ASTM D1720-03
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Dilution Ratio of Active Solvents in Cellulose Nitrate Solutions
Standard Test Method for Dilution Ratio of Active Solvents in Cellulose Nitrate Solutions
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
By use of standard or reference grade materials for any two of the three components, namely, oxygenated solvent, diluent, or cellulose nitrate, the effect of different batches or different types of the third component can be determined.
This test method is applicable for the determination of the following:
4.2.1 The dilution ratio of toluene as the standard diluent to an oxygenated solvent under test, using as the solute standard cellulose nitrate as defined in 5.2.
4.2.2 The dilution ratio of a hydrocarbon diluent under test to n-butyl acetate as the standard solvent, using as a solute standard cellulose nitrate as defined in 5.2.
4.2.3 The dilution ratio of toluene, as the standard diluent, to n-butyl acetate as the standard solvent, using as the solute cellulose nitrate of varying solubility characteristics.
The information developed through this test may be useful in the formulation of cellulose-based lacquers and adhesives.
SCOPE
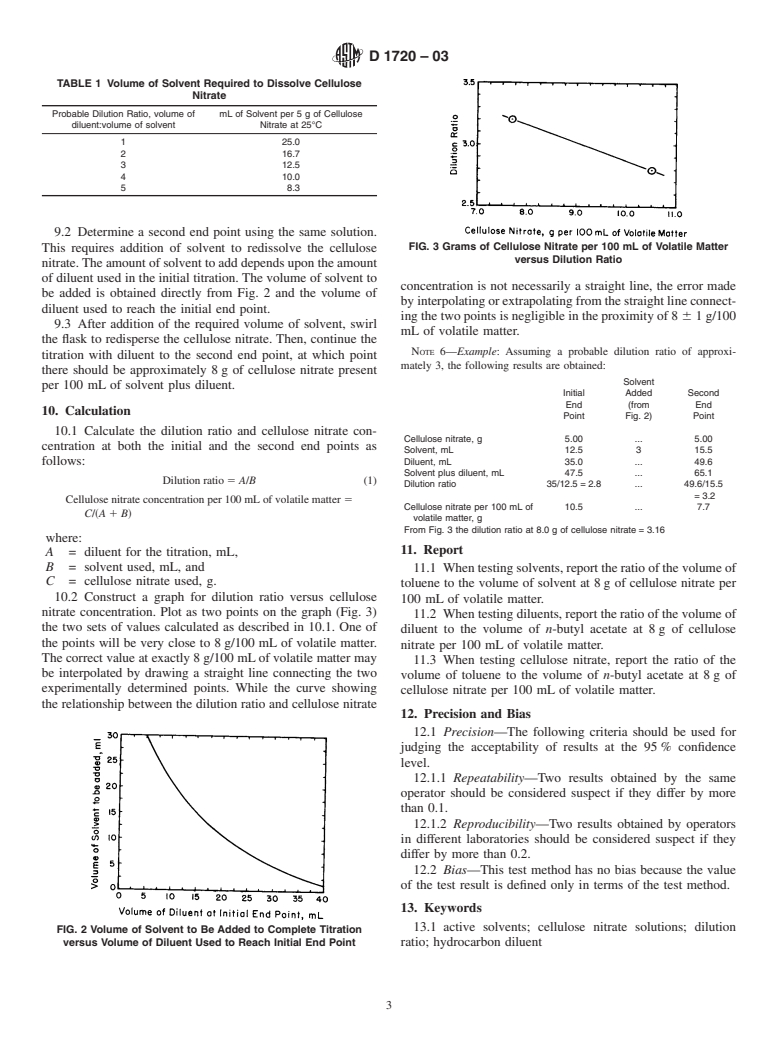
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the volume ratio of hydrocarbon diluent to active solvent required to cause persistent heterogeneity (precipitation) in a solution of cellulose nitrate.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 The following applies to all specified limits in this standard; for purposes of determining conformance with this standard, an observed value or a calculated value shall be rounded off "to the nearest unit" in the last right-hand digit used in expressing the specification limit, in accordance with the rounding-off method of Practice E 29.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see Section 6.
1.5 For hazard information and guidance, see the supplier's Material Safety Data Sheet.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D1720–03
Standard Test Method for
Dilution Ratio of Active Solvents in Cellulose Nitrate
1
Solutions
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 1720; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope* 3. Terminology
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the volume 3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
ratio of hydrocarbon diluent to active solvent required to cause 3.1.1 dilution ratio, n—the maximum number of unit vol-
persistent heterogeneity (precipitation) in a solution of cellu- umes of a diluent that can be added to a unit volume of solvent
lose nitrate. to cause the first persistent heterogeneity (precipitation) in the
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the solution at a concentration of 8 g cellulose nitrate per 100 mL
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information of combined solvent plus diluent and at a temperature of 25 6
only. 3°C.
1.3 The following applies to all specified limits in this
NOTE 1—The dilution ratio decreases as the cellulose nitrate concen-
standard; for purposes of determining conformance with this
tration at the end point increases. It is, therefore, necessary to set an
standard, an observed value or a calculated value shall be
arbitrary concentration of cellulose nitrate as part of the dilution ratio
rounded off “to the nearest unit” in the last right-hand digit
term. For this purpose 8.0 g of cellulose nitrate per 100 mLof solvent plus
diluent has been adopted.
used in expressing the specification limit, in accordance with
the rounding-off method of Practice E 29.
4. Significance and Use
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.1 By use of standard or reference grade materials for any
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
two of the three components, namely, oxygenated solvent,
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
diluent, or cellulose nitrate, the effect of different batches or
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
different types of the third component can be determined.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard
4.2 This test method is applicable for the determination of
statements, see Section 6.
the following:
1.5 For hazard information and guidance, see the supplier’s
4.2.1 The dilution ratio of toluene as the standard diluent to
Material Safety Data Sheet.
an oxygenated solvent under test, using as the solute standard
2. Referenced Documents
cellulose nitrate as defined in 5.2.
2
4.2.2 The dilution ratio of a hydrocarbon diluent under test
2.1 ASTM Standards:
to n-butyl acetate as the standard solvent, using as a solute
D 301 Test Methods for Soluble Cellulose Nitrate
standard cellulose nitrate as defined in 5.2.
D 841 Specification for Nitration Grade Toluene
4.2.3 Thedilutionratiooftoluene,asthestandarddiluent,to
D 4615 Specification for n-Butyl Acetate (All Grades)
n-butyl acetate as the standard solvent, using as the solute
E 29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
cellulose nitrate of varying solubility characteristics.
Determine Conformance with Specifications
4.3 The information developed through this test may be
useful in the formulation of cellulose-based lacquers and
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint adhesives.
and Related Coatings, Materials, andApplications and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D01.35 on Solvents, Plasticizers, and Chemical Intermediates.
5. Materials
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2003. Published December 2003. Originally
5.1 n-Butyl Acetate (90 to 92 %), conforming to Specifi-
approved in 1960. Last previous edition approved in 1996 as D 1720 – 96 (2000).
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
cation D 4615.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
NOTE 2—This grade of n-butyl acetate contains 8 to 10 % n-butyl
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. alcohol.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D1720–03
5.2 Cellulose Nitrate, conforming to the Sampling section by a water aspirator or other vacuum source, the alcohol-wet
(Appearance,Ash, and Stability requirement
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.