ASTM D5228-92(2015)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Butane Working Capacity of Activated Carbon
Standard Test Method for Determination of Butane Working Capacity of Activated Carbon
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The BWC, as determined by this test method, is a measure of the ability of an activated carbon to adsorb and desorb butane from dry air under specified conditions. It is useful for quality control and evaluation of granular activated carbons that are used in applications where the adsorption of butane and desorption with dry air are of interest. The BWC can also provide a relative measure of the effectiveness of the tested activated carbons on other adsorbates.
5.2 The butane activity and retentivity can also be determined under the conditions of the test. The butane activity is an indication of the micropore volume of the activated carbon sample. The butane retentivity is an indication of the pore structure of the activated carbon sample.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the butane working capacity (BWC) of new granular activated carbon. The BWC is defined as the difference between the butane adsorbed at saturation and the butane retained per unit volume of carbon after a specified purge. The test method also produces a butane activity value that is defined as the total amount of butane adsorbed on the carbon sample and is expressed as a mass of butane per unit weight or volume of carbon.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For a specific hazard statement, see 7.1.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D5228 − 92(Reapproved 2015)
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Butane Working Capacity of Activated
1
Carbon
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5228; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the butane 3.1 Definitions— For definitions of terms used in this test
working capacity (BWC) of new granular activated carbon. method, refer to Terminology D2652.
The BWC is defined as the difference between the butane
adsorbed at saturation and the butane retained per unit volume 4. Summary of Test Method
of carbon after a specified purge. The test method also
4.1 An activated carbon bed of known volume and mass is
produces a butane activity value that is defined as the total
saturatedwithbutanevapor.Themassadsorbedatsaturationis
amount of butane adsorbed on the carbon sample and is
noted. The carbon bed is then purged under prescribed condi-
expressed as a mass of butane per unit weight or volume of
tions with dry hydrocarbon free air. The loss of mass is the
carbon.
BWC and is expressed as mass of butane per unit volume of
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as carbon.
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
standard.
5. Significance and Use
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
5.1 The BWC, as determined by this test method, is a
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
measure of the ability of an activated carbon to adsorb and
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
desorb butane from dry air under specified conditions. It is
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
useful for quality control and evaluation of granular activated
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For a specific
carbons that are used in applications where the adsorption of
hazard statement, see 7.1.
butane and desorption with dry air are of interest. The BWC
can also provide a relative measure of the effectiveness of the
2. Referenced Documents
tested activated carbons on other adsorbates.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5.2 The butane activity and retentivity can also be deter-
D2652Terminology Relating to Activated Carbon
minedundertheconditionsofthetest.Thebutaneactivityisan
D2854Test Method for Apparent Density of Activated
indication of the micropore volume of the activated carbon
Carbon
sample. The butane retentivity is an indication of the pore
D2867Test Methods for Moisture in Activated Carbon
structure of the activated carbon sample.
D3195Practice for Rotameter Calibration
E177Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
6. Apparatus
ASTM Test Methods
6.1 Water Bath, capable of maintaining a temperature of 25
E300Practice for Sampling Industrial Chemicals
6 0.2°C and of sufficient depth so the entire carbon bed in the
E691Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
sampletubeisimmersedinthewater.A6-mmODcoppertube
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
with an immersed length of 1.9 m (Fig. 1) provides adequate
heat transfer for gas temperature control.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D28 on
6.2 Sample Tube, as shown in Fig. 2. The glass plate with
Activated Carbon and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D28.04 on Gas
holes is preferred to a fritted disk to support the carbon, since
Phase Evaluation Tests.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2015. Published October 2015. Originally fritted disks can vary widely in pressure drop.
approved in 1992. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as D5228–92 (2010).
6.3 Flow Meters, one capable of delivering air at 0 to 500
DOI: 10.1520/D5228-92R15.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or mL/min, and one capable of delivering butane at 0 to 500
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
mL/min, both calibrated in accordance with Practice D3195.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. 6.4 Balance, capable of weighing to within 60.01 g.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5228 − 92 (2015)
6.7 Apparatus Assembly shown in Fig. 1.
7. Reagents
7.1 n-Butane, C. P. Grade. (Warning—Butane is a flam-
mable gas with a flash point of −138°C and a boiling point of
0.5°C. Its specific gravity is 2.046 relative to air. Butane may
be narcotic in high concentrations and is c
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D5228 − 92 (Reapproved 2010) D5228 − 92 (Reapproved 2015)
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Butane Working Capacity of Activated
1
Carbon
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5228; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the butane working capacity (BWC) of new granular activated carbon. The
BWC is defined as the difference between the butane adsorbed at saturation and the butane retained per unit volume of carbon after
a specified purge. The test method also produces a butane activity value that is defined as the total amount of butane adsorbed on
the carbon sample and is expressed as a mass of butane per unit weight or volume of carbon.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. For a specific hazard statement, see 7.1.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D2652 Terminology Relating to Activated Carbon
D2854 Test Method for Apparent Density of Activated Carbon
D2867 Test Methods for Moisture in Activated Carbon
D3195 Practice for Rotameter Calibration
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in ASTM Test Methods
E300 Practice for Sampling Industrial Chemicals
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions— For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology D2652.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 An activated carbon bed of known volume and mass is saturated with butane vapor. The mass adsorbed at saturation is
noted. The carbon bed is then purged under prescribed conditions with dry hydrocarbon free air. The loss of mass is the BWC and
is expressed as mass of butane per unit volume of carbon.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 The BWC, as determined by this test method, is a measure of the ability of an activated carbon to adsorb and desorb butane
from dry air under specified conditions. It is useful for quality control and evaluation of granular activated carbons that are used
in applications where the adsorption of butane and desorption with dry air are of interest. The BWC can also provide a relative
measure of the effectiveness of the tested activated carbons on other adsorbates.
5.2 The butane activity and retentivity can also be determined under the conditions of the test. The butane activity is an
indication of the micropore volume of the activated carbon sample. The butane retentivity is an indication of the pore structure
of the activated carbon sample.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D28 on Activated Carbon and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D28.04 on Gas Phase
Evaluation Tests.
Current edition approved April 1, 2010Oct. 1, 2015. Published May 2010October 2015. Originally approved in 1992. Last previous edition approved in 20052010 as
D5228 – 92 (2005).(2010). DOI: 10.1520/D5228-92R10.10.1520/D5228-92R15.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5228 − 92 (2015)
6. Apparatus
6.1 Water Bath, capable of maintaining a temperature of 25 6 0.2°C and of sufficient depth so the entire carbon bed in the
sample tube is immersed in the water. A 6-mm OD copper tube with an immersed length of 1.9 m (Fig. 1) provides adequate heat
transfer for gas temperature control.
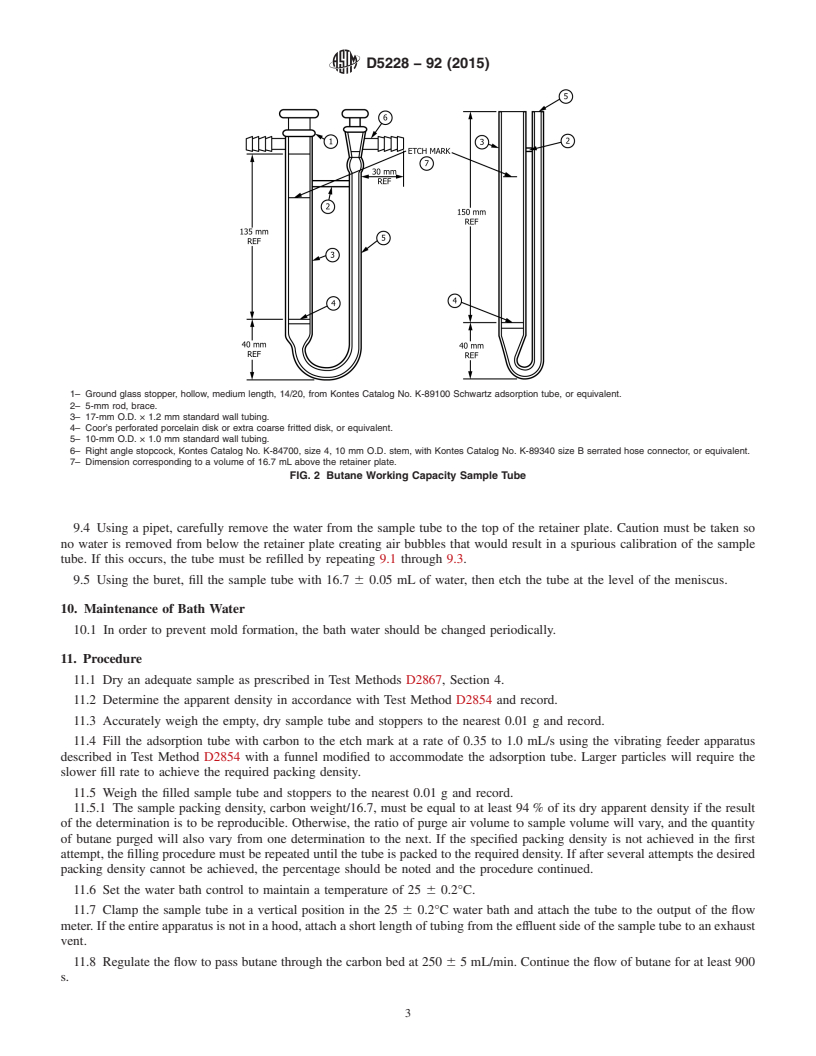
6.2 Sample Tube, as shown in Fig. 2. The glass plate with holes is preferred to a fritted disk to support the carbon, since fritted
disks can vary widely in pressure drop.
6.3 Flow Meters, one capable of delivering air at 0 to 500 mL/min, and one capable of delivering butane
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.