ASTM A710/A710M-02
(Specification)Standard Specification for Precipitation-Strengthened Low-Carbon Nickel-Copper-Chromium-Molybdenum-Columbium Alloy Structural Steel Plates
Standard Specification for Precipitation-Strengthened Low-Carbon Nickel-Copper-Chromium-Molybdenum-Columbium Alloy Structural Steel Plates
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers low-carbon precipitation-strengthened nickel - copper - chromium - molybdenum - columbium alloy steel plates for general applications. The alloys in this specification are strengthened by precipitation in various temperature ranges. Precipitation strengthening can occur upon air cooling after hot rolling, during normalizing, and by another heat treatment. These grades are not intended for use in applications above 900°F [540°C].
1.2 Two grades, each with three classes, are provided as follows:Grade and Class ConditionGrade A, Class 1 as-rolled and precipitation heat treatedGrade A, Class 2normalized and precipitation heat treatedGrade A, Class 3 quenched and precipitation heat treatedGrade B, Class 1as-rolledGrade B, Class 2normalizedGrade B, Class 3normalized and precipitation heat treated
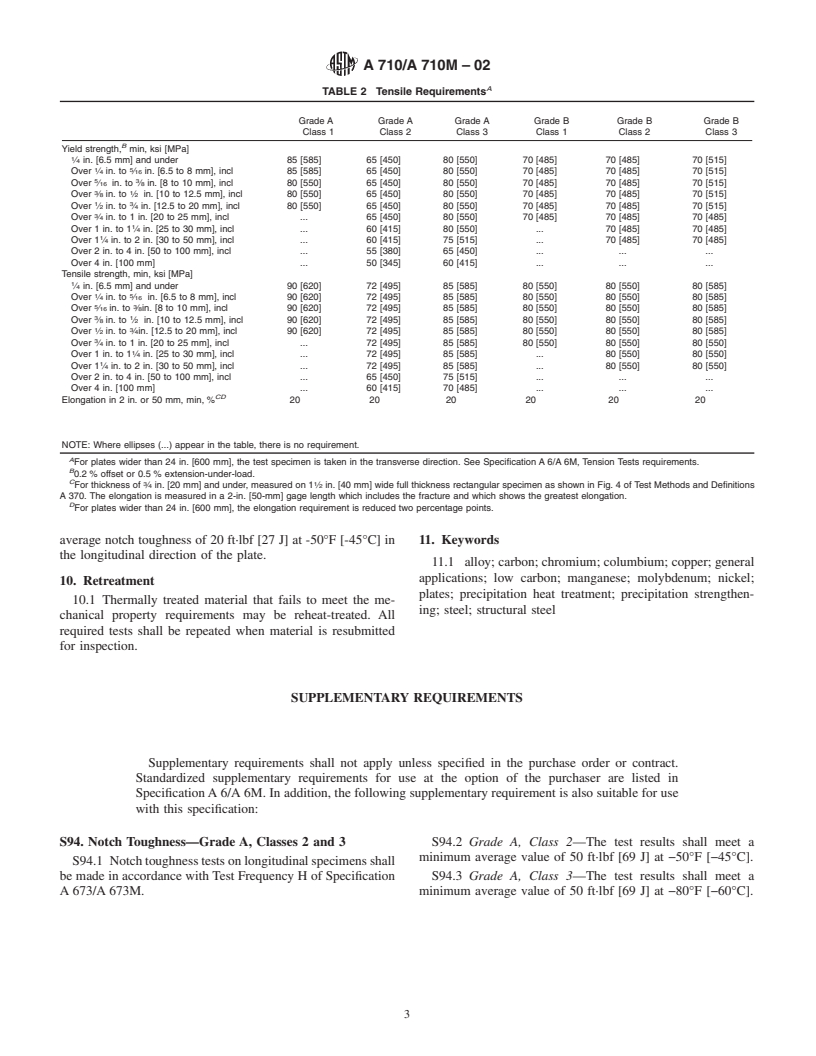
1.3 Grade A provides minimum yield strength levels ranging from 50 to 85 ksi [345 to 585 MPa], depending on thickness and condition.
1.4 Grade A, Class 1, plates are limited to a maximum thickness of 3/4 in. [20 mm]. The maximum thickness of Grade A, Classes 2 and 3, is limited only by the capacity of the composition to meet the specified mechanical property requirements; however, current practice normally limits the maximum thickness to 8 in. [200 mm].
1.5 Mandatory notch toughness requirements are specified for Grade A, Class 1.
1.6 Grade B provides minimum yield strength levels ranging from 70 to 75 ksi [480 to 515 MPa], depending on thickness and condition.
1.7 Grade B plates are limited to a maximum thickness of 2 in. [50 mm].
1.8 Mandatory notch toughness requirements are specified for the three classes of Grade B.
1.9 When the steel is to be welded, it is presupposed that a welding procedure suitable for the grade of steel and intended use or service will be utilized. See Appendix X3 of Specification A 6/A 6M for information on weldability.
1.10 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: A 710/A 710M – 02
Standard Specification for
Precipitation–Strengthened Low-Carbon Nickel-Copper-
Chromium-Molybdenum-Columbium Alloy Structural Steel
1
Plates
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationA 710/A 710M;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyear
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope * 1.7 Grade B plates are limited to a maximum thickness of 2
in. [50 mm].
1.1 This specification covers low-carbon precipitation—
1.8 Mandatory notch toughness requirements are specified
strengthened nickel - copper - chromium - molybdenum -
for the three classes of Grade B.
columbium alloy steel plates for general applications. The
1.9 When the steel is to be welded, it is presupposed that a
alloys in this specification are strengthened by precipitation in
welding procedure suitable for the grade of steel and intended
various temperature ranges. Precipitation strengthening can
use or service will be utilized. See Appendix X3 of Specifica-
occur upon air cooling after hot rolling, during normalizing,
tion A 6/A 6M for information on weldability.
and by another heat treatment. These grades are not intended
1.10 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units
for use in applications above 900°F [540°C].
are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the
1.2 Two grades, each with three classes, are provided as
SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each
follows:
system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must
Grade and Class Condition
beusedindependentlyoftheother.Combiningvaluesfromthe
Grade A, Class 1 as-rolled and precipitation heat treated
Grade A, Class 2 normalized and precipitation heat treated
two systems may result in nonconformance with the specifi-
Grade A, Class 3 quenched and precipitation heat treated
cation.
Grade B, Class 1 as-rolled
Grade B, Class 2 normalized
2. Referenced Documents
Grade B, Class 3 normalized and precipitation heat treated
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.3 Grade A provides minimum yield strength levels rang- A 6/A 6M Specification for General Requirements for
ing from 50 to 85 ksi [345 to 585 MPa], depending on Rolled Structural Steel Bars, Plates, Shapes, and Sheet
2
thickness and condition. Piling
1.4 Grade A, Class 1, plates are limited to a maximum A 673/A 673M Specification for Sampling Procedure for
2
3
thickness of ⁄4 in. [20 mm]. The maximum thickness of Grade Impact Testing of Structural Steel
A, Classes 2 and 3, is limited only by the capacity of the
3. Terminology
compositiontomeetthespecifiedmechanicalpropertyrequire-
ments;however,currentpracticenormallylimitsthemaximum 3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
thickness to 8 in. [200 mm]. 3.1.1 precipitation heat treatment—a sub-critical tempera-
1.5 Mandatory notch toughness requirements are specified ture thermal treatment performed to cause precipitation of
for Grade A, Class 1. submicroscopical constituents, etc., so as to result in enhance-
1.6 Grade B provides minimum yield strength levels rang- ment of some desirable property.
ing from 70 to 75 ksi [480 to 515 MPa], depending on 3.1.2 precipitation strengthening—the precipitation of sub-
thickness and condition. microscopic and/or microscopic constituents of an alloy at
various temperatures, which results in the alteration of certain
properties.
3.1.3 soak—to hold at temperature after the material has
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM CommitteeA01 on Steel,
attained the temperature throughout.
Stainless Steel, and RelatedAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.02 on Structural Steel for Bridges, Buildings, Rolling Stock, and Ships.
Current edition approved Sept. 10, 2002. Published November 2002. Originally
2
published as A 710 – 74. Last previous edition A 710/A 710M – 01. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.04.
*ASummary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A 710/A 710M – 02
4. General Requirements for Delivery 7. Chemical Composition
4.1 Material furnished under this specification shall con-
7.1 The heat analysis shall conform to the requirements as
form to the requirements of the current edition of Specification
to chemical composition prescribed in Table 1.
A 6/A 6M, for the ordered material, unless a conflict exists in
7.2 The steel shall conform on product analysis to the
which case this specification shall prevail.
requ
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.