ASTM C930-99
(Classification)Standard Classification of Potential Health and Safety Concerns Associated With Thermal Insulation Materials and Accessories
Standard Classification of Potential Health and Safety Concerns Associated With Thermal Insulation Materials and Accessories
SCOPE
1.1 This classification identifies potential concerns and effects that could result from direct contact with thermal insulation materials and accessories, or be caused by indirect action of events such as aging, fire, or physical disturbance.
1.2 Intent of Classification:
1.2.1 It is the intent of this classification to alert others to potential concerns, effects, hazards, or risk.
1.2.2 It is not the intent of this classification to establish the degree of risk or hazard or limiting values of potential hazards.
1.2.3 It is not the intent of this classification to establish or recommend methods or markings to reduce or mitigate the potential; however, it is recognized that correct procedures and precautionary measures can substantially reduce or eliminate some of the potential concerns, effects, hazards, or risks. Note 1-See Appendix X1 for commentary.
1.3 This classification recognizes the responsibility of producers and users, as appropriate, to: ( ) provide information on known effects or hazards, ( ) advise on established safety and health practices, and ( ) determine applicable regulatory requirements.
1.4 This classification does not address the health and safety concerns of thermal insulation materials and accessories during manufacture.
1.5 Omission of an item from this classification does not imply an absence of potential concerns or effects.
1.6 There is no importance in the order of listing.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C 930 – 99
Standard Classification of
Potential Health and Safety Concerns Associated With
Thermal Insulation Materials and Accessories
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C 930; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2.1.3 hazard—a condition or set of circumstances that
presents a specific injury or adverse health potential.
1.1 This classification identifies potential concerns and ef-
2.1.4 indirect action or events—the actions or events that
fects that could result from direct contact with thermal insula-
are not directly created by, or straightforwardly caused by, the
tion materials and accessories, or be caused by indirect action
person(s) potentially exposed to the effects or hazards.
of events such as aging, fire, or physical disturbance.
2.1.5 potential—the possible as opposed to the actual; that
1.2 Intent of Classification:
which may, but has not yet, come into being; that which is
1.2.1 It is the intent of this classification to alert others to
latent, unrealized.
potential concerns, effects, hazards, or risk.
2.1.6 risk—the exposure to chance of injury or illness or
1.2.2 It is not the intent of this classification to establish the
loss.
degree of risk or hazard or limiting values of potential hazards.
1.2.3 It is not the intent of this classification to establish or
3. Significance and Use
recommend methods or markings to reduce or mitigate the
3.1 The purpose of this classification is to identify potential
potential; however, it is recognized that correct procedures and
concerns and effects which may occur during the life cycle
precautionary measures can substantially reduce or eliminate
(installation, service, removal, and disposal) of insulation
some of the potential concerns, effects, hazards, or risks.
materials and accessories resulting from direct contact or
NOTE 1—See Appendix X1 for commentary.
indirect action or events.
1.3 This classification recognizes the responsibility of pro- 3.2 This classification does not identify remedial or preven-
tive steps that may be taken to correct potential problems or
ducers and users, as appropriate, to: (1) provide information on
known effects or hazards, (2) advise on established safety and hazards; rather it is intended as a checklist that will make it
health practices, and (3) determine applicable regulatory re- easier to deal constructively with these potentials, and to
determine what, if any, specific requirements need to be added
quirements.
1.4 Thisclassificationdoesnotaddressthehealthandsafety to other standards concerning insulation materials or accesso-
ries. (See Appendix X2 for sources of information.)
concernsofthermalinsulationmaterialsandaccessoriesduring
manufacture. 3.3 This classification recognizes that proper handling and
installation procedures can substantially reduce the potential
1.5 Omission of an item from this classification does not
imply an absence of potential concerns or effects. concerns and effects. Further, it recognizes that in some
situations the presence or creation of potential effects or
1.6 There is no importance in the order of listing.
hazards results from an intervening act of human or natural
2. Terminology
origin, or depends on access to or contact with the materials or
2.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard: accessories. Lack of compatibility of the individual compo-
2.1.1 degree of risk—the probability or expected frequency nents of an insulation system with each other or the environ-
of the event, multiplied by the expected magnitude of exposure mental conditions within which the system will operate, or
and the potential for harm. both, may create unanticipated effects. (See Appendix X3.)
2.1.2 direct contact—the straightforward touching resulting
4. Basis of Classification
from use, manipulation, placement, etc.
4.1 Classification is based on several broad groupings of
potential that could result from direct contact with thermal
This classification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C-16 on
insulation materials and accessories, or be caused by indirect
Thermal Insulation and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C 16.24on
actions or events.
Health and Safety Hazard Potentials.
4.2 Potentials that occur from direct contact or indirect
Current edition approved Feb. 10, 1999. Published May 1999. Originally
published as C 930 – 80. Last previous edition C 930 – 92. action or events are described as follows:
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
C 930
4.2.1 Potential Health Effects—Those effects that create 4.2.2 Potential Traumatic Injury Effects (Table 1)—These
risk of temporary or permanent changes in normal body effects may result from sharp or rough materials or accessories
functions and biochemical activity. The latter may involve which have protrusions or abrasive surfaces, cause overheat-
vapors (such as organic solvent fumes), corrosive liquids ing, or transmit electrical energy, and generally require direct
(acids, alkalies, and organics), and solids (usually high surface contact with the material or accessory causing lacerations,
area particulates) that react with body tissues or fluids. abrasions, punctures, etc.
4.2.1.1 AMaterialSafetyDataSheet(MSDS)isrequiredby 4.2.3 Potential Effects Resulting from Combustion (Table
the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), 2)— Those effects that result principally from the emission of
U.S. Department of Labor (29CFR 1910.1200) for hazardous heat, gases (toxic and non-toxic), fibers, particulates, and
chemicals produced in the United States, or imported. (The depletion of oxygen which takes place during combustion that
MSDS for any product or material is issued and available from exposes or involves insulation materials or accessories.
the organization producing the product or material.) 4.2.4 Potential Effects from Structural Conditions (Table
4.2.1.2 The MSDS for any insulation product, system, or 3)—Those effects that result principally from the overloading
accessory (including adhesives) should be obtained and re- ordeteriorationofstructuralmembersofabuildingresultingin
viewed to determine any potential effect on humans using or failure of the structure, or a portion of it, and its collapse on
installing the material. occupants.
4.2.1.3 When tests are included in a standard, the MSDS for
5. Keywords
chemicals required ahould be reviewed to ensure that proper
guidance for safe handling and use is incorporated. 5.1 hazsards; health effects; injury; safety
TABLE 1 Potential Traumatic Injury
Insulation Product, Potential Exposure Potential Effect on Humans
System, or Accessory
Cellular glass abrasive surface Contact may abrade skin
Encapsulated or reflective insulation high surface temperature Contact may cause thermal burns.
Insulation materials and accessories application of thermal insulation
around or adjacent to electrical
wiring or fixtures (particularly
important if the covering on the
electrical circuit is old) may
A
produce:
(a) overheating that could result Electrical shock
in deterioration of the wire
covering and contact with
electrical energy
(b) if subject to moisture Electrical shock
accumulation could result in
deterioration of the wire covering
and contact with electrical energy
(c) overheating that could result Thermal burns
in fire
Man-made vitreous fibers: fiber stalks or bundles Contact may abrade or puncture skin.
Glass
Mineral wool
Refractory
Metal encapsulated or reflective insulation electrically conductive Contact may transmit electrical energy if
touching an electrical circuit resulting in minor
or serious electrical shock.
Metal foil electrically conductive Contact may transmit electrical energy if
touching an electrical circuit resulting in minor
or serious electrical shock.
Sheet metal lagging, bands, fasteners, sheet sharp or pointed edges Contact may cause skin cuts, tears or
metal punctures.
A
Also see Table 3.
C 930
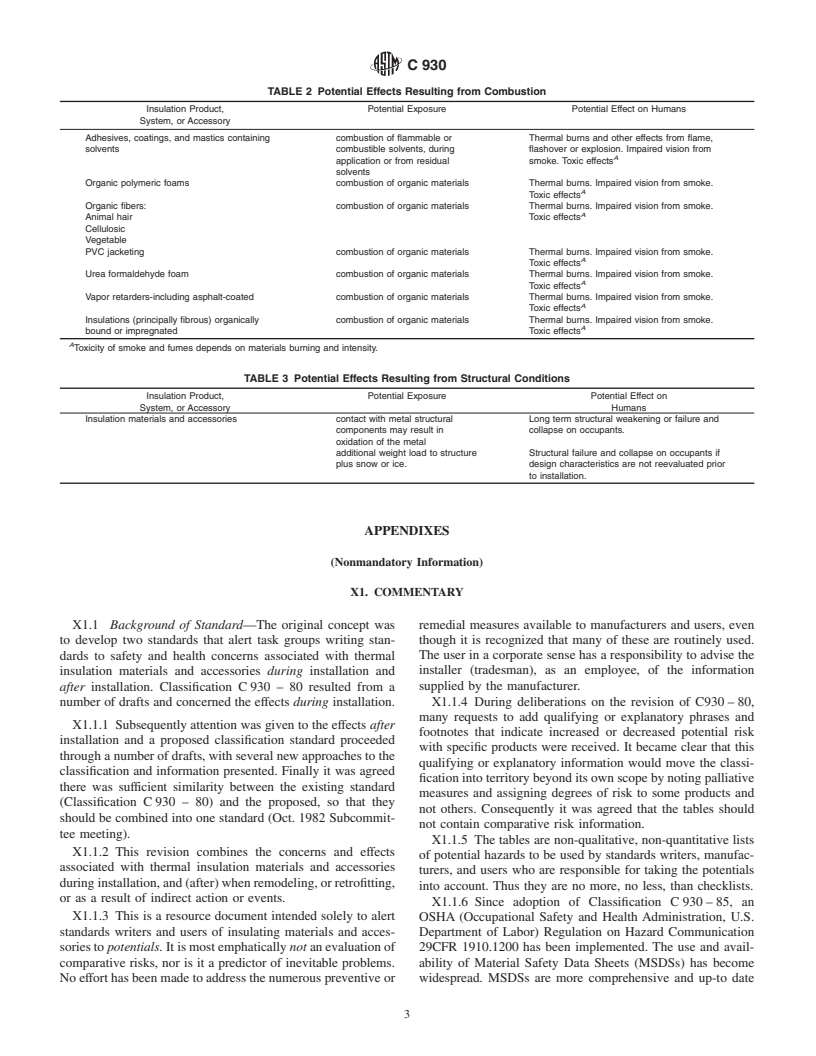
TABLE 2 Potential Effects Resulting from Combustion
Insulation Product, Potential Exposure Potential Effect on Humans
System, or Accessory
Adhesives, coatings, and mastics containing combustion of flammable or Thermal burns and other effects from flame,
solvents combustible solvents, during flashover or explosion. Impaired vision from
A
application or from residual smoke. Toxic effects
solvents
Organic polymeric foams combustion of organic materials Thermal burns. Impaired vision from smoke.
A
Toxic effects
Organic fibers: combustion of organic materials Thermal burns. Impaired vision from smoke.
A
Animal hair Toxic effects
Cellulosic
Vegetable
PVC jacketing combustion of organic materials Thermal burns. Impaired vision from smoke.
A
Toxic effects
Urea formaldehyde foam combustion of organic materials Thermal burns. Impaired vision from smoke.
A
Toxic effects
Vapor retarders-including asphalt-coated combustion of organic materials Thermal burns. Impaired vision from smoke.
A
Toxic effects
Insulations (principally fibrous) organically combustion of organic materials Thermal burns. Impaired vision from smoke.
A
bound or impregnated Toxic effects
A
Toxicity of smoke and fumes depends on materials burning and intensity.
TABLE 3 Potential Effects Resulting from Structural Conditions
Insulation Product, Potential Exposure Potential Effect on
System, or Accessory Humans
Insulation materials and accessories contact with metal structural Long term structural weakening or failure and
components may result in collapse on occupants.
oxidation of the metal
additional weight load to structure Structural failure and collapse on occupants if
plus snow or ice. design characteristics are not reevaluated prior
to installation.
APPENDIXES
(Nonmandatory Information)
X1. COMMENTARY
X1.1 Background of Standard—The original concept was remedial measures available to manufacturers and users, even
though it is recognized that many of these are routinely used.
to develop two standards that alert task groups writing stan-
dards to safety and health concerns associated with thermal The user in a corporate sense has a responsibility to advise the
installer (tradesman), as an employee, of the information
insulation materials and accessories during installation and
supplied by the manufacturer.
after installation. Classification C 930 – 80 res
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.