ASTM D6034-17
(Test Method)Standard Test Method (Analytical Procedure) for Determining the Efficiency of a Production Well in a Confined Aquifer from a Constant Rate Pumping Test
Standard Test Method (Analytical Procedure) for Determining the Efficiency of a Production Well in a Confined Aquifer from a Constant Rate Pumping Test
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
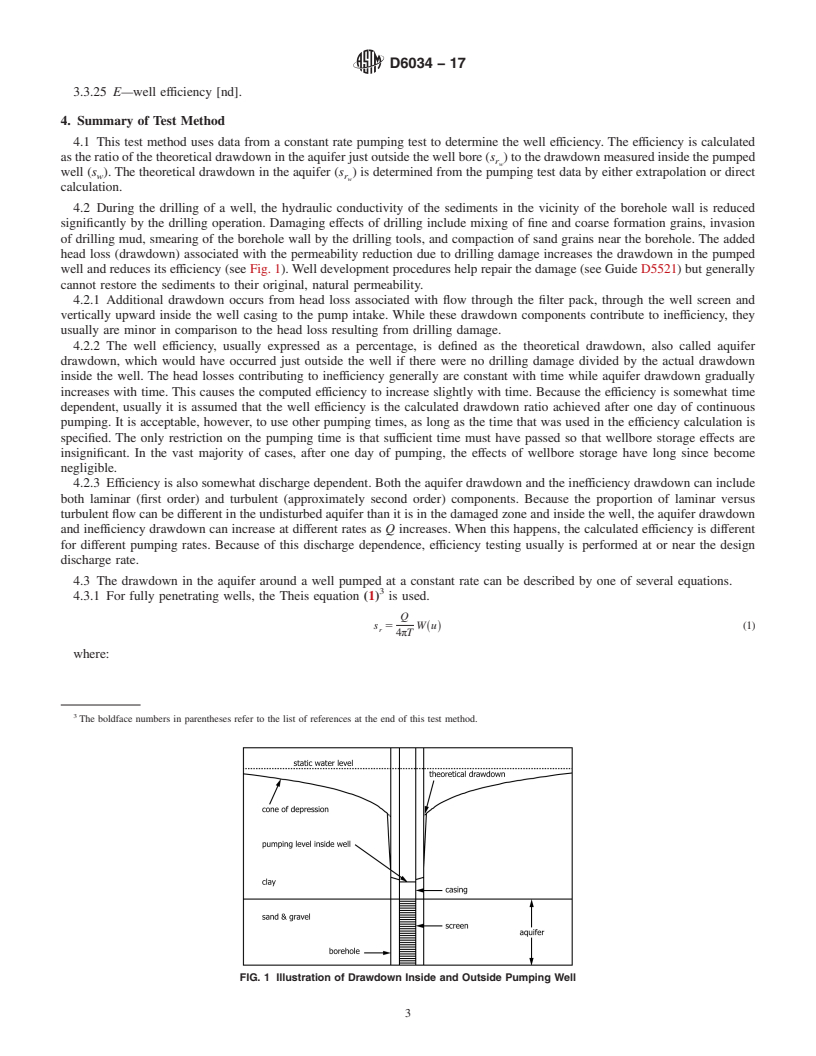
5.1 This test method allows the user to compute the true hydraulic efficiency of a pumped well in a confined aquifer from a constant rate pumping test. The procedures described constitute the only valid method of determining well efficiency. Some practitioners have confused well efficiency with percentage of head loss associated with laminar flow, a parameter commonly determined from a step-drawdown test. Well efficiency, however, cannot be determined from a step-drawdown test but only can be determined from a constant rate test.
5.2 Assumptions:
5.2.1 Control well discharges at a constant rate, Q.
5.2.2 Control well is of infinitesimal diameter.
5.2.3 Data are obtained from the control well and, if available, a number of observation wells.
5.2.4 The aquifer is confined, homogeneous, and extensive. The aquifer may be anisotropic, and if so, the directions of maximum and minimum hydraulic conductivity are horizontal and vertical, respectively.
5.2.5 Discharge from the well is derived exclusively from storage in the aquifer.
5.3 Calculation Requirements—For the special case of partially penetrating wells, application of this test method may be computationally intensive. The function fs shown in Eq 6 should be evaluated using arbitrary input parameters. It is not practical to use existing, somewhat limited, tables of values for fs and, because this equation is rather formidable, it may not be tractable by hand. Because of this, it is assumed the practitioner using this test method will have available a computerized procedure for evaluating the function fs. This can be accomplished using commercially available mathematical software including some spreadsheet applications. If calculating fs is not practical, it is recommended to substitute the Kozeny equation for the Hantush equation as previously described.
Note 1: The quality of the result produced by this standard is dependent on the competence of the personnel performing it, and the suitabilit...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes an analytical procedure for determining the hydraulic efficiency of a production well in a confined aquifer. It involves comparing the actual drawdown in the well to the theoretical minimum drawdown achievable and is based upon data and aquifer coefficients obtained from a constant rate pumping test.
1.2 This analytical procedure is used in conjunction with the field procedure, Test Method D4050.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard, except as noted below. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units, which are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3.1 The gravitational system of inch-pound units is used when dealing with inch-pound units. In this system, the pound (lbf) represents a unit of force (weight), while the unit for mass is slugs.
1.4 Limitations—The limitations of the technique for determination of well efficiency are related primarily to the correspondence between the field situation and the simplifying assumption of this test method.
1.5 All observed and calculated values shall conform to the guidelines for significant digits and round established in Practice D6026, unless superseded by this standard.
1.5.1 The procedures used to specify how data are collected/recorded or calculated, in this standard are regarded as the industry standard. In addition, they are representative of the significant digits that generally should be retained. The procedures used do not consider material variation, purpose for obtaining the data, special purpose studies, or any considerations for the user’s objectives; and it is common practice to increase or reduce significant digits of reported date to be commensurate with these considerations. It is beyond the scope of this standard to consider significant digits used in analysis method for engineering design.
1.6 This standard does not pur...
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D6034 −17
Standard Test Method (Analytical Procedure) for
Determining the Efficiency of a Production Well in a
1
Confined Aquifer from a Constant Rate Pumping Test
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6034; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* of this standard to consider significant digits used in analysis
method for engineering design.
1.1 This test method describes an analytical procedure for
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
determining the hydraulic efficiency of a production well in a
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
confinedaquifer.Itinvolvescomparingtheactualdrawdownin
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
the well to the theoretical minimum drawdown achievable and
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
is based upon data and aquifer coefficients obtained from a
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
constant rate pumping test.
1.2 Thisanalyticalprocedureisusedinconjunctionwiththe
2. Referenced Documents
field procedure, Test Method D4050.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
D653Terminology Relating to Soil, Rock, and Contained
as standard, except as noted below. The values given in
Fluids
parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units, which
D3740Practice for Minimum Requirements for Agencies
are provided for information only and are not considered
Engaged in Testing and/or Inspection of Soil and Rock as
standard.
Used in Engineering Design and Construction
1.3.1 The gravitational system of inch-pound units is used
D4050Test Method for (Field Procedure) for Withdrawal
when dealing with inch-pound units. In this system, the pound
and Injection Well Testing for Determining Hydraulic
(lbf)representsaunitofforce(weight),whiletheunitformass
Properties of Aquifer Systems
is slugs.
D5521Guide for Development of Groundwater Monitoring
1.4 Limitations—The limitations of the technique for deter-
Wells in Granular Aquifers
mination of well efficiency are related primarily to the corre-
D6026Practice for Using Significant Digits in Geotechnical
spondence between the field situation and the simplifying
Data
assumption of this test method.
3. Terminology
1.5 All observed and calculated values shall conform to the
guidelines for significant digits and round established in
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of common terms used in
Practice D6026, unless superseded by this standard.
this test method, see Terminology D653.
1.5.1 Theproceduresusedtospecifyhowdataarecollected/
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
recorded or calculated, in this standard are regarded as the
3.2.1 well effıciency, n—the ratio, usually expressed as a
industry standard. In addition, they are representative of the
percentage, of the measured drawdown inside the control well
significant digits that generally should be retained. The proce-
divided into the theoretical drawdown which would occur in
dures used do not consider material variation, purpose for
the aquifer just outside the borehole if there were no drilling
obtaining the data, special purpose studies, or any consider-
damage, that is, no reduction in the natural permeability of the
ations for the user’s objectives; and it is common practice to
sediments in the vicinity of the borehole.
increase or reduce significant digits of reported date to be
3.3 Symbols:
commensuratewiththeseconsiderations.Itisbeyondthescope
3.3.1 Symbols and Dimensions:
−1
3.3.2 K—hydraulic conductivity [LT ].
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD18onSoiland
Rock and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D18.21 on Groundwater and
2
Vadose Zone Investigations. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2017. Published January 2017. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
ɛ1
approved in 1996. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as D6034–96(2010) . Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/D6034-17. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6034−17
3.3.2.1 Discussion—The use of the symbol K for the term 4.2 During the drilling of a well, the hydraulic conductivity
hydraulic conductivity is the predominant
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: D6034 − 96 (Reapproved 2010) D6034 − 17
Standard Test Method (Analytical Procedure) for
Determining the Efficiency of a Production Well in a
1
Confined Aquifer from a Constant Rate Pumping Test
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6034; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—A units statement was added editorially in August 2010.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This test method describes an analytical procedure for determining the hydraulic efficiency of a production well in a
confined aquifer. It involves comparing the actual drawdown in the well to the theoretical minimum drawdown achievable and is
based upon data and aquifer coefficients obtained from a constant rate pumping test.
1.2 This analytical procedure is used in conjunction with the field procedure, Test Method D4050.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard, except as noted below. The values given in parentheses
are mathematical conversions to SI units, which are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3.1 The gravitational system of inch-pound units is used when dealing with inch-pound units. In this system, the pound (lbf)
represents a unit of force (weight), while the unit for mass is slugs.
1.4 Limitations—The limitations of the technique for determination of well efficiency are related primarily to the correspon-
dence between the field situation and the simplifying assumption of this test method.
1.5 All observed and calculated values shall conform to the guidelines for significant digits and round established in Practice
D6026, unless superseded by this standard.
1.5.1 The procedures used to specify how data are collected/recorded or calculated, in this standard are regarded as the industry
standard. In addition, they are representative of the significant digits that generally should be retained. The procedures used do not
consider material variation, purpose for obtaining the data, special purpose studies, or any considerations for the user’s objectives;
and it is common practice to increase or reduce significant digits of reported date to be commensurate with these considerations.
It is beyond the scope of this standard to consider significant digits used in analysis method for engineering design.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D653 Terminology Relating to Soil, Rock, and Contained Fluids
D3740 Practice for Minimum Requirements for Agencies Engaged in Testing and/or Inspection of Soil and Rock as Used in
Engineering Design and Construction
D4050 Test Method for (Field Procedure) for Withdrawal and Injection Well Testing for Determining Hydraulic Properties of
Aquifer Systems
D5521 Guide for Development of Groundwater Monitoring Wells in Granular Aquifers
D6026 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Geotechnical Data
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of common terms used in this test method, see Terminology D653.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D18 on Soil and Rock and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D18.21 on Groundwater and Vadose
Zone Investigations.
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2010Jan. 1, 2017. Published September 2010January 2017. Originally approved in 1996. Last previous edition approved in 20042010
ɛ1
as D6034–96(2004).D6034–96(2010) . DOI: 10.1520/D6034-96R10E01.10.1520/D6034-17.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6034 − 17
3.2.1 aquifer, confined, n—an aquifer bounded above and below by confining beds and in whi
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.