ASTM B32-00e1
(Specification)Standard Specification for Solder Metal
Standard Specification for Solder Metal
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers solder metal alloys (commonly known as soft solders) used in non-electronic applications, including but not limited to, tin-lead, tin-antimony, tin-antimony-copper-silver, tin-antimony-coppersilver-nickel, tin-silver, tin-copper-silver, and lead-tin-silver, used for the purpose of joining together two or more metals at temperatures below their melting points. Electronic grade solder alloys and fluxed and non-fluxed solid solders for electronic soldering applications are not covered by this specification as they are under the auspices of IPC - Association Connecting Electronic Industries.
1.1.1 These solders include those alloys having a liquidus temperature not exceeding 800F (430°C).
1.1.2 This specification includes solders in the form of solid bars, ingots, powder and special forms, and in the form of solid and flux-core ribbon, wire, and solder paste.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
e1
Designation: B 32 – 00
Standard Specification for
1
Solder Metal
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B 32; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A superscript
epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1
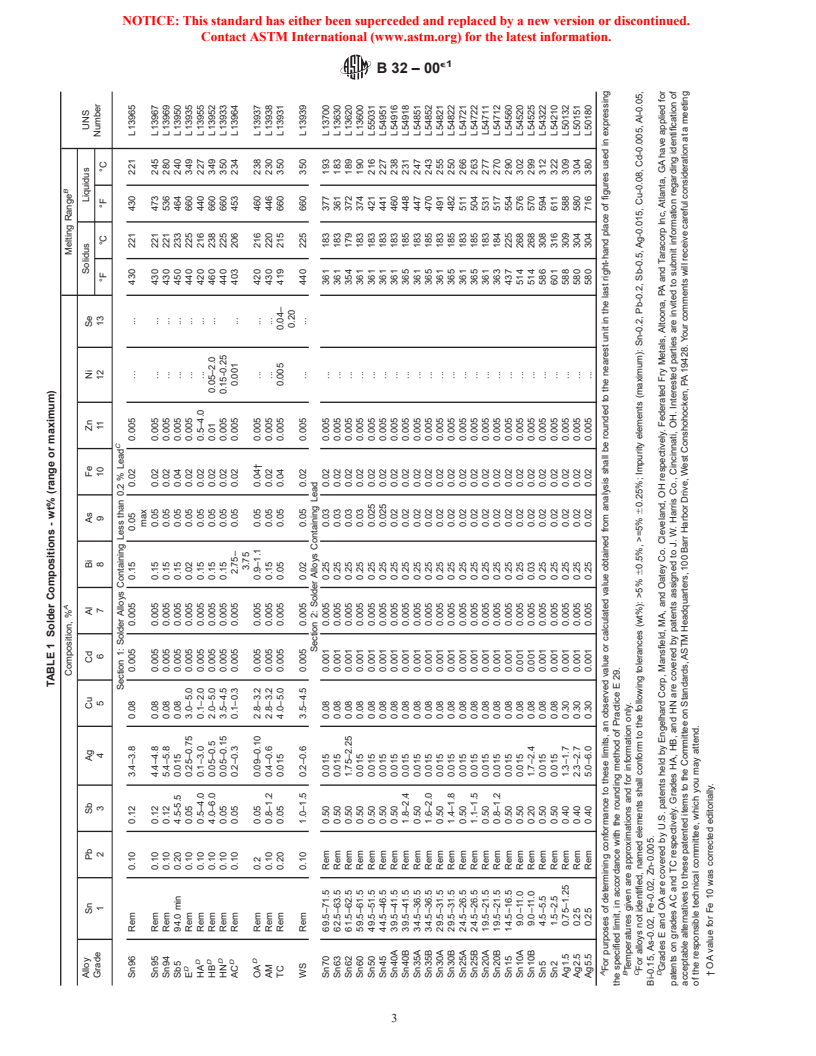
e NOTE—OA value for Fe 10 in Table 1 was corrected editorially in December 2002.
2
1. Scope Products Including Tall Oil and Other Related Products
2
D 509 Test Methods of Sampling and Grading Rosin
1.1 This specification covers solder metal alloys (commonly
E 28 Test Method for Softening Point by Ring-and-Ball
known as soft solders) used in non-electronic applications,
2
Apparatus
including but not limited to, tin-lead, tin-antimony, tin-
E 29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
antimony-copper-silver, tin-antimony-coppersilver-nickel, tin-
3
Determine Conformance with Specifications
silver, tin-copper-silver, and lead-tin-silver, used for the pur-
E 46 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Lead- and
pose of joining together two or more metals at temperatures
4
Tin-Base Solder
below their melting points. Electronic grade solder alloys and
E 51 Method for Spectrographic Analysis of Tin Alloys by
fluxed and non-fluxed solid solders for electronic soldering
5
the Powder Technique
applications are not covered by this specification as they are
E 55 Practice for Sampling Wrought Nonferrous Metals and
under the auspices of IPC - Association Connecting Electronic
6
Alloys for Determination of Chemical Composition
Industries.
E 87 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Lead, Tin, Anti-
1.1.1 These solders include those alloys having a liquidus
7
mony, and Their Alloys (Photometric Method)
temperature not exceeding 800°F (430°C).
E 88 Practice for Sampling Nonferrous Metals and Alloys
1.1.2 This specification includes solders in the form of solid
6
in Cast Form for Determination of Chemical Composition
bars, ingots, powder and special forms, and in the form of solid
8
2.2 Federal Standard:
and flux-core ribbon, wire, and solder paste.
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies)
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
9
2.3 Military Standard:
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for
MIL-STD-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3. Terminology
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1 Definition:
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1.1 producer, n—the primary manufacturer of the mate-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
rial.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
2. Referenced Documents 3.2.1 lot, n—The term “lot” as used in this specification is
defined as follows:
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.2.1.1 Discussion—For solid solder metal, a lot consists of
D 269 Test Method for Insoluble Matter in Rosin and Rosin
2
all solder of the same type designation, produced from the
Derivatives
same batch of raw materials under essentially the same
D 464 Test Methods for Saponification Number of Naval
conditions, and offered for inspection at one time.
Store Products Including Tall Oil and Other Related
2
Products
D 465 Test Methods for Acid Number of Naval Stores
3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
4
Discontinued—See 1994 Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.05.
5
Discontinued—See 1984 Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.06.
1 6
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B02 on Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.05.
7
Nonferrous Metals and Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee Discontinued—See 1984 Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.05.
8
B02.02 on Refined Lead, Tin, Antimony, and Their Alloys. Available from Global Engineering Documents, 15 Inverness Way East,
Current edition approved Oct. 10, 2000. Published November 2000. Originally Englewood, CO 80112.
9
published as B 32–19 T. Last previous edition B 32-96. Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, Bldg. 4 Section D, 700
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 06.03. Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, Attn: NPODS.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
e1
B32–00
3.2.1.2 Discussion—For flux–core
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.