ASTM D5927-09
(Specification)Standard Classification System for Thermoplastic Polyester (TPES) Injection and Extrusion Materials Based on ISO Test Methods
Standard Classification System for Thermoplastic Polyester (TPES) Injection and Extrusion Materials Based on ISO Test Methods
ABSTRACT
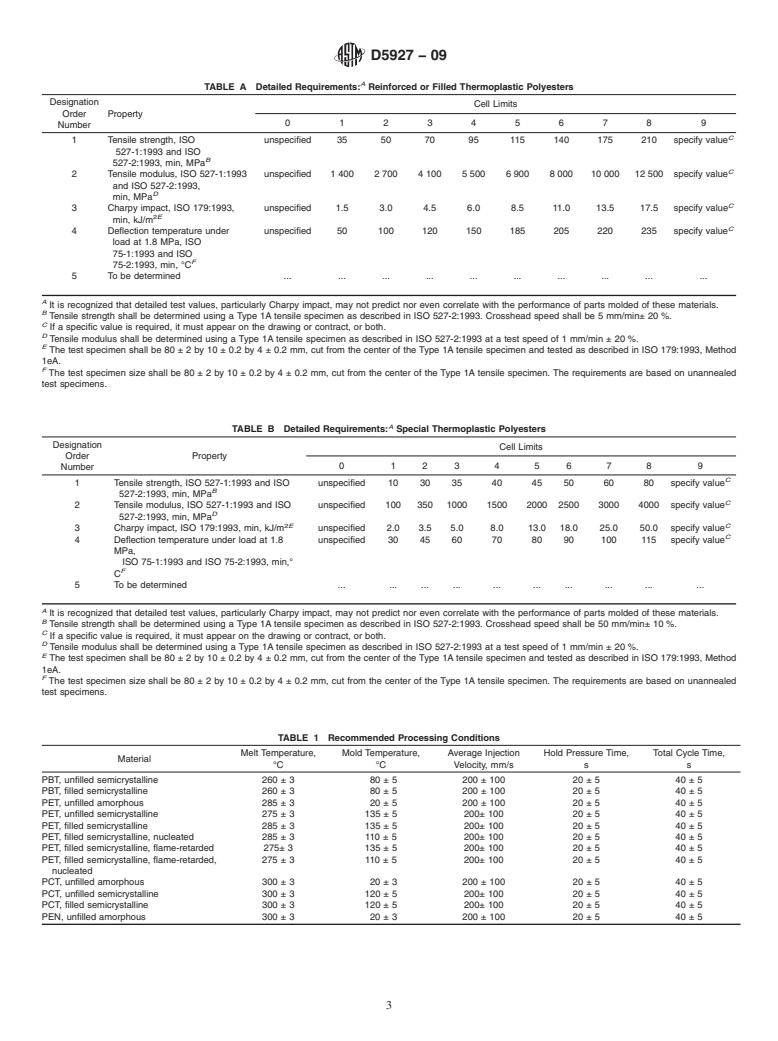
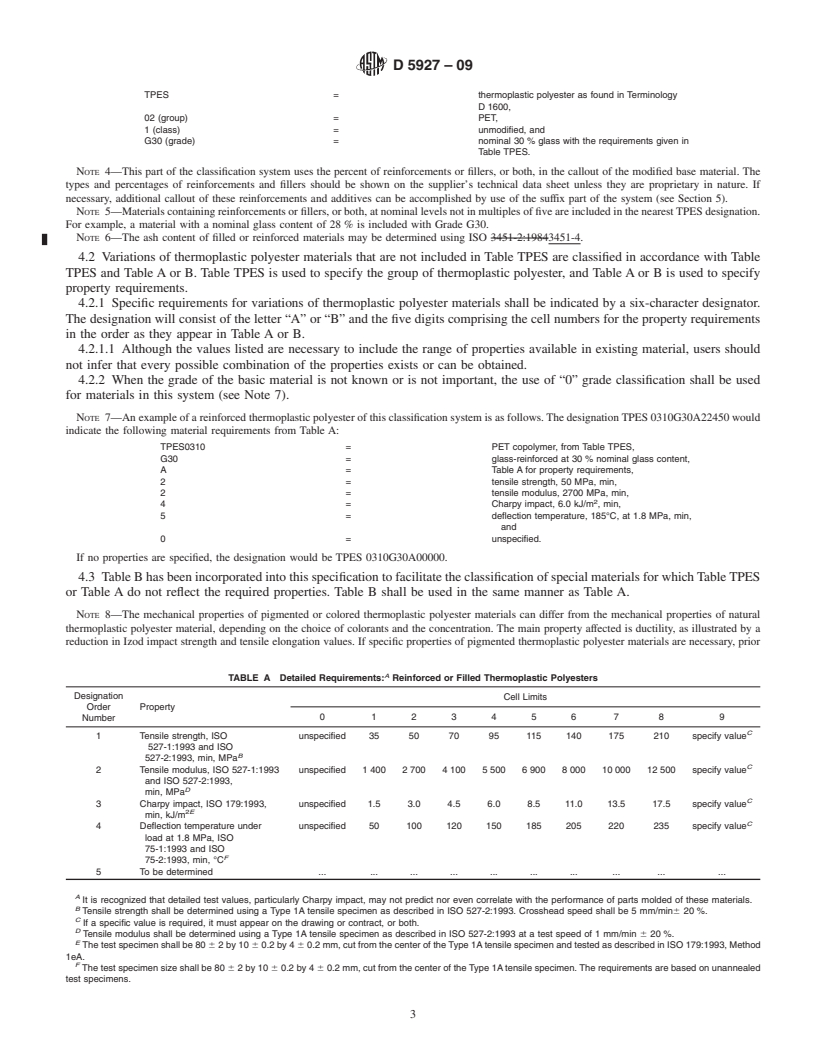
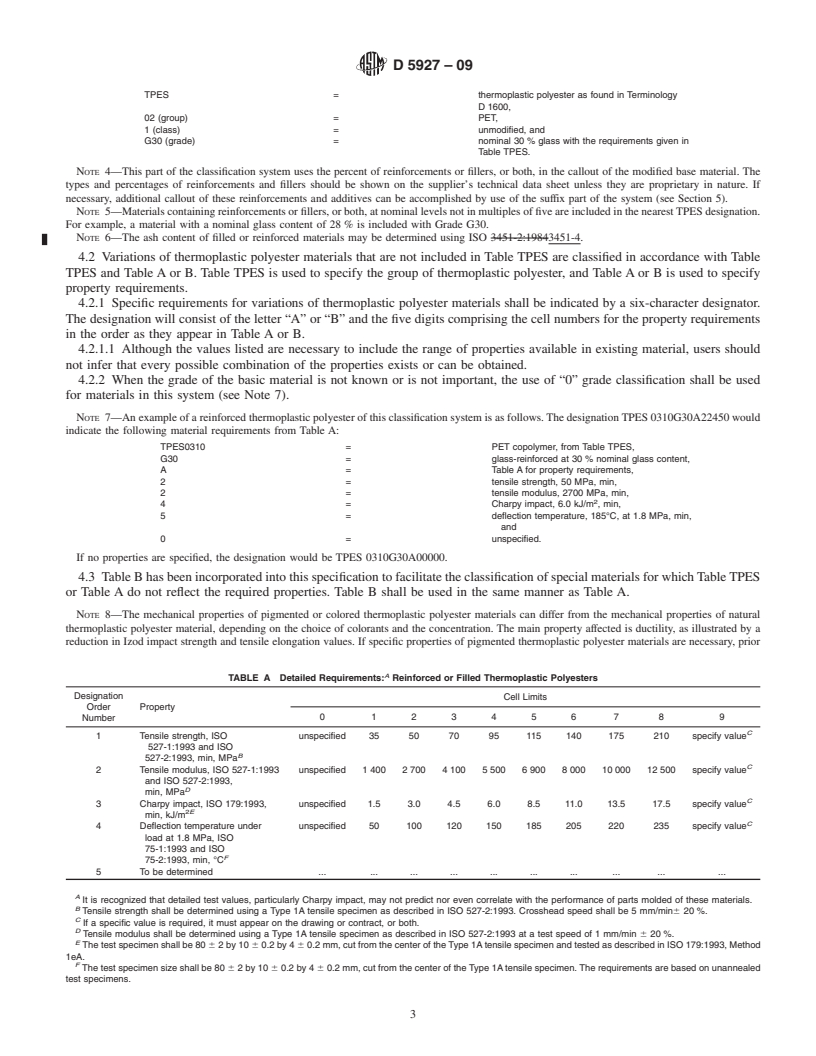
This specification is intended to provide a callout system for thermoplastic polyester (TPES) injection and extrusion materials, both virgin and recycled, based on ISO test methods. However, the proportions of recycled material used, and the nature and amount of any contaminant, as well as the selection of materials cannot be covered practically in this specification. Materials are classified into groups according to their composition, and are further subdivided into classes and grades as specified. Individual groups shall be identified in accordance to performance properties as to tensile strength, tensile modulus, Charpy impact strength, deflection temperature, melt flow rate, and density.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers thermoplastic polyester materials suitable for molding or extrusion.
1.2 This specification allows for the use of recycled thermoplastic polyester materials provided that the requirements as stated in this specification are met. The proportions of recycled material used, as well as the nature and amount of any contaminant, however, cannot be covered practically in this specification.
1.3 The properties included in this specification are those required to identify the compositions covered. There may be other requirements necessary to identify particular characteristics important to specialized applications. These may be specified by using the suffixes as given in Section 5.
1.4 This classification system and subsequent line callout (specification) are intended to provide a means of calling out plastic materials used in the fabrication of end items or parts. It is not intended for the selection of materials. Material selection should be made by those having expertise in the plastic field after careful consideration of the design and performance required of the part, the environment to which it will be exposed, the fabrication process to be used, the costs involved, and the inherent properties of the material other than those covered by this specification.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.6 The following hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 11, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 1—This specification is similar to ISO 7792-1:1995 and ISO 7792-2:1988, although the technical content is significantly different.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D5927 −09
StandardClassification System for
Thermoplastic Polyester (TPES) Injection and Extrusion
1
Materials Based on ISO Test Methods
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5927; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
This material specification is intended to provide a callout system for thermoplastic polyester
materials based on ISO test methods.
1. Scope* dard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if
any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
1.1 This specification covers thermoplastic polyester mate-
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health
rials suitable for molding or extrusion.
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita-
1.2 This specification allows for the use of recycled ther-
tions prior to use.
moplasticpolyestermaterialsprovidedthattherequirementsas
NOTE 1—This specification is similar to ISO 7792-1:1995 and ISO
stated in this specification are met.The proportions of recycled
7792-2:1988, although the technical content is significantly different.
material used, as well as the nature and amount of any
contaminant, however, cannot be covered practically in this
2. Referenced Documents
specification.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.3 The properties included in this specification are those
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
required to identify the compositions covered. There may be
D1600 TerminologyforAbbreviatedTermsRelatingtoPlas-
other requirements necessary to identify particular character-
tics
istics important to specialized applications. These may be
D3892 Practice for Packaging/Packing of Plastics
specified by using the suffixes as given in Section 5.
D4000 Classification System for Specifying Plastic Materi-
als
1.4 This classification system and subsequent line callout
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
(specification) are intended to provide a means of calling out
Determine Conformance with Specifications
plastic materials used in the fabrication of end items or parts.
3
It is not intended for the selection of materials. Material 2.2 IEC and ISO Standards:
selection should be made by those having expertise in the
IEC 112 Recommended Method for Determining the Com-
plastic field after careful consideration of the design and parative Tracking Index of Solid Insulation Materials
performance required of the part, the environment to which it IEC 243 Recommended Methods of Test for Electrical
will be exposed, the fabrication process to be used, the costs Strength of Solid Insulating Materials at Power Frequen-
involved, and the inherent properties of the material other than cies
those covered by this specification. ISO 62 Plastics—Determination of Water Absorption
ISO 75-1:1993 Plastics—Determination of Temperature of
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
Deflection Under Load—Part 1: General Test Methods
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
ISO 75-2:1993 Plastics—Determination of Temperature of
only.
Deflection Under Load—Part 2: Plastics and Ebonite
1.6 The following hazards caveat pertains only to the test
ISO 179-1:1993 Plastics—Determination of Charpy Impact
methods portion, Section 11, of this specification: This stan-
Strength
1 2
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.15 on Thermoplastic contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Materials. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2009. Published February 2009. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 1996. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D5927 – 03. DOI: Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
10.1520/D5927-09. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5927−09
ISO 291:1997 Plastics—Standard Atmospheres for Condi- level of 35 %. The reinforcement letter designations and
tioning and Testing associated tolerance levels are shown as tabulated as follows:
ISO 294-1:1996 Plastics—InjectionMouldingofTestSpeci-
Symbol Material Tolerance
mens of Thermoplastic Materials—Part 1: General
C carbon- and grap
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D5927–03
Standard Specification for Designation: D 5927 – 09
Standard Classification System for
Thermoplastic Polyester (TPES) Injection and Extrusion
1
Materials Based on ISO Test Methods
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 5927; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
This material specification is intended to provide a callout system for thermoplastic polyester
materials based on ISO test methods.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers thermoplastic polyester materials suitable for molding or extrusion.
1.2 This specification allows for the use of recycled thermoplastic polyester materials provided that the requirements as stated
in this specification are met. The proportions of recycled material used, as well as the nature and amount of any contaminant,
however, cannot be covered practically in this specification.
1.3 The properties included in this specification are those required to identify the compositions covered. There may be other
requirements necessary to identify particular characteristics important to specialized applications.These may be specified by using
the suffixes as given in Section 5.
1.4 This classification system and subsequent line callout (specification) are intended to provide a means of calling out plastic
materials used in the fabrication of end items or parts. It is not intended for the selection of materials. Material selection should
bemadebythosehavingexpertiseintheplasticfieldaftercarefulconsiderationofthedesignandperformancerequiredofthepart,
the environment to which it will be exposed, the fabrication process to be used, the costs involved, and the inherent properties of
the material other than those covered by this specification.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.6 The following hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 11, of this specification: This standard does
not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard
to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
NOTE 1—This specification is similar to ISO 7792-1:1995 and ISO 7792-2:1988, although the technical content is significantly different.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D 1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to Plastics
D 3892 Practice for Packaging/Packing of Plastics
D 4000 Classification System for Specifying Plastic Materials
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to Determine Conformance with Specifications
3
2.2 IEC and ISO Standards:
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.15 on Thermoplastic Materials
.
Current edition approved March 10, 2003. Published April 2003. Originally approved in 1996. Last previous edition approved in 2000 as D5927–00.
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2009. Published February 2009. Originally approved in 1996. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D 5927 – 03.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
, Vol 08.01.volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.02.
3
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5927–09
IEC 112 Recommended Method for Determining the Comparative Tracking Index of Solid Insulation Materials
IEC 243 Recommended Methods of Test for Electrical Strength of Solid Insulating Materials at Power Frequencies
ISO 62 Plastics—Determination of Water Absorption
ISO 75-1:1993 Plastics—Determination of Temperature of Deflection Under Load—Part 1: General Test Methods
ISO 75-2:1993 Plastics—
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D5927–03
Standard Specification for Designation: D 5927 – 09
Standard Classification System for
Thermoplastic Polyester (TPES) Injection and Extrusion
1
Materials Based on ISO Test Methods
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 5927; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
This material specification is intended to provide a callout system for thermoplastic polyester
materials based on ISO test methods.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers thermoplastic polyester materials suitable for molding or extrusion.
1.2 This specification allows for the use of recycled thermoplastic polyester materials provided that the requirements as stated
in this specification are met. The proportions of recycled material used, as well as the nature and amount of any contaminant,
however, cannot be covered practically in this specification.
1.3 The properties included in this specification are those required to identify the compositions covered. There may be other
requirements necessary to identify particular characteristics important to specialized applications.These may be specified by using
the suffixes as given in Section 5.
1.4 This classification system and subsequent line callout (specification) are intended to provide a means of calling out plastic
materials used in the fabrication of end items or parts. It is not intended for the selection of materials. Material selection should
bemadebythosehavingexpertiseintheplasticfieldaftercarefulconsiderationofthedesignandperformancerequiredofthepart,
the environment to which it will be exposed, the fabrication process to be used, the costs involved, and the inherent properties of
the material other than those covered by this specification.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.6 The following hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 11, of this specification: This standard does
not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard
to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
NOTE 1—This specification is similar to ISO 7792-1:1995 and ISO 7792-2:1988, although the technical content is significantly different.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D 1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to Plastics
D 3892 Practice for Packaging/Packing of Plastics
D 4000 Classification System for Specifying Plastic Materials
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to Determine Conformance with Specifications
3
2.2 IEC and ISO Standards:
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.15 on Thermoplastic Materials
.
Current edition approved March 10, 2003. Published April 2003. Originally approved in 1996. Last previous edition approved in 2000 as D5927–00.
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2009. Published February 2009. Originally approved in 1996. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D 5927 – 03.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
, Vol 08.01.volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.02.
3
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5927–09
IEC 112 Recommended Method for Determining the Comparative Tracking Index of Solid Insulation Materials
IEC 243 Recommended Methods of Test for Electrical Strength of Solid Insulating Materials at Power Frequencies
ISO 62 Plastics—Determination of Water Absorption
ISO 75-1:1993 Plastics—Determination of Temperature of Deflection Under Load—Part 1: General Test Methods
ISO 75-2:1993 Plastics—
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.