ASTM D6021-22
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Measurement of Total Hydrogen Sulfide in Residual Fuels by Multiple Headspace Extraction and Sulfur Specific Detection
Standard Test Method for Measurement of Total Hydrogen Sulfide in Residual Fuels by Multiple Headspace Extraction and Sulfur Specific Detection
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Residual fuel oils can contain H2S in the liquid phase, and this can result in hazardous vapor phase levels of H2S in storage tank headspaces. The vapor phase levels can vary significantly according to the headspace volume, fuel temperature, and agitation. Measurement of H2S levels in the liquid phase provides a useful indication of the residual fuel oil’s propensity to form high vapor phase levels, and lower levels in the residual fuel oil will directly reduce risk of H2S exposure. It is critical, however, that anyone involved in handling fuel oil, such as vessel owners and operators, continue to maintain appropriate safety practices designed to protect the crew, tank farm operators and others who can be exposed to H2S.
5.1.1 The measurement of H2S in the liquid phase is appropriate for product quality control, while the measurement of H2S in the vapor phase is appropriate for health and safety purposes.
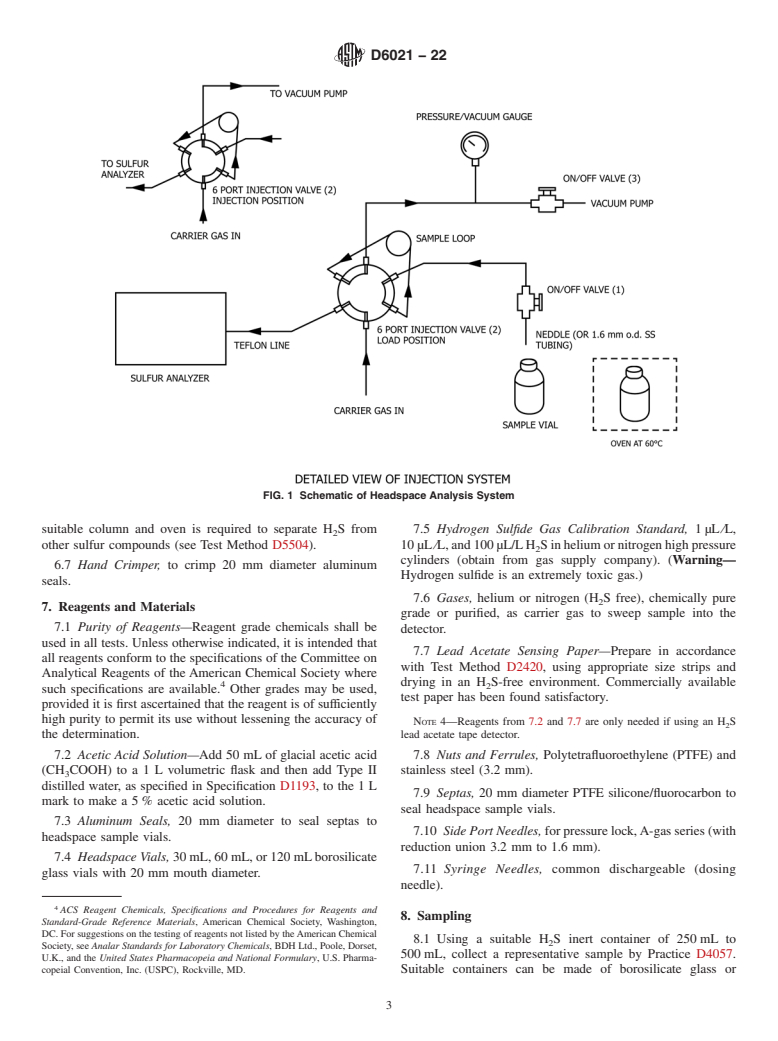
5.2 This test method was developed so refiners, fuel terminal operators and independent testing laboratory personnel can analytically measure the amount of H2S in the liquid phase of residual fuel oils.
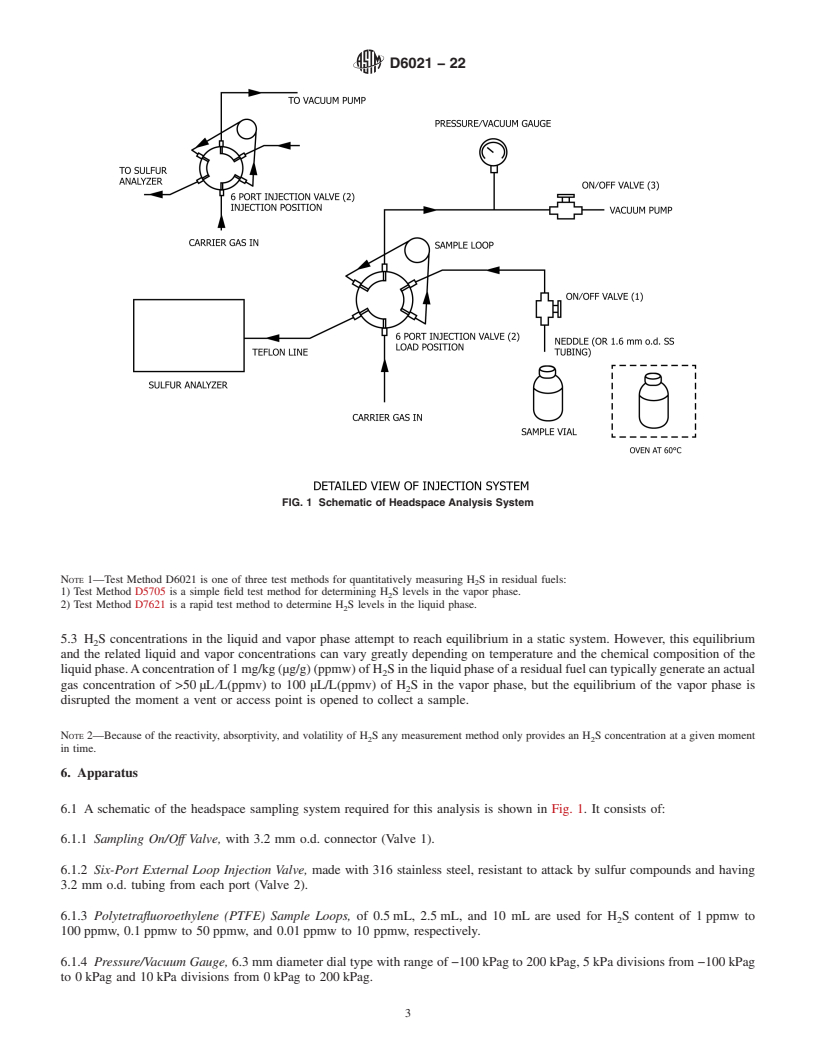
Note 1: Test Method D6021 is one of three test methods for quantitatively measuring H2S in residual fuels:
1) Test Method D5705 is a simple field test method for determining H2S levels in the vapor phase.
2) Test Method D7621 is a rapid test method to determine H2S levels in the liquid phase.
5.3 H2S concentrations in the liquid and vapor phase attempt to reach equilibrium in a static system. However, this equilibrium and the related liquid and vapor concentrations can vary greatly depending on temperature and the chemical composition of the liquid phase. A concentration of 1 mg/kg (μg/g) (ppmw) of H2S in the liquid phase of a residual fuel can typically generate an actual gas concentration of >50 μL/L(ppmv) to 100 μL/L(ppmv) of H2S in the vapor phase, but the equilibrium of the vapor phase is disrupted the moment a vent or access point is opened ...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a method suitable for measuring the total amount of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) in heavy distillates, heavy distillate/residual fuel blends, or residual fuels as defined in Specification D396 Grade 4, 5 (Light), 5 (Heavy), and 6, when the H2S concentration in the fuel is in the 0.01 μg/g (ppmw) to 100 μg/g (ppmw) range.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific warning statements, see 7.5, 8.2, 9.2, 10.1.4, and 11.1.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:D6021 −22
Standard Test Method for
Measurement of Total Hydrogen Sulfide in Residual Fuels
by Multiple Headspace Extraction and Sulfur Specific
1
Detection
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6021; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* D3609Practice for Calibration Techniques Using Perme-
ation Tubes
1.1 Thistestmethodcoversamethodsuitableformeasuring
D4057Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
thetotalamountofhydrogensulfide(H S)inheavydistillates,
2
Petroleum Products
heavydistillate/residualfuelblends,orresidualfuelsasdefined
D4084Test Method for Analysis of Hydrogen Sulfide in
in Specification D396 Grade 4, 5 (Light), 5 (Heavy), and 6,
Gaseous Fuels (Lead Acetate Reaction Rate Method)
when the H S concentration in the fuel is in the 0.01µg⁄g
2
D4175Terminology Relating to Petroleum Products, Liquid
(ppmw) to100µg⁄g (ppmw) range.
Fuels, and Lubricants
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
D4323TestMethodforHydrogenSulfideintheAtmosphere
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
by Rate of Change of Reflectance
standard.
D5504TestMethodforDeterminationofSulfurCompounds
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the in Natural Gas and Gaseous Fuels by Gas Chromatogra-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
phy and Chemiluminescence
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- D5705Test Method for Measurement of Hydrogen Sulfide
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
in the Vapor Phase Above Residual Fuel Oils
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. D7621Test Method for Determination of Hydrogen Sulfide
For specific warning statements, see 7.5, 8.2, 9.2, 10.1.4, and
in Fuel Oils by Rapid Liquid Phase Extraction
11.1.
3. Terminology
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard- 3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom- to Terminology D4175.
3.1.2 heavy distillate, n—a fuel produced from the distilla-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee. tion of crude oil which has a kinematic viscosity at 40°C
2 2
between 5.5mm /s and 24.0 mm /s, inclusive.
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.3 heavy distillate/residual fuel blend, n—a blend of
2
heavydistillateandresidualfueloilhavingaviscosityat40°C
2.1 ASTM Standards:
2 2
between 5.5mm /s and 24.0 mm /s, inclusive.
D396Specification for Fuel Oils
D1193Specification for Reagent Water
3.1.4 multiple headspace extraction, n—a technique to de-
D2420Test Method for Hydrogen Sulfide in Liquefied
termine the total concentration of a gas trapped in a liquid by
Petroleum (LP) Gases (Lead Acetate Method)
analysis of successive gas extractions from the vapor space of
a closed vessel containing a known amount of the sample.
3.1.5 residual fuel oil, n—any liquid or liquefiable petro-
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
leum product having a kinematic viscosity at 100°C between
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
2 2
5.0mm /sand50.0mm /s,inclusive,burnedforthegeneration
Subcommittee D02.14 on Stability, Cleanliness and Compatibility of Liquid Fuels.
ofheatinafurnaceorfireboxorforthegenerationofpowerin
Current edition approved April 1, 2022. Published May 2022. Originally
approved in 1996. Last previous edition approved in 2017 as D6021–12 (2017).
an engine.
DOI: 10.1520/D6021-22.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or 4. Summary of Test Method
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
4.1 A representative sample of residual fuel oil is obtained
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. in sufficient quantity to completely fill the sample container.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6021−22
NOTE 1—Test Method D6021 is one of three test methods for
The sample is taken to the laborator
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D6021 − 12 (Reapproved 2017) D6021 − 22
Standard Test Method for
Measurement of Total Hydrogen Sulfide in Residual Fuels
by Multiple Headspace Extraction and Sulfur Specific
1
Detection
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6021; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This test method covers a method suitable for measuring the total amount of hydrogen sulfide (H S) in heavy distillates, heavy
2
distillate/residual fuel blends, or residual fuels as defined in Specification D396 Grade 4, 5 (Light), 5 (Heavy), and 6, when the
H S concentration in the fuel is in the 0.01 μg ⁄g (ppmw) to 100 μg ⁄g (ppmw) range.
2
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific warning statements, see 7.5, 8.2, 9.2, 10.1.4, and 11.1.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D396 Specification for Fuel Oils
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D2420 Test Method for Hydrogen Sulfide in Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases (Lead Acetate Method)
D3609 Practice for Calibration Techniques Using Permeation Tubes
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products
D4084 Test Method for Analysis of Hydrogen Sulfide in Gaseous Fuels (Lead Acetate Reaction Rate Method)
D4175 Terminology Relating to Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants
D4323 Test Method for Hydrogen Sulfide in the Atmosphere by Rate of Change of Reflectance
D5504 Test Method for Determination of Sulfur Compounds in Natural Gas and Gaseous Fuels by Gas Chromatography and
Chemiluminescence
D5705 Test Method for Measurement of Hydrogen Sulfide in the Vapor Phase Above Residual Fuel Oils
D7621 Test Method for Determination of Hydrogen Sulfide in Fuel Oils by Rapid Liquid Phase Extraction
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.14 on on Stability, Cleanliness and Compatibility of Liquid Fuels.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2017April 1, 2022. Published November 2017May 2022. Originally approved in 1996. Last previous edition approved in 20122017 as
D6021D6021 – 12 (2017).–12. DOI: 10.1520/D6021-12R17.10.1520/D6021-22.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6021 − 22
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology D4175.
3.1.2 heavy distillate, n—a fuel produced from the distillation of crude oil which has a kinematic viscosity at 40 °C between
2 2
5.5 mm /s and 24.0 mm /s, inclusive.
3.1.3 heavy distillate/residual fuel blend, n—a blend of heavy distillate and residual fuel oil having a viscosity at 40 °C between
2 2
5.5 mm /s and 24.0 mm /s, inclusive.
3.1.4 multiple headspace extraction, n—a technique to determine the total concentration of a gas trapped in a liquid by analysis
of successive gas extractions from the vapor space of a closed vessel containing a known amount of the sample.
2
3.1.5 residual fuel oil, n—any liquid or liquefiable petroleum product having a kinematic viscosity at 100 °C between 5.0 mm /s
2
and 50.0 mm /s, inclusive, burned for the generation of heat in a furnace o
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.