ASTM F2878-10
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Protective Clothing Material Resistance to Hypodermic Needle Puncture
Standard Test Method for Protective Clothing Material Resistance to Hypodermic Needle Puncture
ABSTRACT
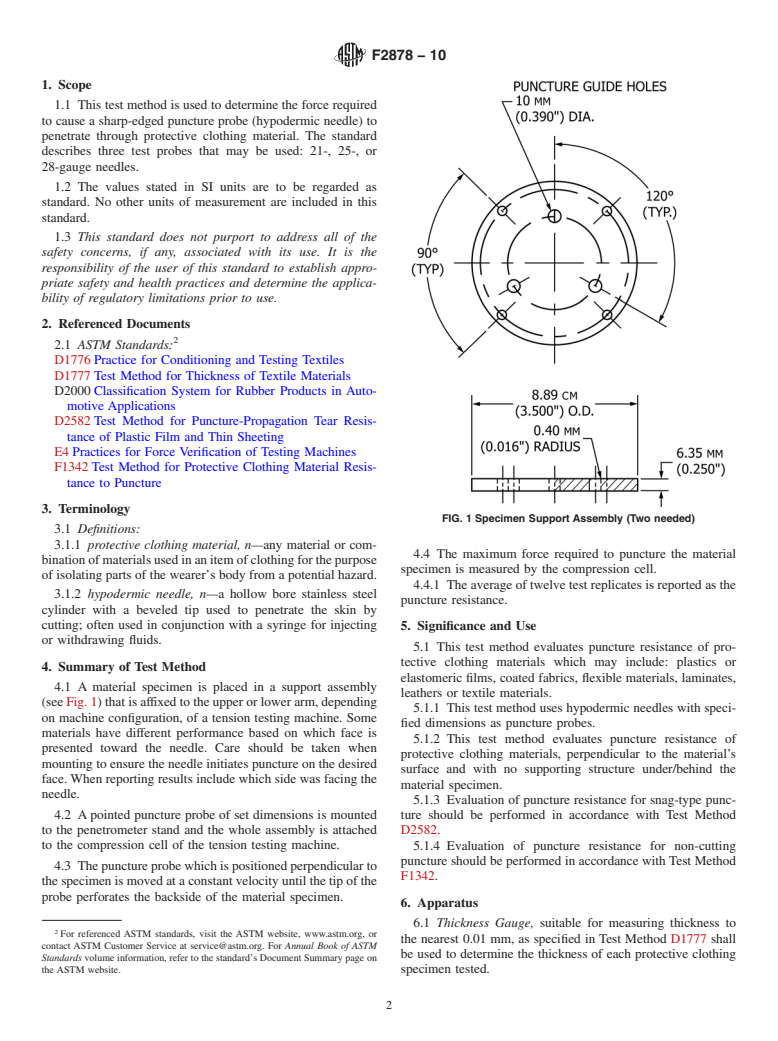
This test method is used for determining the force required to cause a hypodermic needle to penetrate through protective clothing material. It defines three common hypodermic needles - 21-, 25-, 28- gauge needles - to evaluate puncture resistance of protective clothing. This test method does not attempt to simulate all use conditions. A number of variables which impact puncture resistance, such as stiffness of backing materials, presence of lubricants, and tension on the specimen, are not addressed by this test method.
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method evaluates puncture resistance of protective clothing materials which may include: plastics or elastomeric films, coated fabrics, flexible materials, laminates, leathers or textile materials.
This test method uses hypodermic needles with specified dimensions as puncture probes.
This test method evaluates puncture resistance of protective clothing materials, perpendicular to the material’s surface and with no supporting structure under/behind the material specimen.
Evaluation of puncture resistance for snag-type puncture should be performed in accordance with Test Method D2582.
Evaluation of puncture resistance for non-cutting puncture should be performed in accordance with Test Method F1342.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is used to determine the force required to cause a sharp-edged puncture probe (hypodermic needle) to penetrate through protective clothing material. The standard describes three test probes that may be used: 21-, 25-, or 28-gauge needles.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F2878 − 10
Standard Test Method for
Protective Clothing Material Resistance to Hypodermic
1
Needle Puncture
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2878; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
Occupational exposures to bloodborne pathogens (BBP) caused by needlestick injuries are a
concern for healthcare professionals, law enforcement officers, first responders and others.
Transmission of diseases such as Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Hepatitis C (Hep C)
as a result of percutaneous needlestick injuries have been documented worldwide. These diseases can
lead to life-long chronic health problems and possibly death.
Work practice safety procedures, including the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) such as
gloves, aprons, and sleeves, are used to diminish the risk of occupational exposure to BBP’s through
needlestick injury.
The purpose of this standard is to measure relative hypodermic needle puncture resistance offered
by various materials based on the conditions specified within the standard. This standard does not
attempt to simulate all use conditions.Anumber of variables which impact puncture resistance are not
addressed by this standard. For example, stiffness of backing materials, presence of lubricants, and
tension on the specimen may all impact puncture resistance, but are not considered by this standard.
This standard defines three common hypodermic needles to evaluate puncture resistance. Through
development of this standard, it has been observed that needle diameter has an effect on puncture
resistance. Therefore needles of various diameters have been specified. Users of this method may
specify testing with one or more of the needles defined within the standard.
The hypodermic needles referenced have been selected with consideration to three main points:
(1) As needle gauge increases the load required to puncture materials taken from commonly
available hypodermic needle resistant PPE increases. The performance is not linear and therefore
relatively large gauge (21 g) and small gauge (28 g) needles are provided to better understand a
material’s performance against one end of the spectrum or the other.
(2) Certain end-use applications are concerned with protection from either large gauge needles or
small gauge needles. For example, police officers searching suspected intravenous drug users are most
commonly at risk of injury from fine gauge needles (28 g), but not large gauge needles. Whereas,
workers inoculating poultry on commercial farms may be concerned with large gauge needles (21 g),
but not small gauge needles.
(3) Certain materials are optimized to resist either large gauge or small gauge needles and testing
against the other would not be useful. Other materials may be engineered for resistance to the full
breadth of the gauge spectrum. For example, in applications, such as healthcare, where a broad range
of needle gauges are expected, testing against both ends of the spectrum allows for a better
understanding of robustness.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F2878 − 10
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F23 on Personal
Protective Clothing and Equipment and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
F23.20 on Physical.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2010. Published January 2011. DOI:10.1520/
F2878-10.
1
---------------------- Page: 2 ----------------------
F2878 − 10
1. Scope
1.1 This test method is used to determine the force required
to cause a sharp-edged puncture probe (hypodermic needle) to
penetrate through protective clothing material. The standard
describes three test probes that may be used: 21-, 25-, or
28-gauge needles.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1776 Practice for Conditioning and Testing Textiles
D1777 Test Method for Thickness of Textile Materials
D2000 Classification System for Rubber Products in Auto-
motive Applications
D2582 Test Method for Puncture-Propagation Tear Resis-
tance of Plastic Film and Thin Sheetin
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.