ASTM F138-08
(Specification)Standard Specification for Wrought 18Chromium-14Nickel-2.5Molybdenum Stainless Steel Bar and Wire for Surgical Implants (UNS S31673)
Standard Specification for Wrought 18Chromium-14Nickel-2.5Molybdenum Stainless Steel Bar and Wire for Surgical Implants (UNS S31673)
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the requirements for wrought 18chromium-14nickel-2.5molybdenum stainless steel bar and wire used for the manufacture of surgical implants. Bar and wire shall be furnished, as specified, in the hot-worked, annealed, cold -worked, or extra hard condition. Fine wire shall be furnished, as specified, in the cold-drawn condition. Types of finish available for bar and wire products are cold-drawn, pickled, ground, and ground and polished. On the other hand, types of finish available for fine wire products are cold-drawn, ground, and ground and polished. The heat analysis shall conform to the requirements as to chemical composition specified and the material shall contain no delta ferrite, chi, or sigma phases when it is examined by metallography. Different tests shall be performed in order to determine the following mechanical properties of the wire and bar: ultimate tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, and Brinell hardness.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers the chemical, mechanical, and metallurgical requirements for wrought 18chromium-14nickel-2.5molybdenum stainless steel bar and wire used for the manufacture of surgical implants.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F138 −08
StandardSpecification for
Wrought 18Chromium-14Nickel-2.5Molybdenum Stainless
1
Steel Bar and Wire for Surgical Implants (UNS S31673)
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF138;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope* E112Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size
E354 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of High-
1.1 This specification covers the chemical, mechanical, and
Temperature,Electrical,Magnetic,andOtherSimilarIron,
metallurgicalrequirementsforwrought18chromium-14nickel-
Nickel, and Cobalt Alloys
2.5molybdenum stainless steel bar and wire used for the
E407Practice for Microetching Metals and Alloys
manufacture of surgical implants.
F981Practice for Assessment of Compatibility of Biomate-
1.2 Thevaluesstatedininch-poundunitsaretoberegarded
rials for Surgical Implants with Respect to Effect of
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
Materials on Muscle and Bone
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
F1350Specification for Wrought 18Chromium-14Nickel-
and are not considered standard.
2.5Molybdenum Stainless Steel Surgical Fixation Wire
(UNS S31673)
2. Referenced Documents
4
2.2 ISO Standards:
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
ISO 5832–1Implants for Surgery—Metallic Materials—
A262Practices for Detecting Susceptibility to Intergranular
Part 1:Wrought Stainless Steel
Attack in Austenitic Stainless Steels
ISO 6892Metallic Materials—Tensile Testing
A484/A484MSpecification for General Requirements for
ISO 9001Quality Management Systems—Requirements
Stainless Steel Bars, Billets, and Forgings
5
2.3 ASQ Standard:
A555/A555MSpecification for General Requirements for
ASQC1Specification of General Requirements for a Qual-
Stainless Steel Wire and Wire Rods
ity Program
A751Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology for Chemi-
cal Analysis of Steel Products
3. Terminology
E8Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
E8MTestMethodsforTensionTestingofMetallicMaterials
3
3.1.1 bar, n—rounds, flats, or other shapes from 0.1875 in.
[Metric] (Withdrawn 2008)
(4.76 mm) to 4 in. (101.60 mm) in diameter or thickness.
E10Test Method for Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materials
(Other sizes and shapes by special order.)
E18Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness of Metallic Ma-
terials 3.1.2 finewire,n—wireasdescribedin3.1.5,lessthan0.063
E29Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to in. (1.60 mm) in diameter or thickness.
Determine Conformance with Specifications
3.1.3 forging bar, n—bar as described in 3.1.1, used for the
E45Test Methods for Determining the Inclusion Content of
production of forgings, may be furnished in the hot worked
Steel
condition.
3.1.4 lot, n—the total number of mill products produced
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F04 on
from the same melt heat under the same conditions at essen-
Medical and Surgical Materials and Devices and is the direct responsibility of
tially the same time.
Subcommittee F04.12 on Metallurgical Materials.
Current edition approved May 1, 2008. Published May 2008. Originally
3.1.5 wire, n—rounds, flats or other shapes less than 0.1875
approved in 1971. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as F138–03. DOI:
in. (4.76 mm) in diameter or thickness.
10.1520/F0138-08.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
the ASTM website. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
5
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on Available from American Society for Quality (ASQ), 600 N. Plankinton Ave.,
www.astm.org. Milwaukee, WI 53203, http://www.asq.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F138−08
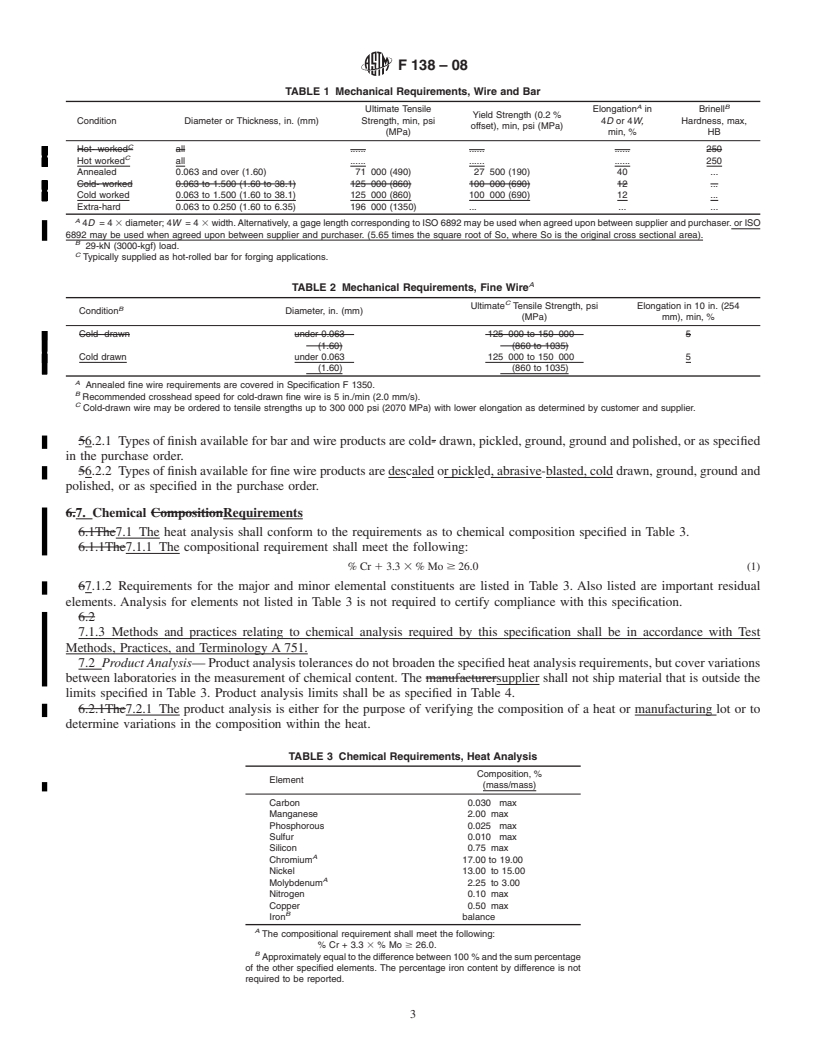
4. General Requirements for Delivery 7.1.2 Requirements for the major and minor elemental
constituents are listed in Table 3. Also listed are important
4.1 In addition to the requirements of this specification, all
residualelements.AnalysisforelementsnotlistedinTable3is
requirements of the current editions of Specifications A484/
not required to certify compliance with this specification
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:F138–03 Designation: F 138 – 08
Standard Specification for
Wrought 18Chromium-14Nickel-2.5Molybdenum Stainless
1
Steel Bar and Wire for Surgical Implants (UNS S31673)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 138; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1This specification covers the requirements for wrought 18chromium-14nickel-2.5molybdenum stainless steel bar and wire
used for the manufacture of surgical implants.
1.2Thevaluesstatedininch-poundunitsaretoberegardedasthestandard.TheSIunitsgiveninparenthesesareforinformation
only.
1.1 This specification covers the chemical, mechanical, and metallurgical requirements for wrought 18chromium-14nickel-
2.5molybdenum stainless steel bar and wire used for the manufacture of surgical implants.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A 262 Practices for Detecting Susceptibility to Intergranular Attack in Austenitic Stainless Steels
A 484/A 484M Specification for General Requirements for Stainless Steel Bars, Billets, and Forgings
A 555/A 555M Specification for General Requirements for Stainless Steel Wire and Wire Rods
A 751 Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology for Chemical Analysis of Steel Products
E 8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
3
E 8MTest Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials [Metric] Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
[Metric]
E 10 Test Method for Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materials
E 18 Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness of Metallic Materials
E 29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to Determine Conformance with Specifications
E 45 Test Methods for Determining the Inclusion Content of Steel
3
E 112Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size
E 354 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of High-Temperature, Electrical, Magnetic, and Other Similar Iron, Nickel, and
Cobalt Alloys
E 407 Practice for Microetching Metals and Alloys
F 981 Practice forAssessment of Compatibility of Biomaterials for Surgical Implants with Respect to Effect of Materials inon
Muscle and Bone
F 1350 Specification for Wrought 18Chromium-14Nickel-2.5Molybdenum Stainless Steel Surgical Fixation Wire (UNS
S31673)
2.2 ISO Standards:
ISO 5832-1 Implants for Surgery—Metallic Materials—Part 1:Wrought Stainless Steel
53
ISO 6892Metallic Materials—Tensile Testing
ISO 5832–1 Implants for Surgery—Metallic Materials—Part 1:Wrought Stainless Steel
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F04 on Medical and Surgical Materials and Devices and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
F04.12 on Metallurgical Materials.
Current edition approved June 10, 2003. Published July 2003. Originally approved in 1971. Last previous edition approved in 2000 as F138–00.
Current edition approved May 1, 2008. Published May 2008. Originally approved in 1971. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as F 138 – 03.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
, Vol 01.03.volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01.
3
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F138–08
ISO 6892 Metallic Materials—Tensile Testing
ISO 9001 Quality Management Systems—Requirements
4
2.3 ASQ Standard:
ASQ C1 Specification of General Requirements for a Quality Program
3. General Requirements for Delivery
3.1In addition to the requirements of this specification, all requirements of the current editions of Specifications
A484Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific t
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.