ASTM F37-00
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Sealability of Gasket Materials
Standard Test Methods for Sealability of Gasket Materials
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods provide a means of evaluating the sealing properties of sheet and solid form-in-place gasket materials at room temperature. Test Method A is restricted to liquid leakage measurements, whereas Test Method B may be used for both liquid and gas leakage measurements.
1.2 These test methods are suitable for evaluating the sealing characteristics of a gasket material under different compressive flange loads. The test method may be used as an acceptance test when the supplier and the purchaser have agreed to specific test conditions for the following parameters: test medium, internal pressure on medium, and flange load on gasket specimens.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. (For specific hazard statements, see Section 6, Note 3, and Note 8.)
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F37–00
Standard Test Methods for
Sealability of Gasket Materials
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF 37;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope 2.2 ANSI Standard:
B57.1 Compressed Gas Cylinder Valve Outlet and Inlet
1.1 These test methods provide a means of evaluating the
Connections
sealing properties of sheet and solid form-in-place gasket
materials at room temperature. Test Method A is restricted to
3. Summary of Test Methods
liquid leakage measurements, whereas Test Method B may be
3.1 Both test methods utilize a test specimen compressed
used for both liquid and gas leakage measurements.
betweenthesurfacesoftwosmoothsteelflangefaces.Afterthe
1.2 These test methods are suitable for evaluating the
specified flange load is applied, the test medium is introduced
sealing characteristics of a gasket material under different
into the center of the annular gasket compressed between the
compressive flange loads. The test method may be used as an
flangesandthespecifiedpressureisappliedtothemedium.For
acceptance test when the producer and user have agreed to
liquid sealability tests (Test MethodsAand B), Reference Fuel
specific test conditions for the following parameters: test
A (see Test Method D 471, Motor Fuel Section of Annex) is
medium, internal pressure on medium, and flange load on
recommended and the leakage rate is measured by a change in
gasket specimens.
the level of a sight-glass located in the line upstream from the
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
gasket testing fixture. Nitrogen is the recommended gas for the
standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
gas sealability test (Test Method B) and the leakage rate is
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
measured by a change in the level of a water manometer
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
located in the line upstream from the gasket testing fixture.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1.1 Test MethodAuses a test fixture (Fig. 1) by which an
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
external load is transferred into the fixture to produce a
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.(Forspecifichazard
compressive force on the gasket specimen.
statements, see Section 6, Note 3, and Note 8.)
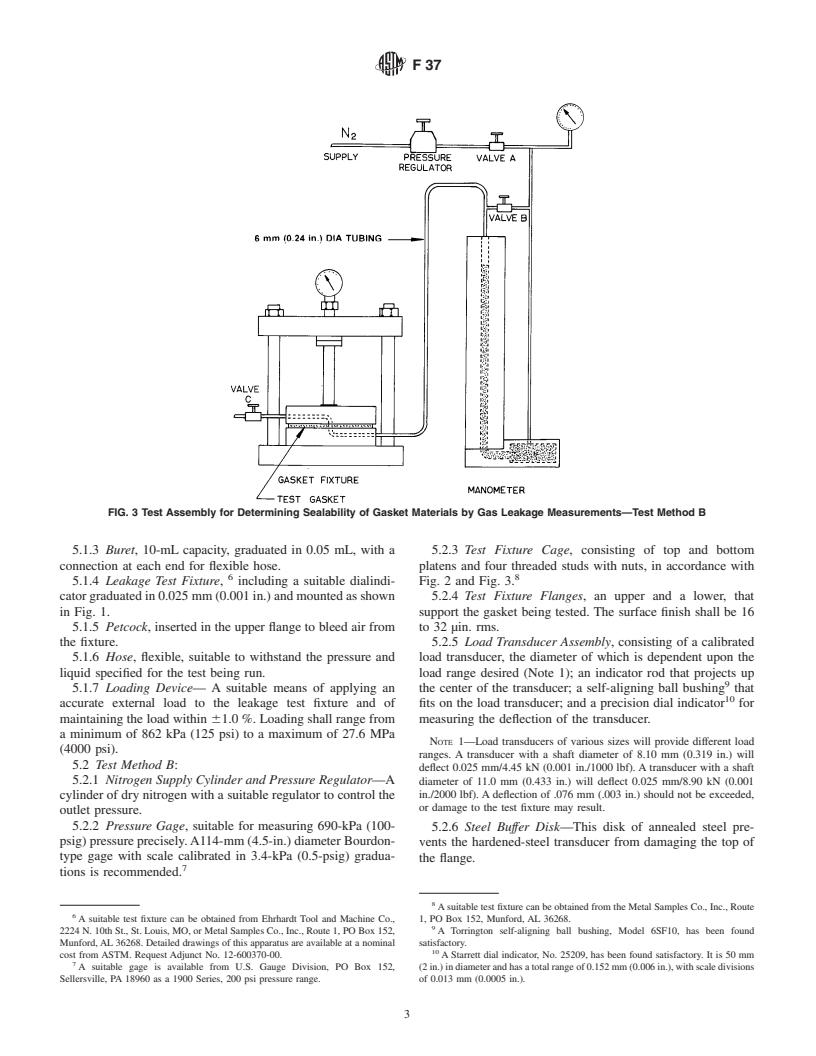
3.1.2 Test Method B uses a test fixture (Fig. 2 and Fig. 3) in
2. Referenced Documents which the flanges are held within a four-bolt cage that permits
loading the flanges at various force levels. The flange load is
2.1 ASTM Standards:
measured by a transducer held within the cage.
D 471 Test Method for Rubber Property—Effect of Liq-
2 3.2 Resultsofthesealabilitytestsareexpressedasaleakage
uids
rate in millilitres per hour for the test specimen under the
D 2000 Classification System for Rubber Products inAuto-
3 specific conditions of the test.
motive Applications
E 691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
4. Significance and Use
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
4.1 These test methods are designed to compare gasket
F 38 Test Methods for Creep Relaxation of a Gasket Mate-
3 materials under controlled conditions and to provide a precise
rial
measure of leakage rate.
F 104 Classification System for Nonmetallic Gasket Mate-
4.2 These test methods are suitable for measuring leakage
rials
rates as high as 6 L/h and as low as 0.3 mL/h. In many cases,
“zero” leakage may not be attainable.
4.3 These test methods evaluate leakage rates after time
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F03 on
periods that are typically 5 to 30 min under load. Holding a
Gaskets and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F 03.40 on Composite
Gaskets. gasket material under load for extended time periods may give
Current edition approved Apr. 10, 2000. Published May 2000. Originally
different results.
designated as D 2025. Redesignated in 1963 as F 37 – 62T. Last previous edition
e1
F37–95 .
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 09.01.
3 5
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 09.02. Available from American National Standards Institute, 11 W. 42nd St., 13th
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02. Floor, New York, NY 10036.
Copyright ©ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA19428-2959, United States.
F37
FIG. 1 Test Assembly for Determining Sealability of Gasket Materials by Liquid Leakage Measurements—Test Method A
FIG. 2 Test Assembly for Determining Sealability of Gasket Materials by Liquid Leakage Measurements—Test Method B
4.4 Ifthefluidbeingusedinthetestcauseschanges,suchas 5.1.1 Compressed Air Supply and Regulator—A source of
swelling, in the gasket material, then unpredictable results may compressed air with a suitable regulator to control the pressure
be obtained. at a point between 0 and 760 mm (30 in.) of mercury.
5.1.2 Mercury Manometer or Pressure Gage—A 760-mm
5. Apparatus
(30-in.) mercury manometer or suitable pressure gage to read
5.1 Test Method A: the pressure to the nearest 5 mm (0.2 in.).
F37
FIG. 3 Test Assembly for Determining Sealability of Gasket Materials by Gas Leakage Measurements—Test Method B
5.1.3 Buret, 10-mL capacity, graduated in 0.05 mL, with a 5.2.3 Test Fixture Cage, consisting of top and bottom
connection at each end for flexible hose. platens and four threaded studs with nuts, in accordance with
6 8
5.1.4 Leakage Test Fixture, including a suitable dialindi- Fig. 2 and Fig. 3.
catorgraduatedin0.025mm(0.001in.)andmountedasshown 5.2.4 Test Fixture Flanges, an upper and a lower, that
in Fig. 1. support the gasket being tested. The surface finish shall be 16
5.1.5 Petcock, inserted in the upper flange to bleed air from to 32 µin. rms.
the fixture. 5.2.5 Load Transducer Assembly, consisting of a calibrated
5.1.6 Hose, flexible, suitable to withstand the pressure and load transducer, the diameter of which is dependent upon the
liquid specified for the test being run. load range desired (Note 1); an indicator rod that projects up
5.1.7 Loading Device— A suitable means of applying an the center of the transducer; a self-aligning ball bushing that
accurate external load to the leakage test fixture and of fits on the load transducer; and a precision dial indicator for
maintaining the load within 61.0 %. Loading shall range from measuring the deflection of the transducer.
a minimum of 862 kPa (125 psi) to a maximum of 27.6 MPa
NOTE 1—Load transducers of various sizes will provide different load
(4000 psi).
ranges. A transducer with a shaft diameter of 8.10 mm (0.319 in.) will
5.2 Test Method B:
deflect 0.025 mm/4.45 kN (0.001 in./1000 lbf). A transducer with a shaft
5.2.1 Nitrogen Supply Cylinder and Pressure Regulator—A
diameter of 11.0 mm (0.433 in.) will deflect 0.025 mm/8.90 kN (0.001
in./2000 lbf). A deflection of .076 mm (.003 in.) should not be exceeded,
cylinder of dry nitrogen with a suitable regulator to control the
or damage to the test fixture may result.
outlet pressure.
5.2.2 Pressure Gage, suitable for measuring 690-kPa (100-
5.2.6 Steel Buffer Disk—This disk of annealed steel pre-
psig) pressure precisely.A114-mm (4.5-in.) diameter Bourdon-
vents the hardened-steel transducer from damaging the top of
type gage with scale calibrated in 3.4-kPa (0.5-psig) gradua-
the flange.
tions is recommended.
Asuitable test fixture can be obtained from the Metal Samples Co., Inc., Route
A suitable test fixture can be obtained from Ehrhardt Tool and Machine Co., 1, PO Box 152, Munford, AL 36268.
2224 N. 10th St., St. Louis, MO, or Metal Samples Co., Inc., Route 1, PO Box 152, A Torrington self-aligning ball bushing, Model 6SF10, has been found
Munford,AL 36268. Detailed drawings of this apparatus are available at a nominal satisfactory.
cost from ASTM. Request Adjunct No. 12-600370-00. A Starrett dial indicator, No. 25209, has been found satisfactory. It is 50 mm
A suitable gage is available from U.S. Gauge Division, PO Box 152, (2in.)indiameterandhasatotalrangeof0.152mm(0.006in.),withscaledivisions
Sellersville, PA 18960 as a 1900 Series, 200 psi pressure range. of 0.013 mm (0.0005 in.).
F37
5.2.7 Adapter Collet— The adapter collet is used to attach ating pressure control in accordance with ANSI Standard
the dial indicator to the threaded end of the load transducer. B 57.1. Full details are also included in the Handbook of
When attached properly, the indicating member on the load Compressed Gases.
transducer contacts the actuating button on the dial indicator.
7. Test Specimens
NOTE 2—Depending on the exact equipment used, sometimes the
7.1 Preparation of Test Specimens for Test Method A:
adapter collet used inTest Methods F 38,Test Method B, can be used with
7.1.1 When sheet gasket material (see Classification F 104)
this fixture.
is to be tested, test specimens shall be die-cut so that the edges
5.2.8 Manometer—A standard Meriam-type 760-mm (30-
are flat, clean, and free of burrs. The size shall be 32.26 to
in.) manometer suitable for use with water and suitable for
32.31 mm (1.270 to 1.272 in.) in inside diameter and 44.20 to
2.07-MPa (300-psig) pressure. The scale shall be calibrated
44.32 mm (1.740 to 1.745 in.) in outside diameter. The
with 1.0-mm (0.04-in.) graduations.
thickness shall be approximately 0.76 mm (0.030 in.) unless
5.2.9 Sight Glass and Reservoir—The liquid testing proce-
otherwise agreed upon between the producer and user. The
durerequiresaliquidreservoirthatmaybeanymetalcontainer
assumed average area of this test specimen is 719.35 mm
3 3
of approximately 1500-cm (100-in. ) capacity that can be
(1.115 in. ).
piped into the system and conveniently filled. A sightglass
7.1.2 For reporting purposes, measure the thickness of the
made from 2.07-MPa (300-psig) boiler-gage glass tubing is
gasket test specimens with a dial-type micrometer in accor-
usedforobservingthefluidlevel.Apieceof16-mm(0.625-in.)
dance with Classification F 104.
outside diameter glass tubing approximately 280- mm (11-in.)
7.1.3 The test specimens shall be inspected and rejected for
long has proven satisfactory. This glass gage shall be as-
surface irregularities, such as scratches, tears, and clumps of
sembled with appropriate fittings and a stand. The scale used
fibers.
with the gage shall be calibrated with 1.0-mm (0.04-in.)
7.2 Preparation of Test Specimens for Test Method B:
graduations. If desired, the manometer described in 5.2.8 can
7.2.1 Sheet Gasket Material (see Classification F 104):
be used as a sightglass (see 9.2).
7.2.1.1 Test specimens shall be die-cut so that the edges are
flat, clean, and free of burrs. They shall be of circular
5.2.10 Tubing, Fittings, and Valves—Suitable high-pressure
flexible tubing and either flare or compression adapter fittings construction having concentric inside and outside diameters
such that they fit the sealability test cell. The thickness shall be
shall be used. Small hand valves shall be used where indicated.
The tubing connecting the manometer or sightglass to the test approximately 0.76 mm (0.030 in.) unless otherwise agreed
upon between the producer and user.
fixture shall be of small bore to reduce the internal volume.
Capillary tubing with a 1.6-mm (0.0625-in.) inside diameter is 7.2.1.2 For reporting purposes, measure the thickness of the
gasket specimens with a dial-type micrometer in accordance
suggested.
with Classification F 104.
5.2.11 Laboratory Stress-Strain Equipment—Suitable ten-
7.2.2 Types 4 and 5 Form-In-Place Gasket Material (see
sion equipment with calibrated load cell to produce and
Classification F 104)—A 122-mm (4.8-in.) long piece of
measure a force required for a given deflection of the trans-
standard size material, between 4.76 and 6.35-mm (0.1875 and
ducer tube. The tension equipment shall have an accuracy of
0.250-in.) nominal size or width, shall be formed into a circle
65 % of the load value read (see Note 3).
of 38-mm (1.5-in.) mean diameter. The ends of the Type 4
5.2.12 Prepare some type of holding fixture to hold the
material shall be so laid as to have a 6.35 6 1.59-mm (0.25 6
bottom platen of the test fixture cage when the nuts at the top
0.0625-in.) overlap to complete the seal. The Type 5 material
are tightened.
shallhaveanoverlapof1.59 60.79mm(0.0625 60.0313in.)
to complete the seal.
6. Hazards
7.2.3 The test specimens shall be inspected, and surface
6.1 Normal safety practices required for operating pressure
irregularities such as scratches and tears shall be cause for
equipment shall be observed by the personnel conducting the
rejection.
tests.
8. Preparation of Apparatus
6.2 A suitably mounted, transparent safety shield shall be
usedasabarrierbetweentheoperatorandthepressurizedglass
8.1 Test Method A:
tubing.
8.1.1 Prior to running any tests, check the setup for leaks.
For Test Method A, this is accomplished by inserting in the
6.3 All components of the system must be designed to
fixture a rubber gasket cut from an approximately 3.2-mm
safely accommodate a maximum working pressure of 1.03
(0.12-in.)thickrubbercompoundconformingtoGradeBG515
MPa (150 psig), in order to satisfy the requirements of the user
in accordance with Classification D 2000. Adjust the external
and ensure the safety of the operator (see Note 3).
flange pressure to 862 kPa (125 psi) and the internal pressure
6.4 Care shall be exercised to ensure proper support of
of the test liquid to 760 mm (30 in.) of mercury. The system
nitrogen gas cylinders and pressure regulators used for oper-
shall be free of leaks for 15 min under these conditions.
Available from the Compressed Gas Association, Inc., 500 Fifth Ave., New
York, NY 10110.
F37
8.2 Test Method B: 10. Conditioning
8.2.1 Maintain a light film of oil on the various parts of the
10.1 Test Methods A and B:
apparatus, including the cage nuts and washers, and the
10.1.1 Condition all types of the test specimens, except
transducer self-aligning ball bushing.
Type4,inanatmosphereof50to55 %relativehumidityfor24
8.2.2 Clean the exposed surfaces of the top and bottom
h prior to use. If a humidity cabinet with gentle air circulation
flanges of the test fixture so that all residue from previous tests
is not available, then place a tray containing a saturated
is removed. Before each test, inspect the flange for nicks or
solution of magnes
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.