ASTM D1720-03(2008)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Dilution Ratio of Active Solvents in Cellulose Nitrate Solutions
Standard Test Method for Dilution Ratio of Active Solvents in Cellulose Nitrate Solutions
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
By use of standard or reference grade materials for any two of the three components, namely, oxygenated solvent, diluent, or cellulose nitrate, the effect of different batches or different types of the third component can be determined.
This test method is applicable for the determination of the following:
The dilution ratio of toluene as the standard diluent to an oxygenated solvent under test, using as the solute standard cellulose nitrate as defined in 5.2.
The dilution ratio of a hydrocarbon diluent under test to n-butyl acetate as the standard solvent, using as a solute standard cellulose nitrate as defined in 5.2.
The dilution ratio of toluene, as the standard diluent, to n-butyl acetate as the standard solvent, using as the solute cellulose nitrate of varying solubility characteristics.
The information developed through this test may be useful in the formulation of cellulose-based lacquers and adhesives.
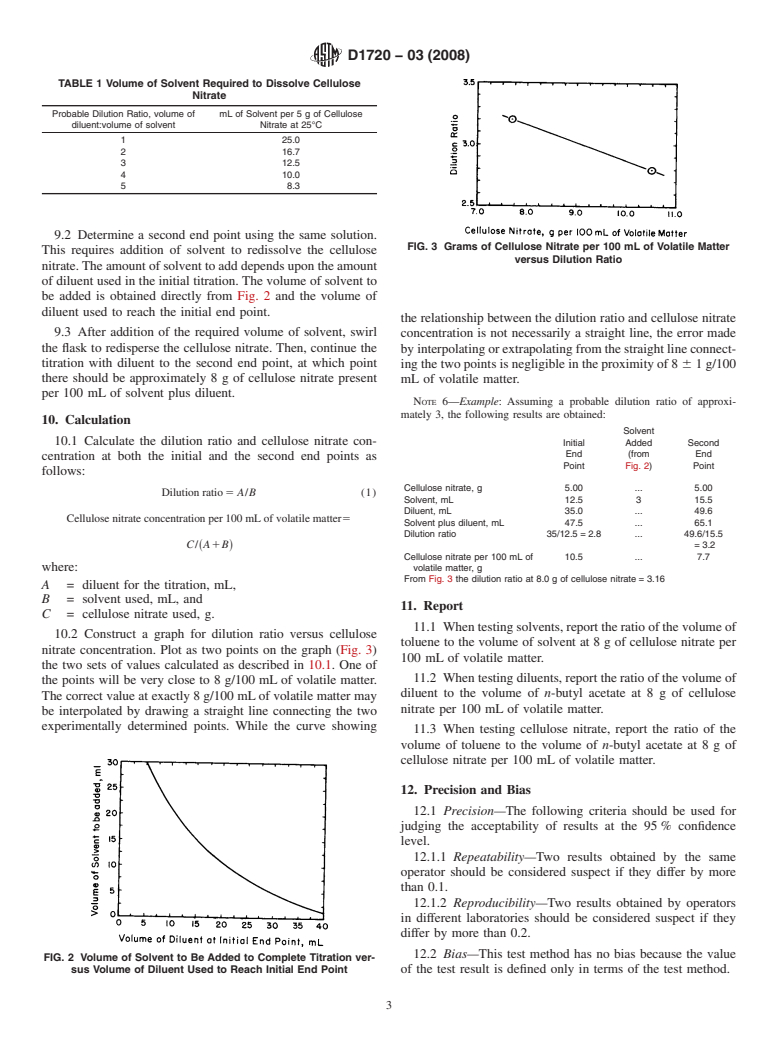
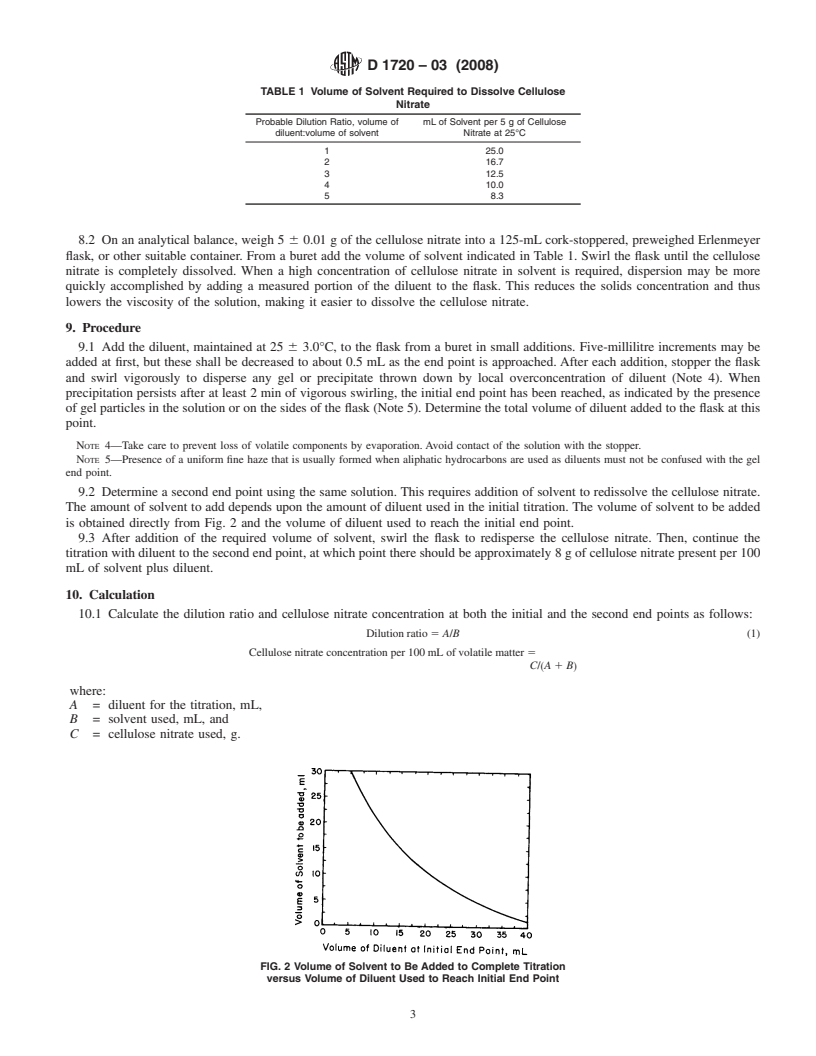
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the volume ratio of hydrocarbon diluent to active solvent required to cause persistent heterogeneity (precipitation) in a solution of cellulose nitrate.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 The following applies to all specified limits in this standard; for purposes of determining conformance with this standard, an observed value or a calculated value shall be rounded off “to the nearest unit” in the last right-hand digit used in expressing the specification limit, in accordance with the rounding-off method of Practice E 29.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see Section 6.
1.5 For hazard information and guidance, see the supplier's Material Safety Data Sheet.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D1720 − 03 (Reapproved2008)
Standard Test Method for
Dilution Ratio of Active Solvents in Cellulose Nitrate
Solutions
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1720; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
Determine Conformance with Specifications
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the volume
ratio of hydrocarbon diluent to active solvent required to cause
3. Terminology
persistent heterogeneity (precipitation) in a solution of cellu-
lose nitrate. 3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 dilution ratio, n—the maximum number of unit vol-
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
umes of a diluent that can be added to a unit volume of solvent
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
to cause the first persistent heterogeneity (precipitation) in the
standard.
solution at a concentration of 8 g cellulose nitrate per 100 mL
1.3 The following applies to all specified limits in this
of combined solvent plus diluent and at a temperature of 25 6
standard; for purposes of determining conformance with this
3°C.
standard, an observed value or a calculated value shall be
NOTE 1—The dilution ratio decreases as the cellulose nitrate concen-
rounded off “to the nearest unit” in the last right-hand digit
tration at the end point increases. It is, therefore, necessary to set an
used in expressing the specification limit, in accordance with
arbitrary concentration of cellulose nitrate as part of the dilution ratio
the rounding-off method of Practice E29.
term. For this purpose 8.0 g of cellulose nitrate per 100 mLof solvent plus
diluent has been adopted.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4. Significance and Use
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
4.1 By use of standard or reference grade materials for any
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard
two of the three components, namely, oxygenated solvent,
statements, see Section 6.
diluent, or cellulose nitrate, the effect of different batches or
1.5 For hazard information and guidance, see the supplier’s
different types of the third component can be determined.
Material Safety Data Sheet.
4.2 This test method is applicable for the determination of
the following:
2. Referenced Documents
4.2.1 The dilution ratio of toluene as the standard diluent to
2.1 ASTM Standards:
an oxygenated solvent under test, using as the solute standard
D301 Test Methods for Soluble Cellulose Nitrate (With-
cellulose nitrate as defined in 5.2.
drawn 2011)
4.2.2 The dilution ratio of a hydrocarbon diluent under test
D841 Specification for Nitration Grade Toluene
to n-butyl acetate as the standard solvent, using as a solute
D4615 Specification forn-Butyl Acetate (All Grades)
standard cellulose nitrate as defined in 5.2.
4.2.3 Thedilutionratiooftoluene,asthestandarddiluent,to
n-butyl acetate as the standard solvent, using as the solute
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint
and Related Coatings, Materials, andApplications and is the direct responsibility of
cellulose nitrate of varying solubility characteristics.
Subcommittee D01.35 on Solvents, Plasticizers, and Chemical Intermediates.
4.3 The information developed through this test may be
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2008. Published November 2008. Originally
approved in 1960. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D1720 – 03. DOI:
useful in the formulation of cellulose-based lacquers and
10.1520/D1720-03R08.
adhesives.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on 5. Materials
the ASTM website.
5.1 n-Butyl Acetate (90 to 92 %), conforming to Specifica-
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
www.astm.org. tion D4615.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D1720 − 03 (2008)
NOTE 2—This grade of n-butyl acetate contains 8 to 10 % n-butyl
thermometer are held in place by means of a rubber stopper.
alcohol.
Whenusinganoventemperatureof85°Candvacuumsupplied
5.2 Cellulose Nitrate, conforming to the Sampling section by a water aspirator or other vacuum source, the alcohol-wet
(Appearance,Ash, and Stability requirements) ofTest Methods cellulose nitrate will be dried in about 4 h.
D301 and of such quality that, when used in determining the
7.3 If larger quantities of cellulose nitrate are required, the
toluene dilution ratios of n-butyl acetate and methyl n-propyl
drying equipment described in the Procedure section of Drying
ketone, it will give results between the following limits:
Samples of Test Methods D301 may be used.
Toluene Dilution Ratio
8. Preparation of Solution
n-butyl acetate 2.73 to 2.83
8.1 When testing either a solvent or diluent, first estimate
methyl n-propyl ketone 3.80 to 3.90
the probable dilution ratio for the unknown component in
5.3 Toluene (Toluol), conforming to Specification D841.
relation to the other to determine the amount of solvent
requiredtodissolvethecellulosenitrate(Table1).Thisvolume
6. Hazards
of solvent should be such that there will be approximately 10
6.1 Soluble cellulose nitrate is a flammable material, the
gofcellulosenitratepresentper100mLofsolventplusdiluent
degree of flammability varying with the extent and nature of
at the end point.
the wetting medium. Cellulose nitrate is always wet with water
or alcohol in commercial handling, shipping, and storage, in NOTE 3—Reference to published data on similar types of solvents or
diluents will provide a good approximation of the amount of solvent
which condition it presents no unusual hazard. Dry cellulose
required. If data are not available, several solutions with varying amounts
nitrate, if ignited by fire, spark, or static electricity, burns very
of solvents may be required to arrive at a suitable volume to use.
rapidly. Do not store samples of dry cellulose nitrate at any
8.2 On an analytical balance, weigh 5 6 0.01 g of the
time. Dry only that portion required for immediate test. Wear a
cellulose nitrate into a 125-mL cork-stoppered, preweighed
face shield when the oven is opened after samples have been
Erlenmeyer flask, or other suitable container. From a buret add
heated. Wet excess material and the samples left after testing
the volume of solvent indicated in Table 1. Swirl the flask until
with water and dispose of properly.
the cellulose nitrate is completely dissolved. When a high
7. Drying Cellulose Nitrate concentration of cellulose nitrate in solvent is required, disper-
sion may be more quickly accomplished by adding a measured
7.1 Dry not more than 20 g of cellulose nitrate at a time
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D1720–96 (Reapproved 2000) Designation:D1720–03(Reapproved2008)
Standard Test Method for
Dilution Ratio of Active Solvents in Cellulose Nitrate
Solutions
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 1720; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the volume ratio of hydrocarbon diluent to active solvent required to cause
persistent heterogeneity (precipitation) in a solution of cellulose nitrate.
1.2
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 The following applies to all specified limits in this standard; for purposes of determining conformance with this standard,
an observed value or a calculated value shall be rounded off “to the nearest unit” in the last right-hand digit used in expressing
the specification limit, in accordance with the rounding-off method of Practice E 29.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see Section 6.
1.3For1.5 For hazard information and guidance, see the supplier’s Material Safety Data Sheet.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 301 Test Methods for Soluble Cellulose Nitrate
D 841 Specification for Nitration Grade Toluene
D 4615Specification for n-Butyl Acetate (All Grades) Specification for n-Butyl Acetate (All Grades)
E 29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to Determine Conformance with Specifications
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 dilution ratio, n—themaximumnumberofunitvolumesofadiluentthatcanbeaddedtoaunitvolumeofsolventtocause
the first persistent heterogeneity (precipitation) in the solution at a concentration of 8 g cellulose nitrate per 100 mL of combined
solvent plus diluent and at a temperature of 25 6 3°C.
NOTE 1—The dilution ratio decreases as the cellulose nitrate concentration at the end point increases. It is, therefore, necessary to set an arbitrary
concentration of cellulose nitrate as part of the dilution ratio term. For this purpose 8.0 g of cellulose nitrate per 100 mLof solvent plus diluent has been
adopted.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 By use of standard or reference grade materials for any two of the three components, namely, oxygenated solvent, diluent,
or cellulose nitrate, the effect of different batches or different types of the third component can be determined.
4.2 This test method is applicable for the determination of the following:
4.2.1 The dilution ratio of toluene as the standard diluent to an oxygenated solvent under test, using as the solute standard
cellulose nitrate as defined in 5.2.
4.2.2 The dilution ratio of a hydrocarbon diluent under test to n-butyl acetate as the standard solvent, using as a solute standard
cellulose nitrate as defined in 5.2.
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint and Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D01.35 on Solvents, Plasticizers, and Chemical Intermediates.
Current edition approved Nov. 10, 1996. Published January 1997. Originally published as D1720–60T. Last previous edition D1720–93.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2008. Published November 2008. Originally approved in 1960. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D 1720 – 03.
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
, Vol 06.03.volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D1720–03 (2008)
4.2.3 Thedilutionratiooftoluene,asthestandarddiluent,to n-butylacetateasthestandardsolvent,usingasthesolutecellulose
nitrate of varying solubility characteristics.
4.3 The information developed through this test may be useful in the formulation of cellulose-based lacquers and adhesives.
5. Materials
5.1 n-Butyl Acetate (90 to 92 %), conforming to Specification D 4615.
NOTE 2—This grade of n-butyl acetate contains 8 to 10 % n-butyl alcohol.
5.2 Cellulose Nitrate,conformingtotheSamplingsection(Appearance,Ash,andStabilityrequirements)ofTestMethodsD 301
and of such quality that, when used in determining the toluene dilution ratios of n-butyl acetate and methyl n-propyl ketone, it will
give results between the following limits:
Toluene Dilution Ratio
n-butyl acetate 2.73 to 2.83
methyl n-propyl ketone 3.80 to 3.90
5.3 Toluene (Toluol), conforming to Specification D 841.
6. Hazards
6.1 Soluble cellulose nitrate is a flammable material, the degree of flammability varying with the extent and nature of the
wetting medium. Cellulose nitrate is always wet with water or alcohol in commercial handling, shipping, and storage, in which
condition it presents no unusual hazard. Dry cellulose nitrate, if ignited by fire, spark, or static electricity, burns very rapidly. Do
not store samples of dry cellulose nitrate at any time. Dry only that portion required for immediate test. Wear a face shield when
the oven is opened after samples have been heated. Wet excess material and the samples left after testing with water and dispose
of properly.
7. Drying Cellulose Nitrate
7.1 Dry not more than 20 g of cellulose nitrate at a time by spreading in a thin layer on a tray at room temperature for 12 to
16 h, or on top of a 100°C oven where the temperature is 35 to 40°C for about8h(Warning, see 6.1).Alternatively, use a steam
or hot water-heated oven maintained at 45 to 50°C to dry specimens in about 8 h. For safety reasons, the oven should have the
latch removed.
7.2 Another simple way to dry small quantities of cellulose nitrate is to use a drier assembled from common laboratory
apparatus. The assembled drier is shown in Fig. 1. Hot air from a laboratory electric oven is drawn through wet cellulose nitrate
contained in a brass tube hooked up through a thistle tube, or small funnel, and suction flask to a water aspirator or other vacuum
source. The brass pipe should be about 40 mm in diameter and 200 mm long, these relative dimensions having been found to give
efficient results. Such a tube will hold about 25 g, dry weight, of wet cellulose nitrate. The pipe is insulated to conserve heat. The
suction flask end of the brass tube is fitted with a thistle tube, or a small funnel, over the mouth of which is tied a silk cloth screen.
An indentation made in the funnel edge allows insertion of the thermometer. The funnel and thermometer are held in place by
means of a rubber stopper. When using an oven temperature of 85°C and vacuum su
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.