ASTM F37-06
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Sealability of Gasket Materials
Standard Test Methods for Sealability of Gasket Materials
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
These test methods are designed to compare gasket materials under controlled conditions and to provide a precise measure of leakage rate.
These test methods are suitable for measuring leakage rates as high as 6 L/h and as low as 0.3 mL/h. In many cases, “zero” leakage may not be attainable.
These test methods evaluate leakage rates after time periods that are typically 5 to 30 min under load. Holding a gasket material under load for extended time periods may give different results.
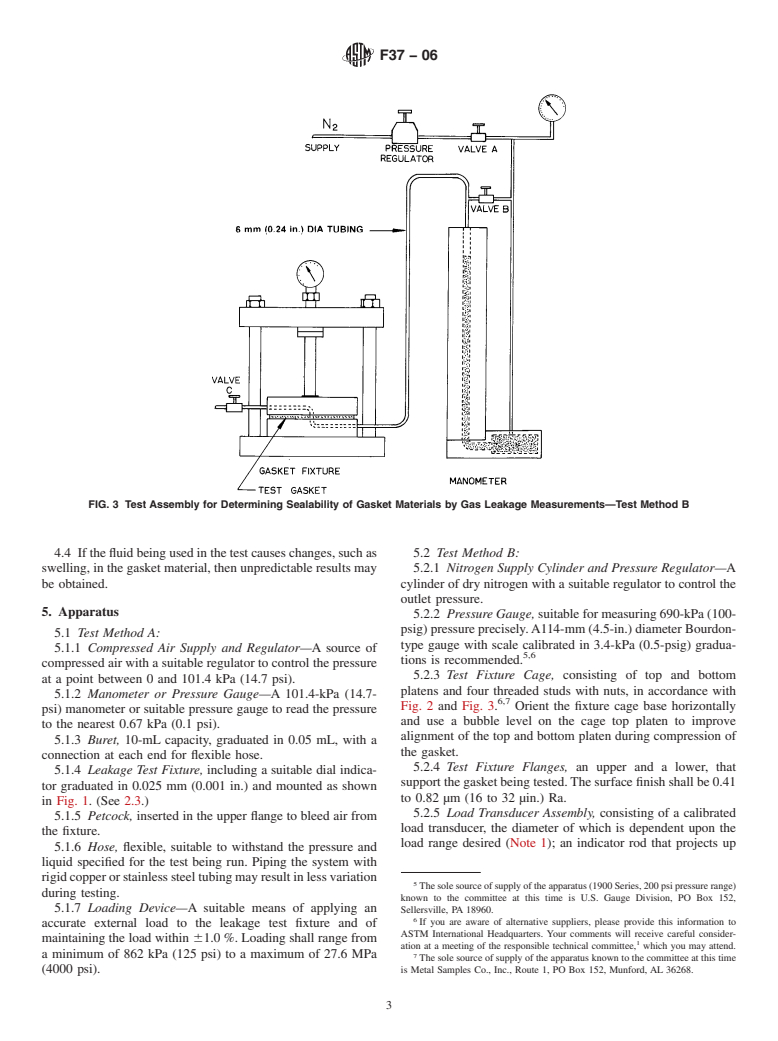
If the fluid being used in the test causes changes, such as swelling, in the gasket material, then unpredictable results may be obtained.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods provide a means of evaluating the sealing properties of sheet and solid form-in-place gasket materials at room temperature. Test Method A is restricted to liquid leakage measurements, whereas Test Method B may be used for both liquid and gas leakage measurements.
1.2 These test methods are suitable for evaluating the sealing characteristics of a gasket material under different compressive flange loads. The test method may be used as an acceptance test when the producer and user have agreed to specific test conditions for the following parameters: test medium, internal pressure on medium, and flange load on gasket specimens.
1.3 These test methods use a small-diameter narrow-width gasket as the test specimen under relatively low gasket loads and relatively low pressures. Test Method F 2378 is another sealability test method that uses a larger gasket specimen and higher internal pressures and flange loads.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. (For specific hazard or warning statements, or both, see 5.2.11, Section 6, 6.3, 8.2.4, 11.3.2, and 11.4.2.)
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F37 − 06
StandardTest Methods for
1
Sealability of Gasket Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F37; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope D2000 Classification System for Rubber Products in Auto-
motive Applications
1.1 These test methods provide a means of evaluating the
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
sealing properties of sheet and solid form-in-place gasket
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
materials at room temperature. Test Method A is restricted to
F38 Test Methods for Creep Relaxation of a Gasket Material
liquid leakage measurements, whereas Test Method B may be
F104 Classification System for Nonmetallic Gasket Materi-
used for both liquid and gas leakage measurements.
als
1.2 These test methods are suitable for evaluating the
F2378 Test Method for Sealability of Sheet, Composite, and
sealing characteristics of a gasket material under different
Solid Form-in-Place Gasket Materials
compressive flange loads. The test method may be used as an
3
2.2 ANSI Standard:
acceptance test when the producer and user have agreed to
B57.1 Compressed Gas Cylinder Valve Outlet and Inlet
specific test conditions for the following parameters: test
Connections
medium, internal pressure on medium, and flange load on
gasket specimens. 2.3 ASTM Adjuncts:
4
Leakage Test Fixtures
1.3 These test methods use a small-diameter narrow-width
gasket as the test specimen under relatively low gasket loads
3. Summary of Test Methods
and relatively low pressures. Test Method F2378 is another
sealability test method that uses a larger gasket specimen and
3.1 Both test methods utilize a test specimen compressed
higher internal pressures and flange loads.
betweenthesurfacesoftwosmoothsteelflangefaces.Afterthe
specified flange load is applied, the test medium is introduced
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
into the center of the annular gasket compressed between the
standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
flangesandthespecifiedpressureisappliedtothemedium.For
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
liquid sealability tests (Test MethodsAand B), Reference Fuel
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
A (see Test Method D471, Motor Fuel Section of Annex) is
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
recommended and the leakage rate is measured by a change in
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
the level of a sight-glass located in the line upstream from the
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.(Forspecifichazard
gasket testing fixture. Nitrogen is the recommended gas for the
orwarningstatements,orboth,see5.2.11,Section6,6.3,8.2.4,
gas sealability test (Test Method B) and the leakage rate is
11.3.2, and 11.4.2.)
measured by a change in the level of a water manometer
located in the line upstream from the gasket testing fixture.
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.1 Test MethodAuses a test fixture (Fig. 1) by which an
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
external load is transferred into the fixture to produce a
D471 Test Method for Rubber Property—Effect of Liquids
compressive force on the gasket specimen.
3.1.2 Test Method B uses a test fixture (Fig. 2 and Fig. 3)in
which the flanges are held within a four-bolt cage that permits
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F03 on
loading the flanges at various force levels. The flange load is
Gaskets and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F03.10 on Composite
measured by a transducer held within the cage.
Gaskets.
Current edition approved Nov. 15, 2006. Published December 2006. Originally
approved in 1962. Last previous edition approved in 2000 as F37 – 00. DOI:
10.1520/F0037-06.
2 3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Available from American National Standards Institute, 11 W. 42nd St., 13th
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Floor, New York, NY 10036.
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from ASTM International Headquarters. Order Adjunct No.
the ASTM website. ADJF0037. Original adjunct produced in 1962.
Copyright ©ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F37−06
FIG. 1 Test Assembly for Determining Sealability of Gasket Materials by Liquid Leakag
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.