ASTM F3052-14
(Guide)Standard Guide for Conducting Small Boat Stability Test (Deadweight Survey and Air Inclining Experiment) to Determine Lightcraft Weight and Centers of Gravity of a Small Craft
Standard Guide for Conducting Small Boat Stability Test (Deadweight Survey and Air Inclining Experiment) to Determine Lightcraft Weight and Centers of Gravity of a Small Craft
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 From the lightcraft characteristics, calculations of the stability characteristics of the small craft for all load conditions can determine compliance to applicable stability criteria or provide mass properties information for other analyses or investigations. Accurate results from an air incline stability test may therefore determine future survival of the boat, the crew and compliment. If the small craft is not 100 % complete or there is fuel or other liquids in a tank that is supposed to be clean and dry then the person leading the stability test must determine the acceptability of all variances from the guide based on the ability to correct for these variances analytically. A complete understanding of the principles behind the stability test and knowledge of the factors that affect the results is therefore necessary.
4.2 The results of the stability test typically supersede the corresponding values in the weight estimate for any subsequent use in ascertaining compliance to stability or weight control criteria and may be used in weight margin adjudication.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide covers the determination of a small boat’s lightcraft characteristics. The air incline stability test can be considered two separate tasks; a deadweight survey and an air-inclining experiment. The stability test is recommended, but not required, for all small craft upon their construction completion and/or after major conversions where stability information is required. It is typically conducted indoors and an enclosed facility to protect the vessels from unprotected environmental conditions.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F3052 − 14 An American National Standard
Standard Guide for
Conducting Small Boat Stability Test (Deadweight Survey
and Air Inclining Experiment) to Determine Lightcraft Weight
1
and Centers of Gravity of a Small Craft
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F3052; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
Small craft operators, builders, buyers, accident investigators and others may be required to
determine the centers of gravity for their craft in order to apply stability criteria or perform other
analyses. The conventional in-water stability test can be difficult to perform accurately on small craft,
so an in-air inclining experiment may be specified. However, there are no guidelines available to help
standardize and explain the process.
This guide provides the marine industry with an understanding of an Air-Incline stability test for
small craft. It contains procedures to ensure that valid results are obtained with precision at a minimal
cost to owners, shipyards and the government. The guide is not intended to direct a person(s) in the
actualcalculationsofthelightcraftweightandcentersofgravity,buttobeaguidetotherecommended
procedures required to gather accurate data for use in the calculation of the lightcraft characteristics.
A complete understanding and documentation of proper procedures to conduct a stability test is
paramounttoconfirmthattheresultsgatheredduringthetestcanbeexaminedforaccuracy,especially
by third parties subsequently reviewing the data. This guide is recommended to be used for all small
craft capable of being lifted safely with forward and aft pick points capable of enduring additional
inclining weights to be used for the stability test.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 This guide covers the determination of a small boat’s 2.1 ASTM Standards:
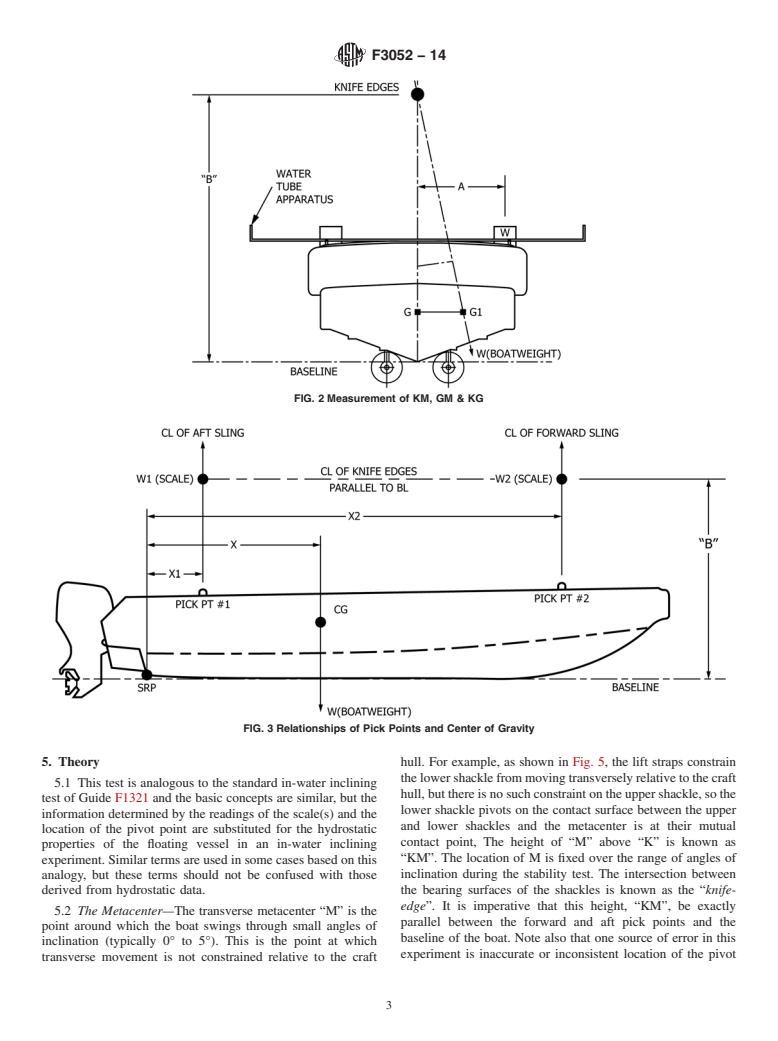
lightcraft characteristics. The air incline stability test can be F1321 Guide for Conducting a Stability Test (Lightweight
considered two separate tasks; a deadweight survey and an Survey and Inclining Experiment) to Determine the Light
air-inclining experiment. The stability test is recommended, Ship Displacement and Centers of Gravity of a Vessel
but not required, for all small craft upon their construction
3. Terminology
completion and/or after major conversions where stability
information is required. It is typically conducted indoors and 3.1 Definitions:
an enclosed facility to protect the vessels from unprotected 3.1.1 inclining experiment—comprises moving a series of
environmental conditions. knownweightsinatransversedirectionandthenmeasuringthe
resulting change in the equilibrium heel angle of the craft.This
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
information is used to calculate the vessel’s vertical center of
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
gravity.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- 3.1.2 lightcraft—a small craft, or boat in the lightest condi-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. tion (“Condition 1”) is a boat complete in all respects without
consumables, stores, cargo crew and effects and without any
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F25 on Ships and
2
Marine Technology and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F25.01 on For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Structures. contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2014. Published February 2014. DOI: 10.1520/ Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
F3052-14. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F3052 − 14
liquids on board except machinery fluids, such as lubricants 3.1.8 X—longitudinal distance from stern reference point
and hydraulics at operating levels. The lightcraft should be as (SRP) to longitudinal center of gravity of the boat.
defined in the craft procurement or other specifications, or in
3.1.9 W1—weight in pounds at the aft pick point.
the operating manual, as to outfit permanently aboard, etc.
3.1.10 W2—weight in pounds at the forward pick point.
3.1.3 deadweight survey—comprises weighing the vessel at
3.1.11 W—W1+ W2, is total weight of the boat.
two longitudinal points to determine the total weight and
3.1.12 B—vertical distance from SRPto pick points and
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.