ASTM F136-11
(Specification)Standard Specification for Wrought Titanium-6Aluminum-4Vanadium ELI (Extra Low Interstitial) Alloy for Surgical Implant Applications (UNS R56401)
Standard Specification for Wrought Titanium-6Aluminum-4Vanadium ELI (Extra Low Interstitial) Alloy for Surgical Implant Applications (UNS R56401)
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the chemical, mechanical, and metallurgical requirements for wrought annealed titanium-6aluminum-4vanadium ELI (extra low interstitial) alloy (R56401) to be used in the manufacture of surgical implants. The products are classified into: strip, sheet, plate, bar, forging bar, and wire. The heat analysis shall conform to the chemical composition requirements specified. Product analysis tolerances do not broaden the specified heat analysis requirements but cover variations between laboratories in the measurement of chemical content. Tension test and bend test shall be performed to meet the requirements specified.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers the chemical, mechanical, and metallurgical requirements for wrought annealed titanium-6aluminum-4vanadium ELI (extra low interstitial) alloy (R56401) to be used in the manufacture of surgical implants.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F136 −11
StandardSpecification for
Wrought Titanium-6Aluminum-4Vanadium ELI (Extra Low
Interstitial) Alloy for Surgical Implant Applications (UNS
1
R56401)
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF136;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* F981Practice for Assessment of Compatibility of Biomate-
rials for Surgical Implants with Respect to Effect of
1.1 This specification covers the chemical, mechanical, and
Materials on Muscle and Bone
metallurgical requirements for wrought annealed titanium-
3
2.2 ISO Standards:
6aluminum-4vanadium ELI (extra low interstitial) alloy
ISO 6892Metallic Materials Tensile Testing at Ambient
(R56401) to be used in the manufacture of surgical implants.
Temperature
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
ISO 9001Quality Management Systems Requirements
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
2.3 ASQ Standard:
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
ASQC1SpecificationsofGeneralRequirementsforaQual-
4
and are not considered standard.
ity Control Program
2.4 Aerospace Material Specifications:
2. Referenced Documents
AMS 2249Chemical Check Analysis Limits, Titanium and
2
5
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Titanium Alloys
E8/E8MTest Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Ma-
3. Terminology
terials
E29Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
Determine Conformance with Specifications
3.1.1 beta transus, n—the minimum temperature at which
E290Test Methods for Bend Testing of Material for Ductil-
the alpha plus beta phase can transform to 100% beta phase.
ity
3.1.2 lot, n—the total number of mill products produced
E539TestMethodforAnalysisofTitaniumAlloysbyX-Ray
fromoneheatunderthesameconditionsatessentiallythesame
Fluorescence Spectrometry
time.
E1409TestMethodforDeterminationofOxygenandNitro-
gen in Titanium and Titanium Alloys by the Inert Gas
4. Product Classification
Fusion Technique
4.1 Strip—Any product under 0.1875 in. (4.76 mm) in
E1447Test Method for Determination of Hydrogen in Tita-
thickness and under 24 in. (610 mm) wide.
nium and Titanium Alloys by Inert Gas Fusion Thermal
4.2 Sheet—Any product under 0.1875 in. (4.76 mm) in
Conductivity/Infrared Detection Method
thickness and 24 in. (610 mm) or more in width.
E1941Test Method for Determination of Carbon in Refrac-
toryandReactiveMetalsandTheirAlloysbyCombustion
4.3 Plate—Any product 0.1875 in. (4.76 mm) thick and
Analysis
over and 10 in. (254 mm) wide and over, with widths greater
E2371Test Method for Analysis of Titanium and Titanium
than five times thickness. Plate up to 4.00 in. (101.60 mm),
Alloys by Atomic Emission Plasma Spectrometry
thick inclusive is covered by this specification.
4.4 Bar—Roundbarsandflatsfrom0.1875in.(4.76mm)to
1
4.00 in. (101.60 mm) in diameter or thickness (other sizes and
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F04 on
Medical and Surgical Materials and Devices and is the direct responsibility of
shapes by special order).
Subcommittee F04.12 on Metallurgical Materials.
Current edition approved Dec. 15, 2011. Published January 2012. Originally
ϵ1
3
published in 1984. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as F136–08 . DOI: Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
10.1520/F0136-11. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
2 4
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Available from American Society for Quality (ASQ), 600 N. Plankinton Ave.,
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Milwaukee, WI 53203, http://www.asq.org.
5
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), 400 Commonwealth
the ASTM website. Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096-0001, http://www.sae.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F136−11
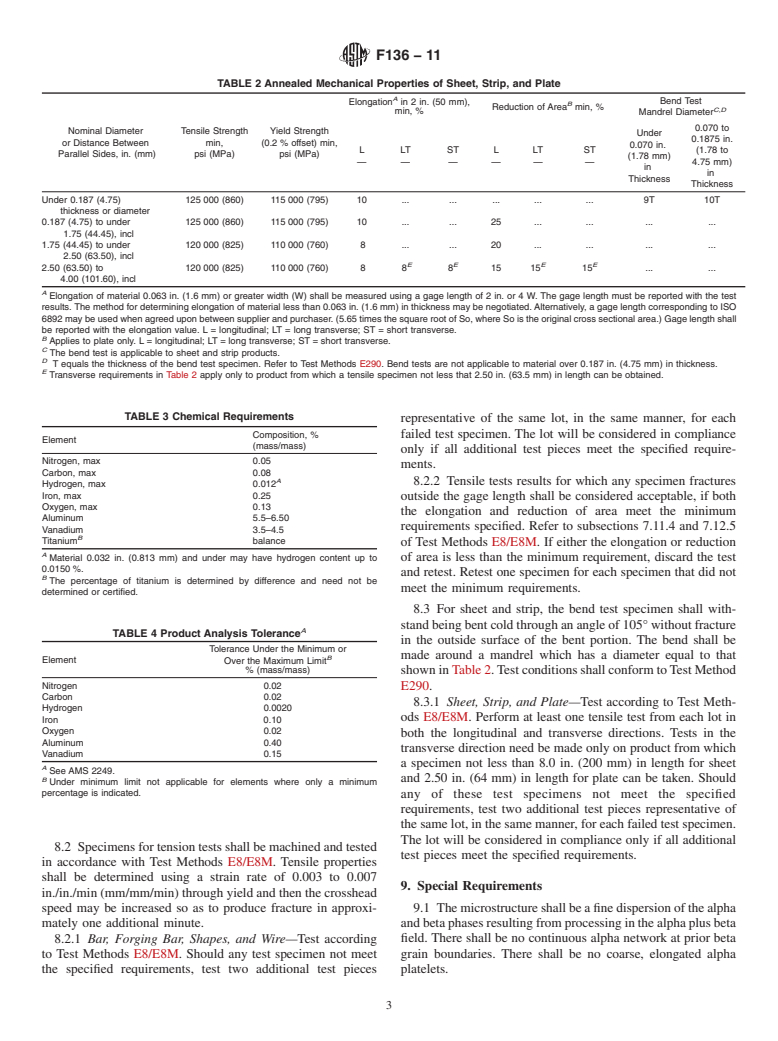
4.5 Forging Bar—Bar as described in 4.4, used for produc- 7. Chemical Requirements
tionofforgings,maybefurnishedinthehotworkedcondition.
7.1 The heat analysis shall conform to the chemical com-
4.6 Wire—Rounds,flats,orothershapeslessthan0.1875in. position specified in Table 3. Ingot analysis may be used for
(4.76 mm) in diameter. reportingallchemicalrequirements,excepthydrogen.Samples
forhydrogenshallbetakenfromthefinishedmillproduct.The
4.7 Other—Other forms and shapes, includi
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation:F136–08 Designation: F136 – 11
Standard Specification for
Wrought Titanium-6Aluminum-4Vanadium ELI (Extra Low
Interstitial) Alloy for Surgical Implant Applications (UNS
1
R56401)
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF136;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
´ NOTE—Subsection 8.3.1 was editorially corrected in December 2008.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers the chemical, mechanical, and metallurgical requirements for wrought annealed titanium-
6aluminum-4vanadium ELI (extra low interstitial) alloy (R56401) to be used in the manufacture of surgical implants.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E8/E8M Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to Determine Conformance with Specifications
E290 Test Methods for Bend Testing of Material for Ductility
E539 Test Method for Analysis of Titanium Alloys by X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometry
E1409 Test Method for Determination of Oxygen and Nitrogen in Titanium and Titanium Alloys by the Inert Gas Fusion
Technique
E1447 Test Method for Determination of Hydrogen in Titanium and Titanium Alloys by Inert Gas Fusion Thermal
Conductivity/Infrared Detection Method
E1941 Test Method for Determination of Carbon in Refractory and Reactive Metals and TheirAlloys by CombustionAnalysis
E2371 Test Method for Analysis of Titanium and Titanium Alloys by Atomic Emission Plasma Spectrometry
F981 Practice for Assessment of Compatibility of Biomaterials for Surgical Implants with Respect to Effect of Materials on
Muscle and Bone
3
2.2 ISO Standards:
ISO 6892 Metallic Materials Tensile Testing at Ambient Temperature
ISO 9001 Quality Management Systems Requirements
2.3 ASQ Standard:
4
ASQ C1 Specifications of General Requirements for a Quality Control Program
2.4 Aerospace Material Specifications:
5
AMS 2249 Chemical Check Analysis Limits, Titanium and Titanium Alloys
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 beta transus, n—the minimum temperature at which the alpha plus beta phase can transform to 100 % beta phase.
3.1.2 lot, n—the total number of mill products produced from one heat under the same conditions at essentially the same time.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F04 on Medical and Surgical Materials and Devices and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
F04.12 on Metallurgical Materials.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2008. Published December 2008. Originally published in 1984. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as F136–02a. DOI:
10.1520/F0136-08E01.
´1
Current edition approved Dec. 15, 2011. Published January 2012. Originally published in 1984. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as F136 – 08 . DOI:
10.1520/F0136-11.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
4
Available from American Society for Quality (ASQ), 600 N. Plankinton Ave., Milwaukee, WI 53203, http://www.asq.org.
5
Available from Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), 400 Commonwealth Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096-0001, http://www.sae.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F136 – 11
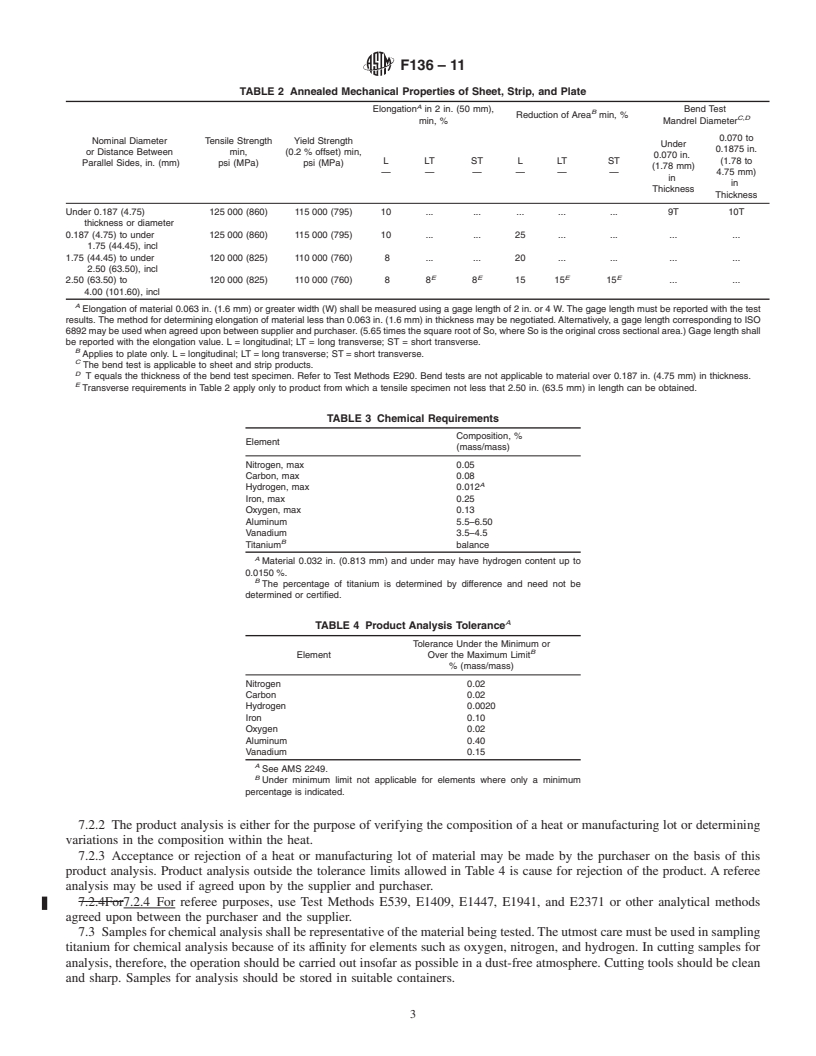
4. Product Classification
4.1 Strip—Any product under 0.1875 in. (4.76 mm) in thickness and under 24 in. (610 mm) wide.
4.2 Sheet—Any product under 0.1875 in. (4.76 mm) in thickness and 24 in. (610 mm) or more in width.
4.3 Plate—Any product 0.1875 in. (4.76 mm) thick and over and 10 in. (254 mm) wide and over, with widths greater than five
times thickness. Plate up to 4.00 in. (101.60 mm), thick inclusive is covered by this specification.
4.4 Bar—Rou
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.