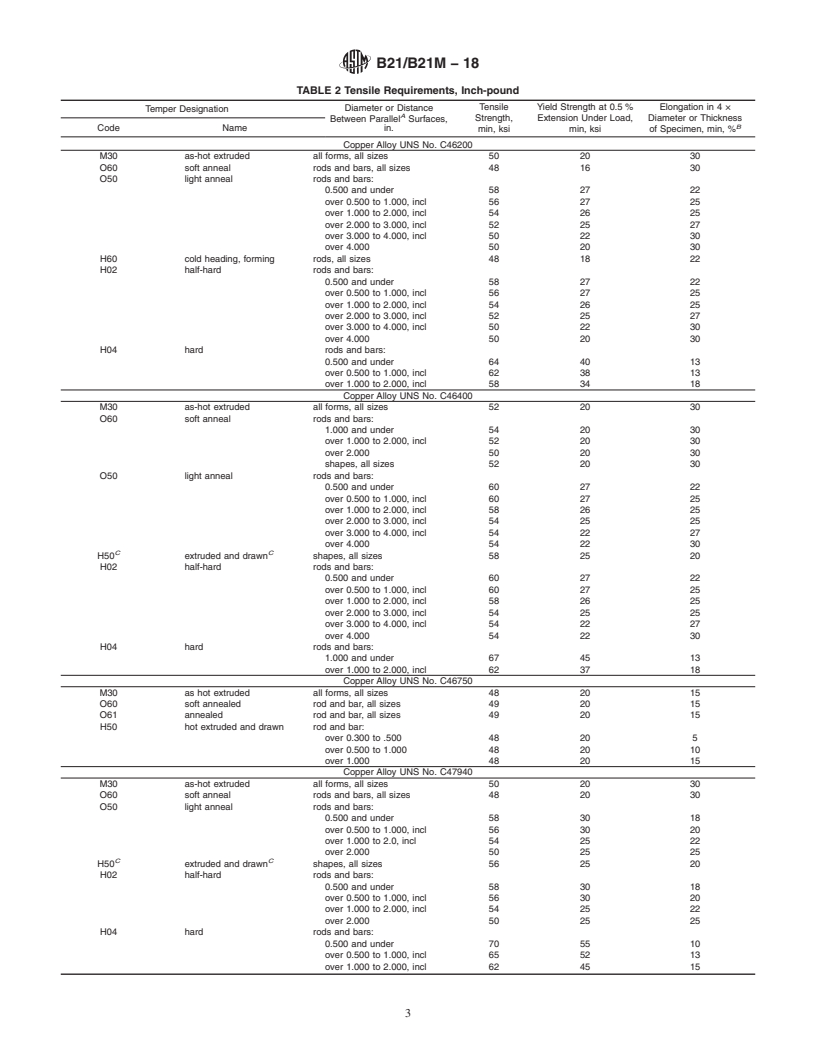
This specification establishes the requirements for rods, bars, and shapes of naval brass with Copper Alloy UNS Nos. C46200, C46400, C47940, C48200, and C48500. Tempers available under this specification are M30 (as-hot extruded), O60 (soft annealed), O50 (light annealed), H60 (cold headed and formed), H02 (½ hard), and H04 (hard). Products shall be tested and shall adhere to dimensional (diameter, shape, length, straightness, and edge contour), mechanical (tensile and yield strength, Rockwell hardness, and elongation), and chemical composition requirements. Products shall also meet piston-finish rod and shafting, and U.S. Government purchase requirements.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for naval brass rod, bar, and shapes produced from Copper Alloy UNS Nos. C46200, C46400, C46750, C47940, C48200, C48500, or C48640.
1.1.1 For piston-finish rod or shafting refer to the Other Requirements Section.
1.1.2 For hot forging material, refer to Specification B124/B124M.
1.2 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification.
1.3 Warning—Mercury is a definite health hazard in use and disposal (see Performance Requirements).
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: B21/B21M −18
Standard Specification for
1
Naval Brass Rod, Bar, and Shapes
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B21/B21M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* B124/B124M Specification for Copper and Copper Alloy
Forging Rod, Bar, and Shapes
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for naval
B154 Test Method for Mercurous Nitrate Test for Copper
brass rod, bar, and shapes produced from Copper Alloy UNS
Alloys
Nos. C46200, C46400, C46750, C47940, C48200, C48500, or
B249/B249M Specification for General Requirements for
C48640.
Wrought Copper and Copper-Alloy Rod, Bar, Shapes and
1.1.1 For piston-finish rod or shafting refer to the Other
Forgings
Requirements Section.
B601 Classification forTemper Designations for Copper and
1.1.2 For hot forging material, refer to Specification B124/
Copper Alloys—Wrought and Cast
B124M.
B858 Test Method forAmmoniaVaporTest for Determining
1.2 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units or SI units
Susceptibility to Stress Corrosion Cracking in Copper
are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, SI
Alloys
units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system
E8/E8M Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Ma-
may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be
terials
used independently of the other. Combining values from the
E18 Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness of Metallic Ma-
two systems may result in nonconformance with the specifi-
terials
cation.
E62 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper and
3
CopperAlloys (Photometric Methods) (Withdrawn 2010)
1.3 Warning—Mercury is a definite health hazard in use
and disposal (see Performance Requirements). E478 Test Methods for ChemicalAnalysis of CopperAlloys
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3. General Requirements
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1 The following sections of Specification B249/B249M
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
constitute a part of this specification:
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
3.1.1 Terminology,
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3.1.2 Materials and Manufacture,
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
3.1.3 Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance,
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
3.1.4 Sampling,
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
3.1.5 Number of Tests and Retests,
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
3.1.6 Specimen Preparation,
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
3.1.7 Test Methods,
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
3.1.8 Significance of Numerical Limits,
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.9 Inspection,
2
3.1.10 Rejection and Rehearing,
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.1.11 Certification,
3.1.12 Mill Test Report,
1
ThisspecificationisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeB05onCopper
3.1.13 Packaging and Product Marking, and
and CopperAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.02 on Rod,
3.1.14 Supplementary Requirements.
Bar, Wire, Shapes and Forgings.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2018. Published October 2018. Originally
3.2 In addition, when a section with a title identical to that
approved in 1918. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as B21/B21M–14. DOI:
referenced in 3.1, above, appears in this specification, it
10.1520/B0021_B0021M–18.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
the ASTM website. www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B21/B21M − 18
contains additional requirements which supplement those ap- 5.3 For alloys in which zinc is listed as the “remainder,”
pearing in Specification B249/B249M. either copper or zinc may be taken as the difference between
the sum of the results of all other elements determined and
4. Ordering Information
100 %. When copper is so determined, that difference value
shall conform to the requirements given in Table 1.
4.1 Include the following specified choices when placing
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: B21/B21M − 14 B21/B21M − 18
Standard Specification for
1
Naval Brass Rod, Bar, and Shapes
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B21/B21M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for naval brass rod, bar, and shapes produced from Copper Alloy UNS Nos.
C46200, C46400, C46750, C47940, C48200, C48500, or C48500.C48640.
1.1.1 For piston-finish rod or shafting refer to the Other Requirements Section.
1.1.2 For hot forging material, refer to Specification B124/B124M.
1.2 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, SI units
are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used
independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification.
1.3 Warning—Mercury is a definite health hazard in use and disposal (see Performance Requirements).
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
B124/B124M Specification for Copper and Copper Alloy Forging Rod, Bar, and Shapes
B154 Test Method for Mercurous Nitrate Test for Copper Alloys
B249/B249M Specification for General Requirements for Wrought Copper and Copper-Alloy Rod, Bar, Shapes and Forgings
B601 Classification for Temper Designations for Copper and Copper Alloys—Wrought and Cast
B858 Test Method for Ammonia Vapor Test for Determining Susceptibility to Stress Corrosion Cracking in Copper Alloys
E8/E8M Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
E18 Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness of Metallic Materials
3
E62 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper and Copper Alloys (Photometric Methods) (Withdrawn 2010)
E478 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper Alloys
3. General Requirements
3.1 The following sections of Specification B249/B249M constitute a part of this specification:
3.1.1 Terminology,
3.1.2 Materials and Manufacture,
3.1.3 Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance,
3.1.4 Sampling,
3.1.5 Number of Tests and Retests,
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B05 on Copper and Copper Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.02 on Rod, Bar,
Wire, Shapes and Forgings.
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2014Oct. 1, 2018. Published September 2014October 2018. Originally approved in 1918. Last previous edition approved in 20122014
as B21/B21M – 12.B21/B21M–14. DOI: 10.1520/B0021_B0021M-14.10.1520/B0021_B0021M–18.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’sstandard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B21/B21M − 18
3.1.6 Specimen Preparation,
3.1.7 Test Methods,
3.1.8 Significance of Numerical Limits,
3.1.9 Inspection,
3.1.10 Rejection and Rehearing,
3.1.11 Certification,
3.1.12 Mill Test Report,
3.1.13 Packaging and Product Marking, and
3.1.14 Supplementary Requirements.
3.2 In addition, when a section with a title identical to that referenced in 3.1, above, appears in this specification, it contains
additional requirements which supplement those appearing in Sp
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.