ASTM B229-12(2023)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Concentric-Lay-Stranded Copper and Copper-Clad Steel Composite Conductors
Standard Specification for Concentric-Lay-Stranded Copper and Copper-Clad Steel Composite Conductors
ABSTRACT
This specification covers concentric-lay-stranded conductors made from uncoated hard-drawn round copper wires in combination with hard-drawn round copper-clad steel wires for general use as overhead electrical conductors. The conductors are classified under the following type designations: Type A, Type C, Type D, Type E, Type EK, Type F, Type G, Type J, Type K, Type N, Type P, and Type V. Welds and brazes may be made in copper rods or in copper wires prior to final drawing. Joints may not be made in the finished copper wires composing concentric-lay-stranded composite conductors containing a total of seven wires or less. In other conductors, welds and brazes may be made in the finished individual copper wires composing the conductor. Also, the joints or splices may be made in the finished individual copper-clad steel wires composing concentric-lay-stranded conductors, provided that such joints or splices have a protection equivalent to that of the wire itself and that they do not decrease the strength of the finished stranded conductor below the minimum breaking strength. The density, mass, and resistance of the wires shall be determined.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers concentric-lay-stranded conductors made from uncoated hard-drawn round copper wires in combination with hard-drawn round copper-clad steel wires for general use as overhead electrical conductors.
1.2 For the purpose of this specification, conductors are classified under the following type designations (see Fig. 1):
Type A
Type G
Type C
Type J
Type D
Type K
Type E
Type N
Type EK
Type P
Type F
Type V
FIG. 1 Standard Types of Composite Conductors
1.3 The SI values for density are regarded as the standard. For all other properties the inch-pound values are to be regarded as standard and the SI units may be approximate.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: B229 − 12 (Reapproved 2023)
Standard Specification for
Concentric-Lay-Stranded Copper and Copper-Clad Steel
1
Composite Conductors
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B229; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2.2 ANSI Standard:
3
C 42 Definitions of Electrical Terms
1.1 This specification covers concentric-lay-stranded con-
2.3 National Institute of Standards and Technology:
ductors made from uncoated hard-drawn round copper wires in
4
NBS Handbook 100—Copper Wire Tables
combination with hard-drawn round copper-clad steel wires for
general use as overhead electrical conductors.
3. Ordering Information
1.2 For the purpose of this specification, conductors are
3.1 Orders for material under this specification shall include
classified under the following type designations (see Fig. 1):
the following information:
Type A Type G
3.1.1 Quantity of each size and type;
Type C Type J
3.1.2 Conductor size: hard-drawn copper equivalent in
Type D Type K
Type E Type N circular-mil area or AWG (Section 7 and Table 1);
Type EK Type P
3.1.3 Type (see 1.2, Fig. 1, and Table 1);
Type F Type V
3.1.4 Direction of lay of outer layer, if other than left-hand
1.3 The SI values for density are regarded as the standard.
(see 6.3);
For all other properties the inch-pound values are to be
3.1.5 When physical tests shall be made (see section 8.2);
regarded as standard and the SI units may be approximate.
3.1.6 Package size (see 14.1);
3.1.7 Special package marking, if required (Section 15);
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
3.1.8 Lagging, if required (see 14.2); and
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
3.1.9 Place of inspection (Section 13).
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
4. Material for Wires
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee. 4.1 The purchaser shall designate the size and type of
conductor to be furnished. The position of the hard-drawn
copper wires and the copper-clad steel wires in the conductor
2. Referenced Documents
cross section shall be as shown in Fig. 1.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4.2 Before stranding, the wire used shall meet the require-
B1 Specification for Hard-Drawn Copper Wire
ments of Specifications B1 and B227 that are applicable to its
B227 Specification for Hard-Drawn Copper-Clad Steel Wire
type.
B354 Terminology Relating to Uninsulated Metallic Electri-
cal Conductors
5. Joints
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
Determine Conformance with Specifications 5.1 Copper—Welds and brazes may be made in copper rods
or in copper wires prior to final drawing. Joints may not be
made in the finished copper wires composing concentric-lay-
stranded composite conductors containing a total of seven
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B01 on
wires or less. In other conductors, welds and brazes may be
Electrical Conductors and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B01.06 on
Bi-Metallic Conductors.
made in the finished individual copper wires composing the
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2023. Published October 2023. Originally
approved in 1948. Last previous edition approved in 2017 as B229 – 12 (2017).
DOI: 10.1520/B0229-12R23.
2 3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), 100
the ASTM website. Bureau Dr., Stop 1070, Gaithersburg, MD 20899-1070, http://www.nist.gov.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B229 − 12 (2023)
in position when the conductor is cut at any point and shall
permit restranding by hand after being forcibly unraveled at the
end of the conductor.
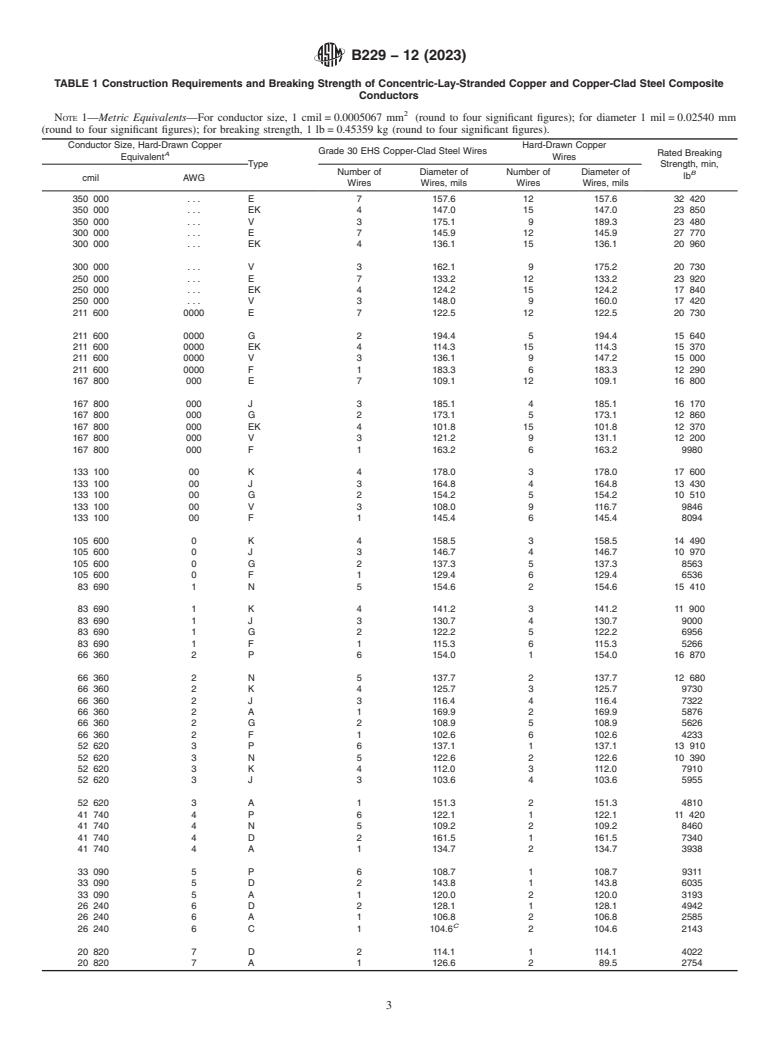
7. Construction
7.1 The numbers and diameters of wires in the various types
of concentric-lay-stranded composite conductors shall conform
to the requirements prescribed in Table 1 (Explanatory Note 2).
8. Physical and
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.