ASTM D2680-95a
(Specification)Standard Specification for Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS) and Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Composite Sewer Piping
Standard Specification for Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS) and Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Composite Sewer Piping
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers thermoplastic composite pipe, fittings and a joining system for use in gravity flow, nonpressure sanitary sewer, and storm drain installations. The pipe and fittings are made of ABS or PVC plastic material. Recommended installation practices are referenced in Appendix XI.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for information only.
1.3 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test method portion, Section 10, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precautionary information is given in 7.2.4.
General Information
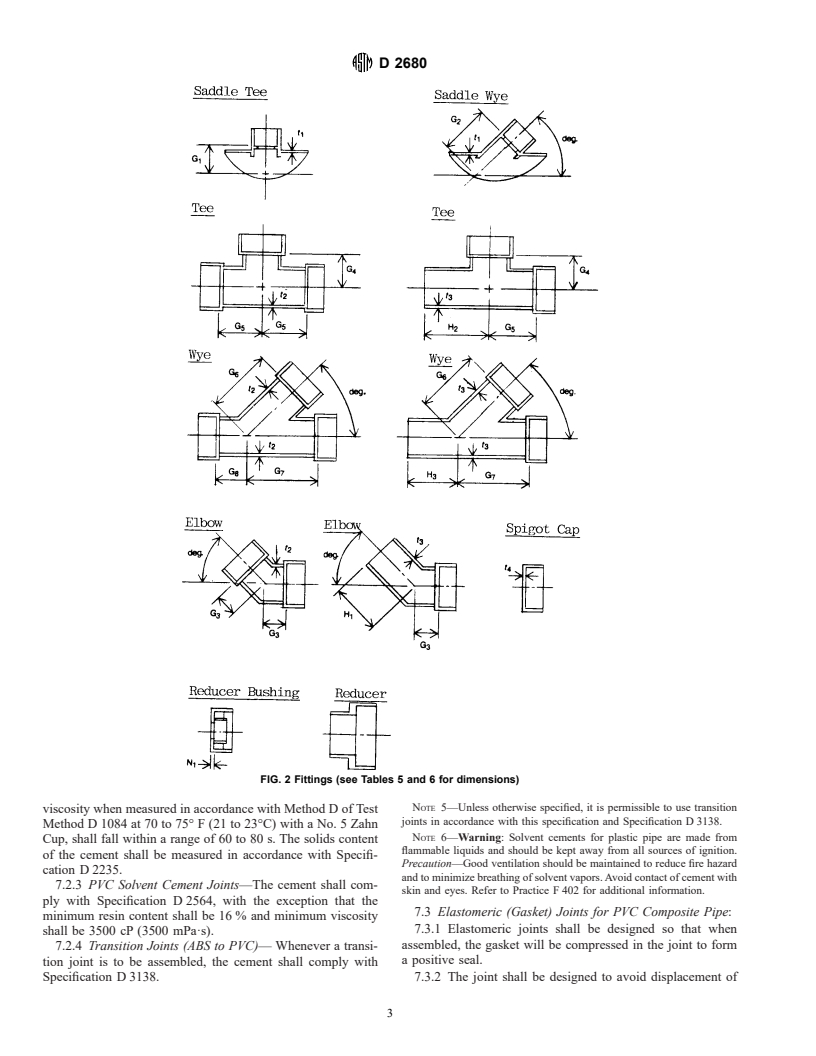
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D 2680 – 95a An American National Standard
Standard Specification for
Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS) and Poly(Vinyl
Chloride) (PVC) Composite Sewer Piping
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 2680; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope plastic Pipe for Sewers and Other Gravity–Flow Applica-
tions
1.1 This specification covers thermoplastic composite pipe,
D 2412 Test Method for Determination of External Loading
fittings and a joining system for use in gravity flow, nonpres-
Characteristics of Plastic Pipe by Parallel-Plate Loading
sure sanitary sewer, and storm drain installations. The pipe and
D 2564 Specification for Solvent Cements for Poly(Vinyl
fittings are made of ABS or PVC plastic material. Recom-
Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Piping Systems
mended installation practices are referenced in Appendix XI.
D 3138 Specification for Solvent Cements for Transition
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
Joints Between Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS)
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided
and Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Non-Pressure Piping
for information only.
Components
1.3 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
D 3212 Specification for Joints for Drain and Sewer Plastic
test method portion, Section 10, of this specification: This
Pipes Using Flexible Elastomeric Seals
standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems,
D 3965 Specification for Rigid Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
Styrene (ABS) Compounds for Pipe and Fittings
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health
D 4396 Specification for Rigid Poly(Vinyl Chloride)(PVC)
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita-
and Related Plastic Compounds for Nonpressure Piping
tions prior to use. Specific precautionary information is given
Products
in Note 6.
F 402 Practice for Safe Handling of Solvent Cements and
2. Referenced Documents
Primers Used for Joining Thermoplastic Pipe and Fittings
F 412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
2.1 ASTM Standards:
F 477 Specification for Elastomeric Seals (Gaskets) for
D 618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics and Electrical
Joining Plastic Pipe
Insulating Materials for Testing
F 913 Specification for Thermoplastic Elastomeric Seals
D 1084 Test Methods for Viscosity of Adhesives
(Gaskets) for Joining Plastic Pipe
D 1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to
2.2 Federal Standard:
Plastics
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies)
D 1784 Specification for Rigid Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC)
2.3 Military Standard:
Compounds and Chlorinated Poly(Vinyl Chloride)
MIL-STD-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
(CPVC) Compounds
D 2122 Test Method for Determining Dimensions of Ther-
3. Terminology
moplastic Pipe and Fittings
3.1 Definitions:
D 2152 Test Method for Degree of Fusion of Extruded
3.1.1 General—Definitions are in accordance with Termi-
Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Pipe and Molded Fittings by
nology F 412 and abbreviations are in accordance with Termi-
Acetone Immersion
nology D 1600, unless otherwise specified. The abbreviation
D 2235 Specification for Solvent Cement for Acrylonitrile-
for acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene is ABS and the abbreviation
Butadiene-Styrene (ABS) Plastic Pipe and Fittings
for poly(vinyl chloride) is PVC.
D 2321 Practice for Underground Installation of Thermo-
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS)—plastics con-
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F-17 on Plastic
taining polymers or blends of polymers, or both, in which the
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.62 on Sewer.
minimum butadiene content is 6 %; the minimum acrylonitrile
Current edition approved Sept. 10, 1995. Published November 1995. Originally
published as D 2680 – 68 T. Last previous edition D 2680 – 95.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01.
3 5
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.06. Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, Bldg. 4 Section D, 700
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.04. Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, Attn: NPODS.
Copyright © ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D 2680
content is 15 %; the minimum styrene or substituted styrene 5.4 Gaskets—Elastomeric seals (gaskets) shall comply with
content, or both, is 15 %; and the maximum content of all other requirements described in Specifications F 477 and F 913.
monomers is not more than 5 %, plus lubricants, stabilizers,
NOTE 1—Gasket joints manufactured for PVC composite pipe only.
and colorants.
5.5 Lubricants—The lubricant used for the assembly of
3.2.2 poly (vinyl chloride) (PVC)—plastic compounds con-
gasket joints shall have no detrimental effect on the gasket or
taining poly(vinyl chloride) homopolymer, and such additives
on the pipe.
as stabilizers, lubricants, processing aids, impact improvers,
and colorants as needed to provide the required processing and
6. Performance Requirements
toughness characteristics.
6.1 Pipe Stiffness—Pipe tested in accordance with 10.2 shall
have a minimum pipe stiffness of 200 lb/in./in. (1380 kPa) at
4. Classification
5% deflection.
4.1 Pipe produced in accordance with this specification shall
6.2 Pipe Deflection—Pipe tested in accordance with 10.2
be classified as ABS composite pipe or PVC composite pipe
shall deflect a minimum of 7.5 % without rupture of inner or
based on plastic materials used in manufacture.
outer wall.
5. Materials and Manufacture
NOTE 2—The purpose of the quality control tests in 6.1 and 6.2 is to
5.1 ABS composite pipe or PVC composite pipe shall furnish test results for a consumer only upon his request at the time of
order and prior to shipment from the point of manufacture.
consist of two concentric thermoplastic tubes integrally braced
across the annulus. The resultant annular space is filled to
6.3 Acid Conditioning—Pipe tested in accordance with 10.3
provide continuous support between the inner and outer tubes.
shall meet the requirements of 6.1 and 6.2.
5.2 Compounds—The ABS and PVC composite pipe and
NOTE 3—This test is intended only for use as a qualification test, not for
fittings shall be produced from the following compounds:
use as a simulated service test nor a quality control test.
5.2.1 ABS—The pipe shall be made from a rigid ABS plastic
6.4 Joint Tightness:
and shall meet or exceed the requirements of Specification
6.4.1 Solvent Cement Joints—Pipe and fittings attached to
D 3965 for a minimum cell classification of 1-0-2-2-3. The
the pipe shall show no signs of leakage when tested in
fittings shall be made from ABS plastic and shall meet or
accordance with 10.4.1 (See Note 3).
exceed the requirements of Specification D 3965 for cell
6.4.2 Gasket Joints for PVC Composite Pipe—Joints shall
classifications of 1-0-2-2-3 or 4-2-2-2-2. Clean rework ABS,
show no signs of leakage when tested in accordance with
generated from the manufacturer’s own pipe extrusion and
10.4.2 (See Note 3).
fittings may be used by the same manufacturer, provided that
6.5 Extrusion Quality—When tested in accordance with
the pipe and fittings produced meet all the requirements of this
10.5, PVC extruded pipe tubes shall not flake or disintegrate.
specification.
5.2.2 PVC—The thermoplastic material shall be a rigid
NOTE 4—This test is intended for use as a quality control test, not for
PVC plastic and shall meet or exceed the requirements of
use as a simulated service test.
Specification D 1784, for a minimum cell classification of
7. Other Requirements
12454B or 12454C or of Specification D 4396, for a minimum
cell classification of 11432. Homopolymer PVC compounds 7.1 Joints and Fittings as shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2, shall
that have higher cell classifications, because one or more be molded or fabricated from materials described in Section 5.
properties are superior to those of the specified compounds, are Joints and fittings may be factory-attached to the pipe or
also acceptable. Clean rework PVC, generated from the manu- furnished loose, at the option of the purchaser.
facturer’s own pipe and fittings production may be used by the 7.2 Solvent Cement Joints:
same manufacturer provided that the pipe and fittings produced 7.2.1 Solvent Cement Joint—In the solvent cement joint, the
meet all the requirements of this specification. pipe spigot wedges into the tapered socket and the surfaces
5.3 The other component shall be portland cement-perlite fuse together.
concrete or other inert filler material exhibiting the same 7.2.2 ABS Solvent Cement Joints—Primer for priming sol-
degree of performance, that essentially fills the truss annulus to vent cemented joints shall be MEK (methyl ethyl ketone) and
form a composite pipe that meets the requirements of this the cement shall be MEK containing a minimum of 20 % by
specification. weight of dissolved ABS as described in 5.2.1. The cement
FIG. 1 Assembly of Joints
D 2680
FIG. 2 Fittings (see Tables 5 and 6 for dimensions)
NOTE 5—Unless otherwise specified, it is permissible to use transition
viscosity when measured in accordance with Method D of Test
joints in accordance with this specification and Specification D 3138.
Method D 1084 at 70 to 75° F (21 to 23°C) with a No. 5 Zahn
NOTE 6—Warning: Solvent cements for plastic pipe are made from
Cup, shall fall within a range of 60 to 80 s. The solids content
flammable liquids and should be kept away from all sources of ignition.
of the cement shall be measured in accordance with Specifi-
Precaution—Good ventilation should be maintained to reduce fire hazard
cation D 2235.
and to minimize breathing of solvent vapors. Avoid contact of cement with
7.2.3 PVC Solvent Cement Joints—The cement shall com-
skin and eyes. Refer to Practice F 402 for additional information.
ply with Specification D 2564, with the exception that the
7.3 Elastomeric (Gasket) Joints for PVC Composite Pipe:
minimum resin content shall be 16 % and minimum viscosity
7.3.1 Elastomeric joints shall be designed so that when
shall be 3500 cP (3500 mPa·s).
assembled, the gasket will be compressed in the joint to form
7.2.4 Transition Joints (ABS to PVC)— Whenever a transi-
a positive seal.
tion joint is to be assembled, the cement shall comply with
Specification D 3138. 7.3.2 The joint shall be designed to avoid displacement of
D 2680
the gasket when assembled in accordance with the manufac- fittings shall be homogeneous throughout and free from visible
turers’ recommendation. cracks, holes, foreign inclusions, and other injurious defects.
7.3.3 The assembly of joints shall be in accordance with the The pipe, joints, and fittings shall be as uniform as commer-
manufacturers’ recommendation. cially practicable in other physical properties.Table 6
8. Dimensions
10. Test Methods
8.1 Diameters and Thickness—The pipe shall conform to
10.1 Conditioning:
the dimensions and tolerances shown in Table 1 for ABS
10.1.1 Referee Testing—When conditioning is required for
composite pipe, and Table 2 for PVC composite pipe, when
referee tests, condition the specimens in accordance with
measured in accordance with 10.6.1 and 10.6.2.
Procedure A of Methods D 618 at 73.4 6 3.6°F (23 6 2°C) and
8.2 Laying Length—Pipe shall be furnished in standard
50 6 5 % relative humidity for not less than 40 h prior to test.
12 ⁄2 ft (3.82 m) lengths with a tolerance of −1 in. (−25 mm)
Conduct tests under the same conditions of temperature and
when measured in accordance 10.6.1. There is no limit for plus
humidity, unless otherwise specified.
variation. Other lengths may be provided, if agreed upon by the
10.1.2 Quality Control Testing—Condition specimens for a
purchaser and the seller.
minimum of4hinairor1hin water at 73.4 6 3°F (23 6 2°C).
8.3 Straightness—Pipe intended to be straight shall have a
Test the specimens at 73.4 6 3°F without regard to relative
maximum deviation from straightness of ⁄16in./ft (4.85 mm/m)
humidity.
of length, when measured in accordance with 10.6.1.
10.1.3 Test Conditions—Conduct tests in the Standard
8.4 End Squareness—Pipe ends shall be cut square to the
Laboratory Atmosphere of 73.4 6 3.6°F (23 6 2°C) and 50 6
longitudinal axis as provided in Table 3, when measured in
5 % relative humidity, unless otherwise specified in the test
accordance with 10.6.3.
methods or in this specification. In cases of disagreement, the
8.5 Joint Couplings, shall conform to the dimensions shown
tolerances shall be 6 1.8°F (6 1°C) and6 2 % relative
in Table 4, when measured in accordance with 10.6.1.
humidity.
8.6 Fittings:
10.2 Stiffness and Deflection:
8.6.1 Molded Fittings—The wall thickness of the water way
10.2.1 Test three specimens in accordance with Test Method
shall be no less than the respective minimum thickness listed in
D 2412. Determine the pipe stiffness at 5 % deflection and
Table 5. The socket dimensions and respective wall thickness
verify that pipe will deflect to 7.5 % without wall rupture.
shall conform to Table 4. The dimensions and wall thicknesses
10.2.2 Calculate the percent vertical deflection as follows:
shall be determined in accordance with 10.6.1.
Vertical deflection,% 5 ~D y / Nominal ID! 3 100 (1)
8.6.2 Fabricated Fittings—Fabricated fittings shall be con-
sidered satisfactory if made from pipe and molded fittings
where:
meeting the requirements of this specification.
D y 5 vertical deflection of the inside diameter as mea-
8.6.3 The spur (lateral) socket shall be suitable for attaching
sured by the plate travel of the apparatus. Both ID
the respective ABS or PVC solid wall pipe or adapters shall be
and Dy must be in the same units.
furnished for attaching other types of pipes.
10.2.3 Calculate the pipe stiffness at 5 % deflection as
9. Workmanship follows:
9.1 The inner and outer surfaces of the pipe, joints, and Pipe stiffness ~PS! 5 F/D y (2)
TABLE 1 Pipe Dimensions for ABS Composite Pipe
Average Concentric
Outside Diameter Average Inside Diameter
Nominal
Tube Thickness
Size, in.
Average Tolerance max min max Inner, min Outer, min
Inches
8 9.41 +0.04 9.51 7.75 7.90 0.060 0.035
−0.03
10 11.75 +0.04 11.87 9.75 9.88 0.068 0.038
−0.04
12 14.07 +0.06 14.22 11.75 11.83 0.079 0.048
−0.05
15 17.
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.