ASTM C964-07
(Guide)Standard Guide for Lock-Strip Gasket Glazing
Standard Guide for Lock-Strip Gasket Glazing
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This guide provides information and guidelines for the design of lock-strip gasket glazing systems. For related standards, see Specifications C 542, C 716, and C 963.
SCOPE
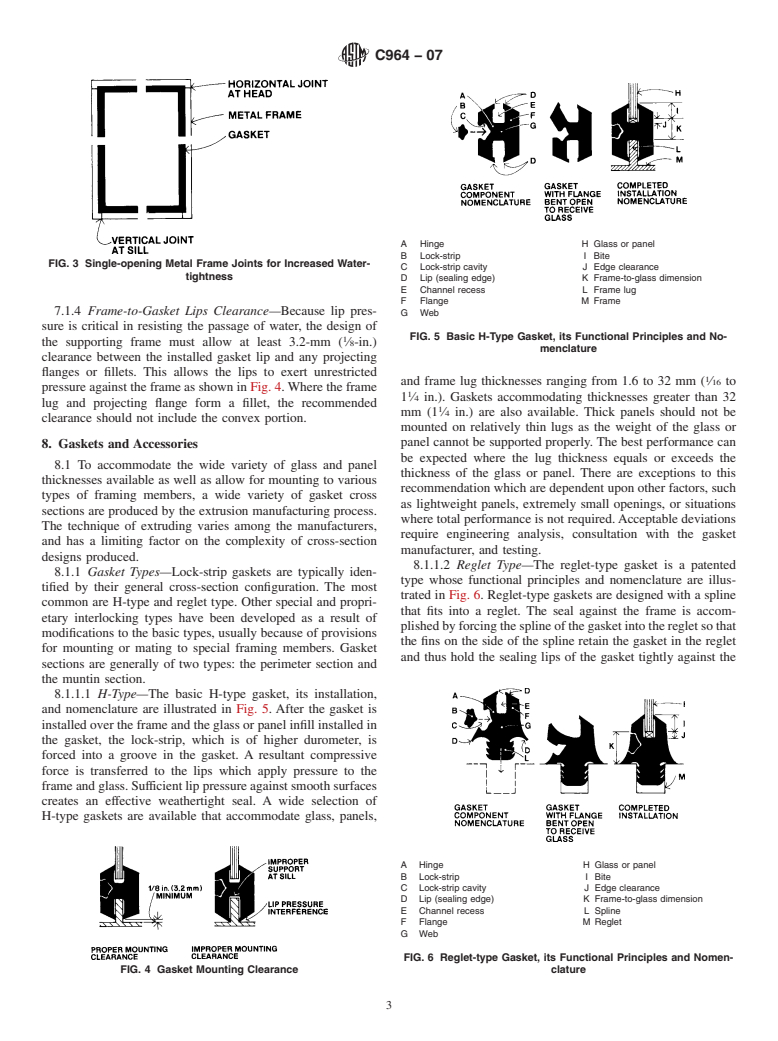
1.1 This guide covers the use of lock-strip gaskets in compliance with Specification C 542 in walls of buildings not over 15 from a vertical plane. The prime performance considerations are weathertightness against air and water infiltration, and structural integrity under wind loads. Included are terminology, design considerations, and fabrication tolerances when using lock-strip gaskets in glazing applications.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The inch-pound units in parentheses are for information only.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C964 − 07
StandardGuide for
1
Lock-Strip Gasket Glazing
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C964; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope Windows, Doors, Skylights and CurtainWalls by Uniform
Static Air Pressure Difference
1.1 This guide covers the use of lock-strip gaskets in
E331 Test Method for Water Penetration of Exterior
compliance with Specification C542 in walls of buildings not
Windows, Skylights, Doors, and Curtain Walls by Uni-
over 15° from a vertical plane. The prime performance
form Static Air Pressure Difference
considerations are weathertightness against air and water
infiltration, and structural integrity under wind loads. Included
3. Significance and Use
are terminology, design considerations, and fabrication toler-
3.1 This guide provides information and guidelines for the
ances when using lock-strip gaskets in glazing applications.
design of lock-strip gasket glazing systems. For related
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
standards, see Specifications C542, C716, and C963.
standard. The inch-pound units in parentheses are for informa-
tion only.
4. Comparison to Other Standards
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.1 Thecommitteewithjurisdictionoverthisstandardisnot
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
aware of any comparable standards published by other orga-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
nizations.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5. General
2. Referenced Documents
2
5.1 Structural integrity and watertightness of a gasket glaz-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
ing system is dependent on interaction of the several compo-
C542 Specification for Lock-Strip Gaskets
nents involved. These systems should be carefully designed
C716 Specification for Installing Lock-Strip Gaskets and
and built.
Infill Glazing Materials
C864 Specification for Dense Elastomeric Compression Seal
6. Components
Gaskets, Setting Blocks, and Spacers
6.1 The major components of lock-strip gasket glazing and
C963 Specification for Packaging, Identification, Shipment,
paneling systems are:
and Storage of Lock-Strip Gaskets
6.1.1 The supporting frame of metal, concrete, or other
C1036 Specification for Flat Glass
structural building materials,
E283 Test Method for Determining Rate of Air Leakage
6.1.2 Lock-strip gasket, serving as an elastomeric mechani-
Through Exterior Windows, Curtain Walls, and Doors
cal seal and as a retainer for panel or glass, and
Under Specified Pressure Differences Across the Speci-
6.1.3 Glass or panel infill.
men
6.1.4 The design of these components and their accessories
E330 Test Method for Structural Performance of Exterior
are interrelated and the total system must be compatible.
7. Supporting Frames
1
ThisguideisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeC24onBuildingSeals
and Sealants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C24.73 on Compres-
7.1 Supporting frames are made of many materials, of
sion Seal and Lock Strip Gaskets.
which the more common are aluminum, steel, and concrete.
CurrenteditionapprovedJune1,2007.PublishedJuly2007.Originallyapproved
´1
7.1.1 Metal—Die marks, ridges, offsets, and scratches in
in 1981. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as C964 – 88 (2002) . DOI:
10.1520/C0964-07.
metal frames in contact with the gasket lips that could cause
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
leakage should be avoided. Metal in contact with any part of
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
the gasket should have sharp edges and burrs removed to avoid
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. the possibility of damage to the gaskets that could result in
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C964 − 07
structural failure through tear propagation. Weathering steel cornerbuttjointsareeliminatedandthegasketlipsmakedirect
frames used in gasket installations should be coated to prevent contact with the concrete frame. With this concept it is
corrosion on the surfaces covered by the gasket to a line not essential to have a continuous smooth surface free of voids or
1
less than 3.2 mm ( ⁄8 in.) beyond the lip edge when inst
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.