ASTM F1864-16
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Dust Erosion Resistance of Optical and Infrared Transparent Materials and Coatings
Standard Test Method for Dust Erosion Resistance of Optical and Infrared Transparent Materials and Coatings
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 All materials on exterior aircraft surfaces are subject to abrasion from airborne particles of various sizes and shapes. Transparent materials are particularly vulnerable to abrasion, since their performance is based on their ability to transmit light with a minimal amount of scatter. Scratches, pitting, and coating removal and delamination as a result of abrasion may increase scatter, reduce transmission, and degrade the performance of transparent materials. Visually transparent materials are required for pilot and air crew enclosures, such as canopies, windshields, and viewpoints. Materials transparent in the IR region (8 to 12 μm) are required for tracking, targeting, and navigational instrumentation.
5.2 This test method is intended to provide a calibrated and repeatable means of determining the relative abrasion resistance of materials and coatings for optical and IR transparent materials and coatings. The test parameters for this test method can be directly related to dust cloud densities and velocities to which transparent materials are exposed in the field.
SCOPE
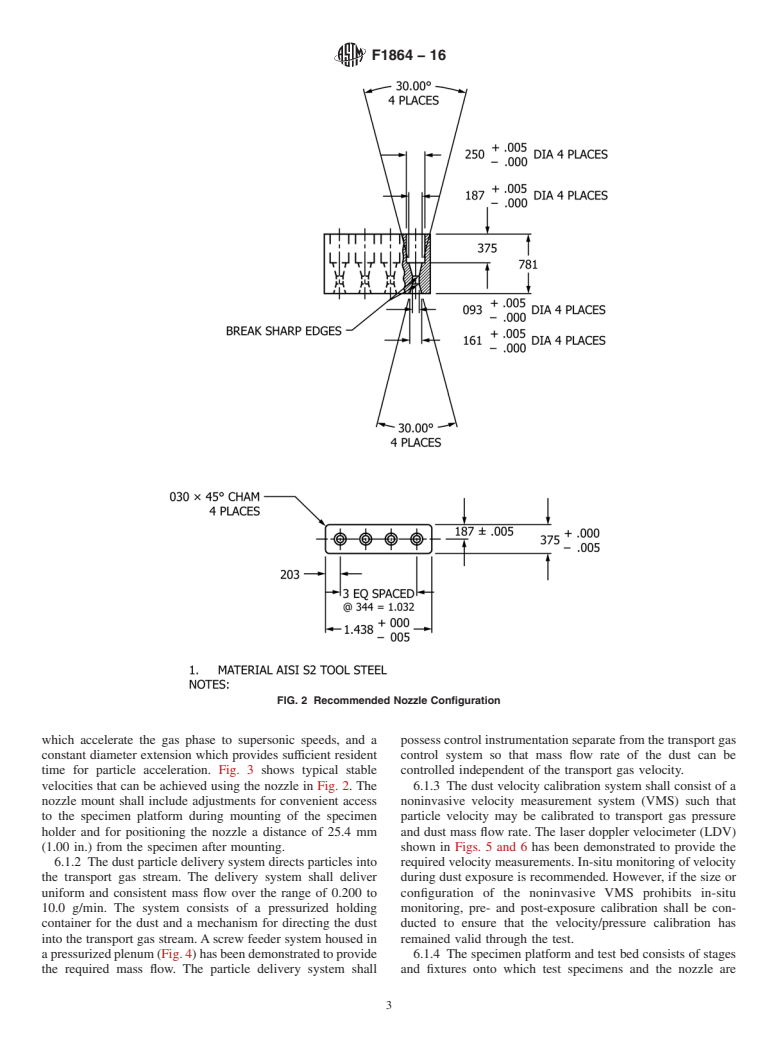
1.1 This test method covers the resistance of transparent plastics and coatings used in aerospace windscreens, canopies, and viewports to surface erosion as a result of dust impingement. This test method simulates flight through a defined particle cloud environment by means of independent control of particle size, velocity, impact angle, mass loading, and test duration.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F1864 − 16
Standard Test Method for
Dust Erosion Resistance of Optical and Infrared Transparent
1
Materials and Coatings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1864; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.1.2 mean IR transmission, n—for the purposes of this
standard, the average percentage of light transmitted by a
1.1 This test method covers the resistance of transparent
material in the 8- to 12-µm bandwidth.
plastics and coatings used in aerospace windscreens, canopies,
3.1.3 sweep time, n—the time required for one translation
and viewports to surface erosion as a result of dust impinge-
pass.
ment. This test method simulates flight through a defined
particlecloudenvironmentbymeansofindependentcontrolof
3.1.4 translation pass, n—the translation of the specimen
particle size, velocity, impact angle, mass loading, and test
platformfromtheverticalorhorizontallimittothecorrespond-
duration.
ing vertical or horizontal limit.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.5 translation cycle, n—the translation of the specimen
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
platformfromtheverticalorhorizontallimittothecorrespond-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
ingverticalorhorizontallimitandbacktotheinitialverticalor
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
horizontal limit. Two translation passes are equivalent to one
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
translation cycle.
3.2 Symbols:
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
2
A = reference surface area of specimen platform (cm ),
D618Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
s
3
C = simulated cloud concentration (g/m ),
D1003Test Method for Haze and Luminous Transmittance
c
h = percent haze before exposure,
of Transparent Plastics o
h = percent haze after exposure,
D1193Specification for Reagent Water e
m˙ = rate of particle mass impacting the reference surface
p
E11Specification forWovenWireTest Sieve Cloth andTest
area (g/min),
Sieves
2
m˙ = incremental mass loading (g/cm ),
i
E168Practices for General Techniques of Infrared Quanti-
2
m = total mass loading (g/cm ),
3
T
tative Analysis (Withdrawn 2015)
N = number of increments,
V = particle impact velocity (m/s),
p
3. Terminology
t = sweep time(s),
s
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard: T = optical or mean infrared (IR) transmission after expo-
e
sure (%),
3.1.1 mass loading, n—the mass of dust per unit of total
T = optical or mean IR transmission before exposure (%),
exposed surface area (including the sample holder) that im-
o
α = impact angle (normal incidence=90°),
pinges on the specimens.
∆t = exposure time (min) for loading increment i,
i
2
φ = incremental dust load (g/cm ) for loading increment i,
i
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F07 on
2
Φ = total dust load (g/cm ),
Aerospace andAircraft and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F07.08 on
∆h = change in percent haze, and
Transparent Enclosures and Materials.
Current edition approved April 1, 2016. Published April 2016. Originally
∆T = change in optical or IR transmission.
approved in 1998. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as F1864–05(2010).
DOI: 10.1520/F1864-16.
4. Summary of Test Method
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
4.1 This test method consists of: (1) measuring and record-
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
ing the light transmission properties, at visual or infrared
the ASTM website.
3
wavelengths, of test coupons; (2) mounting the coupons in a
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
www.astm.org. test fixture; (3) exposing the coupons to a dust particle stream;
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F1864 − 16
and (4) remeasuring the light transmission properties to deter- 5.2 This test method is intended to provide a calibrated and
mine changes in these properties. repeatable means of determining the relative abrasion resis-
tance of materials and coatings for optical and IR transparent
4.2 The dust particle stream simulates flight at a specified
materialsandcoatings.Thetestparametersforthistestmethod
velocitythroughadustcloudofspecifieddensity.Simulationis
can be directly related to dust cloud densities and velocities
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: F1864 − 05 (Reapproved 2010) F1864 − 16
Standard Test Method for
Dust Erosion Resistance of Optical and Infrared Transparent
1
Materials and Coatings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1864; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the resistance of transparent plastics and coatings used in aerospace windscreens, canopies, and
viewports to surface erosion as a result of dust impingement. This test method simulates flight through a defined particle cloud
environment by means of independent control of particle size, velocity, impact angle, mass loading, and test duration.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
D1003 Test Method for Haze and Luminous Transmittance of Transparent Plastics
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
E11 Specification for Woven Wire Test Sieve Cloth and Test Sieves
3
E168 Practices for General Techniques of Infrared Quantitative Analysis (Withdrawn 2015)
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 mass loading, n—the mass of dust per unit of total exposed surface area (including the sample holder) that impinges on
the specimens.
3.1.2 mean IR transmission, n—for the purposes of this standard, the average percentage of light transmitted by a material in
the 8- to 12-μm bandwidth.
3.1.3 sweep time, n—the time required for one translation pass.
3.1.4 translation pass, n—the translation of the specimen platform from the vertical or horizontal limit to the corresponding
vertical or horizontal limit.
3.1.5 translation cycle, n—the translation of the specimen platform from the vertical or horizontal limit to the corresponding
vertical or horizontal limit and back to the initial vertical or horizontal limit. Two translation passes are equivalent to one
translation cycle.
3.2 Symbols:
2
A = reference surface area of specimen platform (cm ),
s
3
C = simulated cloud concentration (g/m ),
c
h = percent haze before exposure,
o
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F07 on Aerospace and Aircraft and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F07.08 on Transparent
Enclosures and Materials.
Current edition approved May 1, 2010April 1, 2016. Published June 2010April 2016. Originally approved in 1998. Last previous edition approved in 20052010 as
F1864 – 05.F1864 – 05 (2010). DOI: 10.1520/F1864-05R10.10.1520/F1864-16.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F1864 − 16
h = percent haze after exposure,
e
m˙ = rate of particle mass impacting the reference surface area (g/min),
p
2
m˙ = incremental mass loading (g/cm ),
i
2
m = total mass loading (g/cm ),
T
N = number of increments,
V = particle impact velocity (m/s),
p
t = sweep time(s),
s
T = optical or mean infrared (IR) transmission after exposure (%),
e
T = optical or mean IR transmission before exposure (%),
o
α = impact angle (normal incidence = 90°),
Δt = exposure time (min) for loading increment i,
i
2
φ = incremental dust load (g/cm ) for loading increment i,
i
2
Φ = total dust load (g/cm ),
Δh = change in percent haze, and
ΔT = change in optical or IR transmission.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 This test method consists of: (1) measuring and recording the light transmission properties, at visual or infrared wavelengths,
of test coupons; (2) mounting the coupons in a test fixture; (3) exposing the coupons to a dust particle stream; and (4) remeasuring
the light transmission properties to determine changes in these properties.
4.2 The dust particl
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.