ASTM B387-18
(Specification)Standard Specification for Molybdenum and Molybdenum Alloy Bar, Rod, and Wire
Standard Specification for Molybdenum and Molybdenum Alloy Bar, Rod, and Wire
ABSTRACT
This specification covers unalloyed molybdenum and molybdenum alloy bar, rod, and wire. The following materials are covered: molybdenum 360, molybdenum 361, molybdenum 363, molybdenum 364, molybdenum 365, and molybdenum 366. These materials shall be manufactured with conventional extrusion, forging, swaging, rolling, and drawing equipment. These shall materials be made by vacuum arc-melted or powder metallurgy methods. The chemical composition shall conform to the required contents of carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, iron, nickel, silicon, titanium, tungsten, zirconium, and molybdenum. Chemical analysis shall be done. Mechanical properties shall conform to the required tension properties: tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, and diamond pyramid hardness. Tension test shall also be done.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers unalloyed molybdenum and molybdenum alloy bar, rod, and wire as follows:
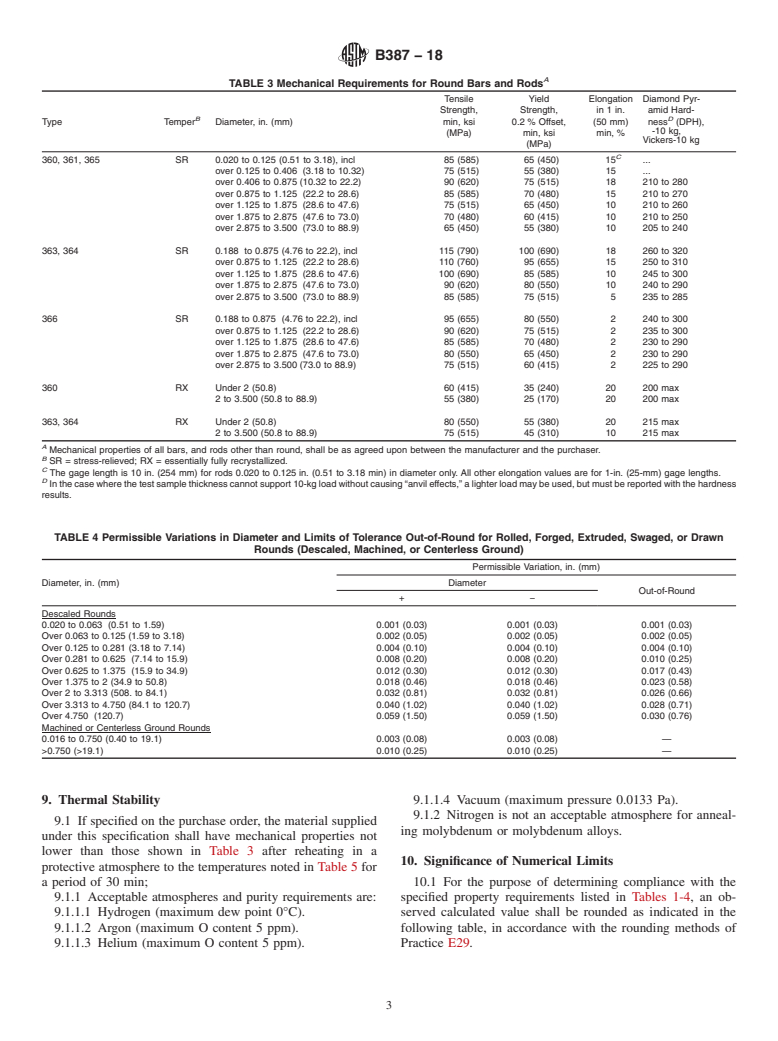
1.1.1 Molybdenum 360—Unalloyed vacuum arc-cast molybdenum.
1.1.2 Molybdenum 361—Unalloyed powder metallurgy molybdenum.
1.1.3 Molybdenum Alloy 363—Vacuum arc-cast molybdenum–0.5 % titanium–0.1 % zirconium (TZM) alloy.
1.1.4 Molybdenum Alloy 364—Powder metallurgy molybdenum–0.5 % titanium–0.1 % zirconium (TZM) alloy.
1.1.5 Molybdenum 365—Unalloyed vacuum arc-cast molybdenum, low carbon.
1.1.6 Molybdenum Alloy 366—Vacuum arc-cast molybdenum, 30 % tungsten alloy.
1.2 This specification covers wire no smaller than 0.020 in. (0.51 mm) in diameter or of equivalent cross-sectional area. Specification F289 covers diameters up to 0.020 in. (0.51 mm).
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the test method portions of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: B387 − 18
Standard Specification for
1
Molybdenum and Molybdenum Alloy Bar, Rod, and Wire
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B387; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1 This specification covers unalloyed molybdenum and
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
molybdenum alloy bar, rod, and wire as follows:
[Metric] E0008_E0008M
1.1.1 Molybdenum 360—Unalloyed vacuum arc-cast mo-
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
lybdenum.
Determine Conformance with Specifications
1.1.2 Molybdenum 361—Unalloyed powder metallurgy mo-
E92 Test Methods for Vickers Hardness and Knoop Hard-
lybdenum.
ness of Metallic Materials
1.1.3 Molybdenum Alloy 363—Vacuum arc-cast molybde-
E384 Test Method for Microindentation Hardness of Mate-
num–0.5 % titanium–0.1 % zirconium (TZM) alloy.
rials
1.1.4 Molybdenum Alloy 364—Powder metallurgy molyb-
E1941 Test Method for Determination of Carbon in Refrac-
denum–0.5 % titanium–0.1 % zirconium (TZM) alloy.
tory and Reactive Metals and Their Alloys by Combustion
1.1.5 Molybdenum 365—Unalloyed vacuum arc-cast
Analysis
molybdenum, low carbon.
F289 Specification for Molybdenum Wire and Rod for
1.1.6 Molybdenum Alloy 366—Vacuum arc-cast
Electronic Applications
molybdenum, 30 % tungsten alloy.
1.2 This specification covers wire no smaller than 0.020 in.
3. Terminology
(0.51 mm) in diameter or of equivalent cross-sectional area.
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
Specification F289 covers diameters up to 0.020 in. (0.51 mm).
3.1.1 bar and rod, n—any straight product with a round,
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded rectangular, hexagonal, or octagonal solid cross section, 4 in.
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical (101.6 mm) in diameter or less, or of equivalent cross-sectional
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only area.
and are not considered standard.
3.1.2 wire, n—any product furnished in coils or on spools or
1.4 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the reels.
test method portions of this specification: This standard does
3.2 Lot Definition:
not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any,
3.2.1 for chemical composition, n—the product of a single
associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
blend of powder or a single vacuum melted ingot.
standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environ-
3.2.2 for mechanical property measurement, n—the product
mental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
manufactured from ingots sintered from either a single powder
limitations prior to use.
lot in a single sintering run in the same furnace or a single
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
ingot, processed through the same processing equipment in a
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
single uninterrupted run, using the same thermomechanical
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
process to reach the same final size.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
4. Ordering Information
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
4.1 Orders for material under this specification shall include
the following information as applicable:
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B10 on
Reactive and Refractory Metals and Alloys and is the direct responsibility of
2
Subcommittee B10.04 on Molybdenum and Tungsten. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved July 1, 2018. Published September 2018. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1962. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as B387 – 10. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/B0387-18. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B387 − 18
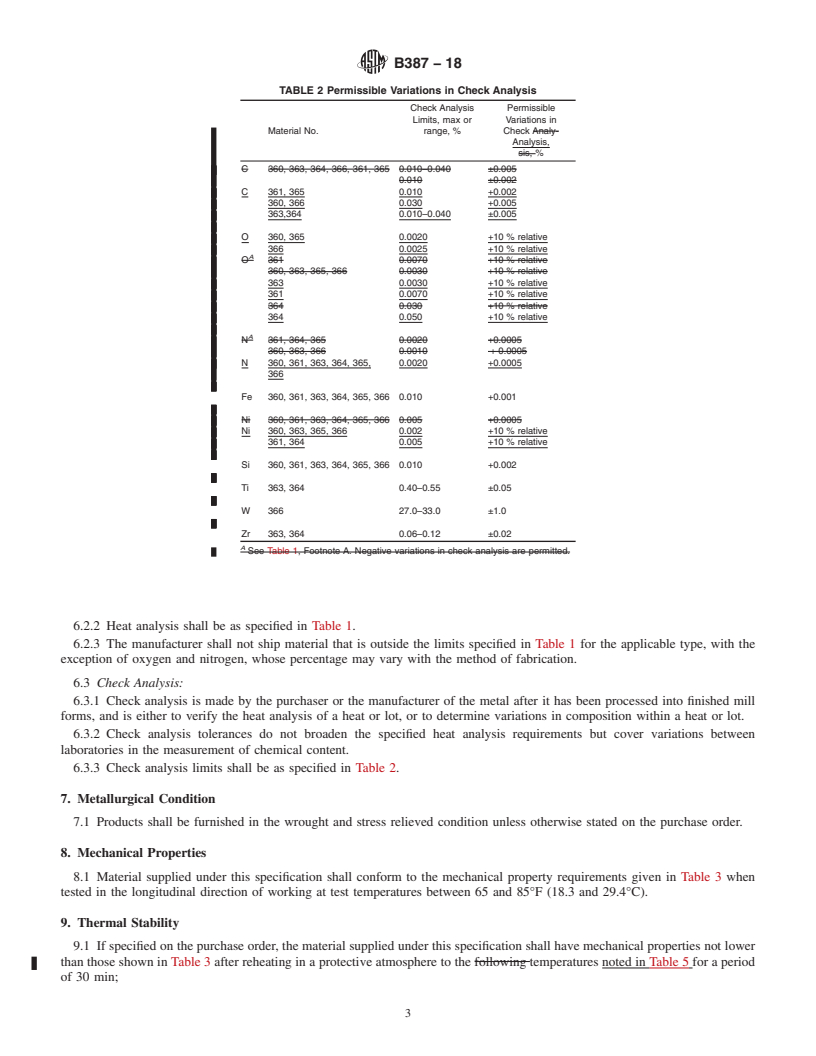
TABLE 2 Permissible Variations in Check Analysis
4.1.1 Material number and temper designation (Section 1
and Table 3), Check Analysis Permissible
Limits, max or Variations in
4.1.2 Product form (Section 3),
Material No.
range, % Check Analysis,
4.1.3 Chemical requirements (Table 1 and Table 2),
%
4.
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: B387 − 10 B387 − 18
Standard Specification for
1
Molybdenum and Molybdenum Alloy Bar, Rod, and Wire
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B387; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This specification covers unalloyed molybdenum and molybdenum alloy bar, rod, and wire as follows:
1.1.1 Molybdenum 360—Unalloyed vacuum arc-cast molybdenum.
1.1.2 Molybdenum 361—Unalloyed powder metallurgy molybdenum.
1.1.3 Molybdenum Alloy 363—Vacuum arc-cast molybdenum–0.5 % titanium–0.1 % zirconium (TZM) alloy.
1.1.4 Molybdenum Alloy 364—Powder metallurgy molybdenum–0.5 % titanium–0.1 % zirconium (TZM) alloy.
1.1.5 Molybdenum 365—Unalloyed vacuum arc-cast molybdenum, low carbon.
1.1.6 Molybdenum Alloy 366—Vacuum arc-cast molybdenum, 30 % tungsten alloy.
1.2 This specification covers wire no smaller than 0.020 in. (0.51 mm) in diameter or of equivalent cross-sectional area.
Specification F289 covers diameters up to 0.020 in. (0.51 mm).
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the test method portions of this specification: This standard does not
purport to address all of the safety concern, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to
establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the test method portions of this specification: This standard does not
purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to
establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior
to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials [Metric] E0008_E0008M
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to Determine Conformance with Specifications
E92 Test Methods for Vickers Hardness and Knoop Hardness of Metallic Materials
E384 Test Method for Microindentation Hardness of Materials
E2626E1941 Guide for Spectrometric Analysis of Reactive and Refractory MetalsTest Method for Determination of Carbon in
Refractory and Reactive Metals and Their Alloys by Combustion Analysis (Withdrawn 2017)
F289 Specification for Molybdenum Wire and Rod for Electronic Applications
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 bar and rod, n—any straight product with a round, rectangular, hexagonal, or octagonal solid cross section, 4 in. (101.6
mm) in diameter or less, or of equivalent cross-sectional area.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B10 on Reactive and Refractory Metals and Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
B10.04 on Molybdenum and Tungsten.
Current edition approved June 1, 2010July 1, 2018. Published July 2010September 2018. Originally approved in 1962. Last previous edition approved in 20012010 as
B387 - 90 (2001)B387 which was withdrawn January 2010 and reinstated in June 2010. DOI: 10.1520/B0387-10. – 10. DOI: 10.1520/B0387-18.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’sstandard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B387 − 18
3.1.2 wire, n—any product furnished in coils or on spools or reels.
NOTE 1—This specificatio
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.