ASTM E2022-06
(Practice)Standard Practice for Calculation of Weighting Factors for Tristimulus Integration
Standard Practice for Calculation of Weighting Factors for Tristimulus Integration
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This practice is intended to provide a method that will yield uniformity of calculations used in making, matching, or controlling colors of objects. This uniformity is accomplished by providing a method for calculation of weighting factors for tristimulus integration consistent with the methods utilized to obtain the weighting factors for common illuminant-observer combinations contained in Practice E 308.
This practice should be utilized by persons desiring to calculate a set of weighting factors for tristimulus integration who have custom source, or illuminant spectral power distributions, or custom observer response functions.
This practice assumes that the measurement interval is equal to the spectral bandwidth integral when applying correction for bandwidth.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice describes the method to be used for calculating tables of weighting factors for tristimulus integration using custom spectral power distributions of illuminants or sources, or custom color-matching functions.
1.2 This practice provides methods for calculating tables of values for use with spectral reflectance or transmittance data, which are corrected for the influences of finite bandpass. In addition, this practice provides methods for calculating weighting factors from spectral data which has not been bandpass corrected. In the latter case, a correction for the influence of bandpass on the resulting tristimulus values is built in to the tristimulus integration through the weighting factors.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to its use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E 2022 – 06
Standard Practice for
1
Calculation of Weighting Factors for Tristimulus Integration
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E 2022; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.2.1 illuminant, n—real or ideal radiant flux, specified by
its spectral distribution over the wavelengths that, in illuminat-
1.1 This practice describes the method to be used for
ing objects, can affect their perceived colors.
calculating tables of weighting factors for tristimulus integra-
3.2.2 source, n—an object that produces light or other
tionusingcustomspectralpowerdistributionsofilluminantsor
radiant flux, or the spectral power distribution of that light.
sources, or custom color-matching functions.
3.2.2.1 Discussion—A source is an emitter of visible radia-
1.2 This practice provides methods for calculating tables of
tion. An illuminant is a table of agreed spectral power
values for use with spectral reflectance or transmittance data,
distribution that may represent a source; thus, IlluminantAis a
which are corrected for the influences of finite bandpass. In
standard spectral power distribution and Source A is the
addition,thispracticeprovidesmethodsforcalculatingweight-
physical representation of that distribution. Illuminant D65 is a
ing factors from spectral data which has not been bandpass
standard illuminant that represents average north sky daylight
corrected. In the latter case, a correction for the influence of
but has no representative source.
bandpass on the resulting tristimulus values is built in to the
3.2.3 spectral power distribution, SPD, S(l),
tristimulus integration through the weighting factors.
n—specification of an illuminant by the spectral composition
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
of a radiometric quantity, such as radiance or radiant flux, as a
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
function of wavelength.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
4. Summary of Practice
bility of regulatory limitations prior to its use.
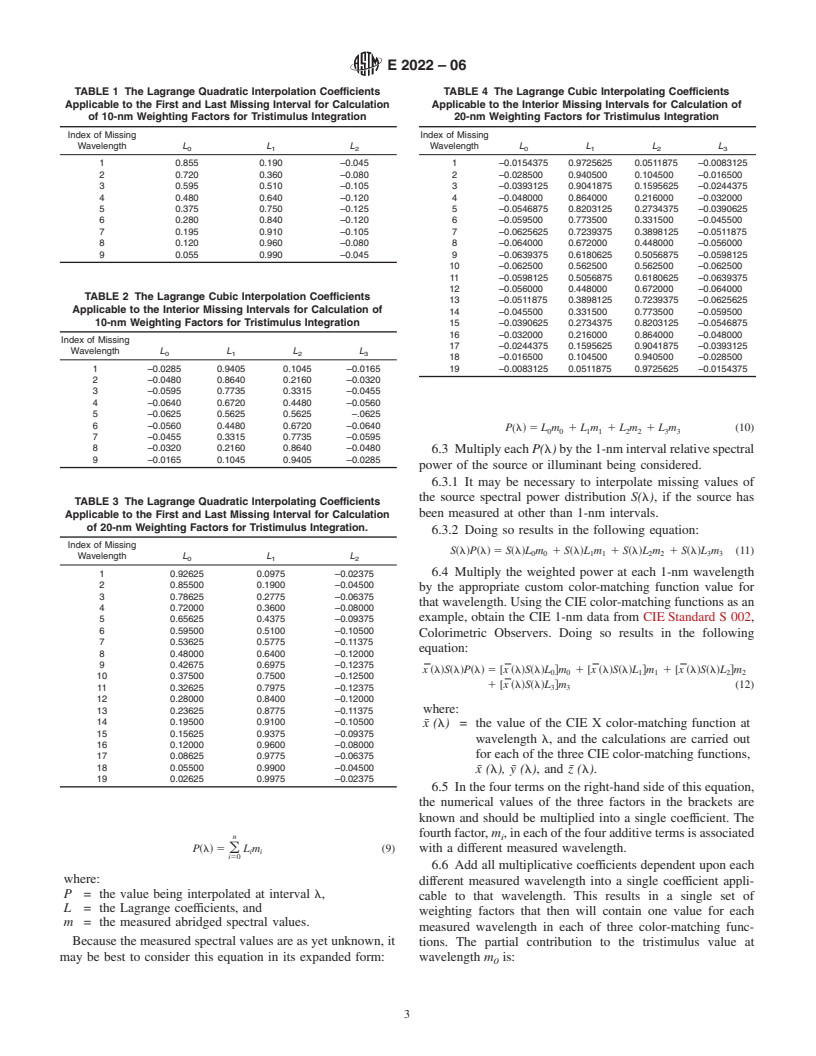
4.1 CIE color-matching functions are standardized at 1-nm
2. Referenced Documents wavelength intervals. Tristimulus integration by multiplication
2
of abridged spectral data into sets of weighting factors occurs
2.1 ASTM Standards:
at larger intervals, typically 10-nm or 20-nm; therefore, inter-
E 284 Terminology of Appearance
mediate 1-nm interval spectral data are missing, but needed.
E 308 Practice for Computing the Colors of Objects by
4.2 Lagrangeinterpolatingcoefficientsarecalculatedforthe
Using the CIE System
missing wavelengths. The Lagrange coefficients, when multi-
2.2 CIE Standard:
3 plied into the appropriate measured spectral data, interpolate
CIE Standard S 002 Colorimetric Observers
the abridged spectrum to 1-nm interval. The 1-nm interval
3. Terminology spectrum is then multiplied into the CIE 1-nm color-matching
data, and into the source spectral power distribution. Each
3.1 Definitions—Appearance terms in this practice are in
separate term of this multiplication is collected into a value
accordance with Terminology E 284.
associated with a measured spectral wavelength, thus forming
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
weighting factors for tristimulus integration.
4.3 A correction may be applied to the resulting table of
1
weighting factors to incorporate a correction for the spectral
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E12 on Color and
Appearance and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E12.04 on Color and
data’s bandpass dependence.
Appearance Analysis.
Current edition approved July 1, 2006. Published July 2006. Originally approved
5. Significance and Use
in 1999. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as E 2022 - 01.
2
5.1 This practice is intended to provide a method that will
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
yield uniformity of calculations used in making, matching, or
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
controlling colors of objects. This uniformity is accomplished
the ASTM website.
3 by providing a method for calculation of weighting factors for
Available from USNC-CIE Publications Office, TLA Lighting Consultants, 7
Pond Street, Salem, MA 01970. tristimulus integration consistent with the methods utilized to
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Cons
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.