ASTM E1289-97(2003)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Reference Specimen for Sound Transmission Loss
Standard Specification for Reference Specimen for Sound Transmission Loss
SCOPE
1.1 This specification describes the construction and installation of a standard reference specimen for quality control of laboratory sound transmission loss measurements using Test Method E90. Test Method E90 allows a significant latitude in the construction and operation of a test facility. It is the objective of standard measurement procedures that the property of a reference specimen being measured have the same value in all facilities.
1.2 This specification addresses the need for a reference specimen for sound transmission loss facilities where measurements are made according to Test Method E90. It describes in detail how the specimen is to be constructed and installed in a test opening.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values in parentheses are provided for information only.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E 1289 – 97 (Reapproved 2003)
Standard Specification for
Reference Specimen for Sound Transmission Loss
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E 1289; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
Duct tape, 50 mm (2 in.) wide.
Drywall screws, Type W—length, 31.8 mm (1.25 in.).
1.1 This specification describes the construction and instal-
Bolts (10–24 by 1 in.)—25 mm long with appropriate nuts and washers.
lation of a standard reference specimen for quality control of
Fasteners, to hold wood frame to the perimeter of the test opening.
Caulking, non-hardening.
laboratory sound transmission loss measurements using Test
Wood framing, approximately 40 mm by 90 mm (2 by 4 in. nominal) in width
Method E 90. Test Method E 90 allows a significant latitude in
and thickness.
the construction and operation of a test facility. It is the
NOTE 1—The quantity and length of each component needed depends
objective of standard measurement procedures that the prop-
on the size of the laboratory test opening.
erty of a reference specimen being measured have the same
4.1.2 The weight of each component of the reference
value in all facilities.
specimen and the assembled specimen shall be measured and
1.2 This specification addresses the need for a reference
kept on record. In addition, the thickness of each of the steel
specimen for sound transmission loss facilities where measure-
panels shall be measured in six locations. (See Appendix X1.)
ments are made according to Test Method E 90. It describes in
4.2 Assembly:
detail how the specimen is to be constructed and installed in a
4.2.1 Sheets—The 1200-mm (4-ft nominal)-wide rectangu-
test opening.
lar galvanized sheets shall be 24 gauge, 0.62 mm (0.024 in.)
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
thick. The weight of the sheets shall be 5.1 6 0.7 kg/m (1.05
standard. The values in parentheses are provided for informa-
6 0.15 lb/ft ). The length of each sheet shall be a few
tion only.
millimeters less than the height of the laboratory test opening.
2. Referenced Documents
The total width of all the sheets shall be a few millimeters less
than the width of the test opening. This may require that one
2.1 ASTM Standards:
sheet be cut lengthwise. The intent is that when installed, the
C 634 Terminology Relating to Environmental Acoustics
panels fill the test opening completely.
E 90 Test Method for Laboratory Measurement of
4.2.2 Frame—Cut steel right angles to size to form a frame
Airborne-Sound Transmission Loss of Building Partitions
for each sheet; the frame shall have the same outside dimen-
3. Terminology
sions as the sheets. Notch and weld the steel angles to form the
four corners of the frame as shown in Fig. 1. Alternatively,
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this speci-
miter the angles and weld similarly. Smooth corners after
fication, see Terminology C 634.
welding.
4. Construction of Reference Specimen
4.2.3 Panels—Construct a panel by riveting steel sheets to
the frames.
4.1 General:
4.2.3.1 Drill holes at 100 mm (4 in.) on-center around the
4.1.1 The reference specimen is composed of framed steel
perimeterofthesheetsfortheinstallationoftheblindrivets.To
panels. The required materials for fabrication and installation
assure proper alignment of the sheets with the frame, it is
are as follows:
recommended to drill a few holes and then install rivets to hold
Galvanized steel sheets—width, 1200 mm (4 ft); thickness, 0.62 mm (0.024 in.
or 24 gauge). Check weight for compliance with limits given in 4.2.1. the sheet in place. Once this is done, the remaining holes may
Steel right angles with 25-mm (1-in.) flanges—thickness, 3.2 mm (0.125 in.).
be drilled and the rivets installed. Position these holes to avoid
Blind rivets—diameter, 3 mm (0.125 in.).
conflict with the clearance holes described in 4.2.3.2.
4.2.3.2 Drill 4 mm (0.16 in.) diameter holes through hori-
zontal members of the frame and sheet as shown in Figs. 2 and
3. These are clearance holes for the drywall screws used to
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E33 on
EnvironmentalAcousticsandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeE33.03on
attach the panel to the wood plate (see 5.5).
Sound Transmission.
4.2.3.3 Drill 6.4 mm (0.25 in.) diameter holes at 400 mm
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2003. Published October 2003. Originally
(16 in.) on-center through the vertical flanges of the steel
approved in 1989. Last previous edition approved in 1997 as E 1289 – 97.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.06. frame. These are clearance holes for the bolts used to connect
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
E 1289 – 97 (2003)
FIG. 3 Construction Details of Steel Panels (not to scale)
caulking between the wood frame and the surface of the
laboratory opening. Use suitable fasteners no more than 300
mm (11.8 in.) on-center.
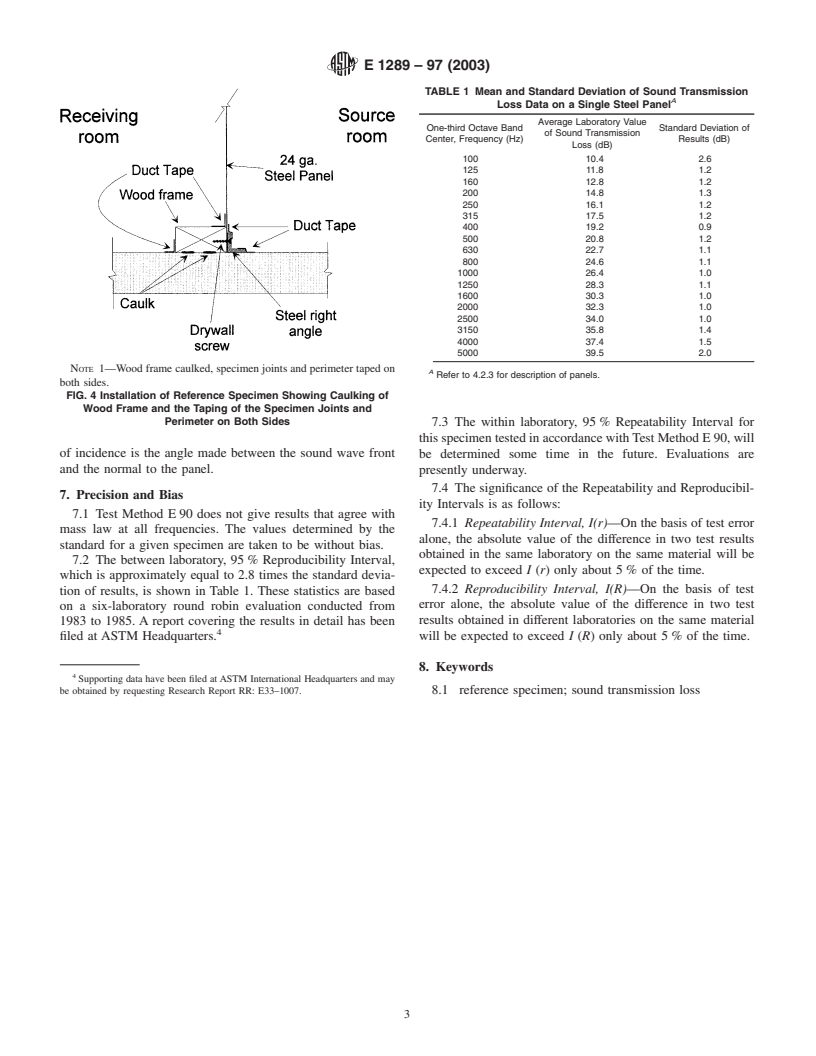
5.2 Place the reference specimen against the wood frame
with the flanges of the panel frames as shown in Fig. 4.
FIG. 1 Notching and Welding Corners of Steel Angles
5.3 Insert 25-mm (1-in.) long No. 10-24 bolts or equivalent
through the holes in adjacent vertical flanges drilled according
to 4.2.3.3. Washers may be used if desired. Tighten nut snugly
to close the gap between adjacent panels.
5.4 Fasten
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.