ASTM A579/A579M-04a(2009)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Superstrength Alloy Steel Forgings
Standard Specification for Superstrength Alloy Steel Forgings
ABSTRACT
This specification deals with the standard requirements for superstrength alloy steel forgings for highly stressed structural members. Covered here are eight types (twenty-seven grades) of alloy steels, namely: quenched and tempered steels (Grades 11, 12, 12a, 13, 21, 22, 23, 31, 32, and 33); air hardened steel (Grade 41); martensitic stainless steels (Grades 51, 52, and 53); No. 1 precipitation hardened stainless steel (Grade 61); No. 2 precipitation hardened stainless steel (Grade 64); No. 3 precipitation hardened stainless steels (Grades 62 and 63); maraging steels (Grades 71, 72, 73, 74, and 75); and miscellaneous steels (Grades 81, 82, 83, and 84). The steels shall be manufactured by melting process and shall be finished by hot-worked forging. Forgings may be furnished in one of the following conditions: stress relieving; annealing; solution treatment; solution treatment and ageing; normalizing; normalizing and tempering; or quenching and tempering. Heat and product analyses shall be employed to assess the conformance of steels with required chemical compositions. Forgings shall examined by tension and Charpy impact tests and conform to required mechanical properties such as yield strength, tensile strength, elongation, reduction of area, minimum room-temperature Charpy V-notch energy absorption, maximum annealed hardness, and section size capability. Nondestructive tests, such as magnetic particle, liquid penetrant, and ultrasonic inspection procedures, shall also be performed.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers requirements for forged steel shapes for highly stressed structural members requiring yield strengths in excess of 140 ksi [965 MPa].
1.2 This specification is not intended for applications limited by creep deformation.
1.3 Twenty-seven grades are covered by this specification. Selection will depend upon design, service conditions, and mechanical properties required.
1.4 Supplementary requirements are provided for use when additional testing or inspection is desired. These shall apply only when specified individually by the purchaser in the order.
1.5 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.6 Unless the order specifies the applicable “M” specification designation, the material shall be furnished to the inch-pound units.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: A579/A579M −04a(Reapproved 2009)
Standard Specification for
Superstrength Alloy Steel Forgings
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA579/A579M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope E3 Guide for Preparation of Metallographic Specimens
E21 TestMethodsforElevatedTemperatureTensionTestsof
1.1 This specification covers requirements for forged steel
Metallic Materials
shapes for highly stressed structural members requiring yield
E45 Test Methods for Determining the Inclusion Content of
strengths in excess of 140 ksi [965 MPa].
Steel
1.2 This specification is not intended for applications lim-
E112 Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size
ited by creep deformation.
E165 Practice for Liquid Penetrant Examination for General
Industry
1.3 Twenty-seven grades are covered by this specification.
Selection will depend upon design, service conditions, and
3. Ordering Information and General Requirements
mechanical properties required.
3.1 In addition to the ordering information required by
1.4 Supplementary requirements are provided for use when
Specification A788/A788M, the purchaser shall include with
additional testing or inspection is desired. These shall apply
the inquiry and order a detailed drawing, sketch, or written
only when specified individually by the purchaser in the order.
description of the forging.
1.5 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
3.2 Material supplied to this specification shall conform to
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
the requirements of Specification A788/A788M, which out-
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
lines additional ordering information, manufacturing
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
requirements, testing and retesting methods and procedures,
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
marking, certification, product analysis variations, and addi-
with the standard.
tional supplementary requirements.
1.6 Unless the order specifies the applicable “M” specifica-
3.3 If the requirements of this specification are in conflict
tion designation, the material shall be furnished to the inch-
with the requirements of Specification A788/A788M, the
pound units.
requirements of this specification shall prevail.
2. Referenced Documents
4. Materials and Manufacture
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A255 Test Methods for Determining Hardenability of Steel
4.1 The steel shall be made in accordance with the Melting
A275/A275M Practice for Magnetic Particle Examination of
Process Section of Specification A788/A788M. A sufficient
Steel Forgings
discard shall be made to secure freedom from injurious pipe
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
and undue segregation.
of Steel Products
4.2 The material shall be forged as close as practical to the
A388/A388M Practice for Ultrasonic Examination of Steel
specified shape and size.
Forgings
4.3 The finished product shall be a hot-worked forging as
A788/A788M Specification for Steel Forgings, General Re-
defined by Specification A788/A788M.
quirements
4.4 Heat Treatment Performed by Forging Supplier—
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
Forgings may be furnished in one of the following conditions
Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
as specified in the inquiry and purchase order (some conditions
A01.06 on Steel Forgings and Billets.
are not applicable to all grades):
Current edition approved April 1, 2009. Published April 2009. Originally
4.4.1 Stress relieved,
approved in 1967. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as A579/A579M – 04a.
DOI: 10.1520/A0579_A0579M-04AR09.
4.4.2 Annealed,
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
4.4.3 Solution treated,
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
4.4.4 Solution treated and aged,
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. 4.4.5 Normalized,
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
A579/A579M − 04a (2009)
4.4.6 Normalized and tempered, or 6. Mechanical Properties
4.4.7 Quenched and tempered.
6.1 The material shall conform to the mechanical properties
4.5 Heat Treatment Performed by Purchaser—When final specified in Table 1, when ordered to 4.4.4 or 4.4.7. For the
other heat treatments specified in 4.4, the provisions of 4.5
heat treatment is to be performed by the purchaser after
machining or fabrication, or both, a capability heat treatment apply.
duplicating the purchaser’s final heat treatment must be per-
6.2 Tension tests are required for all material ordered to this
formed by the supplier on representative samples (see 6.3)to
specification. However, room-temperature Charpy V-notch im-
qualify the forgings. The results of these capability tests shall
pact tests are required only for those grades which have
conform to the requirements of Table 1 and Table 2. See also
minimum impact strength requirements listed in Table 2.
Table 3.
6.3 Tests shall be conducted in accordance with the latest
issue of Test Methods and Definitions A370. The largest
5. Chemical Requirements
obtainable tension test specimen as specified in Test Methods
5.1 Heat Analysis—The heat analysis obtained from sam-
and Definitions A370 shall be used. Impact specimens shall be
pling in accordance with Specification A788/A788M shall
the standard size, Charpy V-notch, as shown in the figure for
comply with Table 4.
the Charpy (Simple-Beam) Impact Test of Test Methods and
5.2 Product Analysis—The product analysis provisions of Definitions A370. The use of subsize impact specimens re-
Specification A788/A788M may be used by the purchaser. quires prior purchaser approval.
TABLE 1 Minimum Tension Test Requirements
A
Grade Yield Strength Tensile Strength, Elongation , Reduction
A
%
(0.2 % offset), ksi [MPa] of Area ,
%
ksi [MPa]
Quench and Tempered
13, 21, 22, 23, 12, 12a 140 [965] 150 [1035] 13 40
13, 21, 22, 23, 11 160 [1100] 175 [1210] 12 36
B
13, 21, 22, 23, 31 180 [1240] 190 [1310] 10 32
B
13, 21, 22, 23 200 [1380] 210 [1450] 9 28
C B
22 , 23, 32, 33 225 [1550] 250 [1720] 6 25
Air Hardening
B
41 200 [1380] 260 [1790] 9 30
B
41 225 [1550] 280 [1930] 8 25
Martensitic Stainless
51, 52, 53 140 [965] 175 [1210] 12 45
52 160 [1100] 220 [1520] 10 40
No. 1 Precipitation Hardening Stainless
61 140 [965] 165 [1140] 12 50
61 160 [1100] 180 [1240] 10 45
B
61 180 [1240] 200 [1380] 8 40
No. 2 Precipitation Hardening Stainless
64 140 [965] 165[(1140] 12 25
64 160 [1100] 185 [1275] 10 25
B
64 180 [1240] 210 [1450] 10 25
No. 3 Precipitation Hardening Stainless
62 140 [965] 165 [1140] 6 25
62, 63 160 [1100] 180 [1240] 6 25
B
63 180 [1240] 200 [1380] 6 25
B
63 200 [1380] 225 [1550] 5 25
Maraging Steels
74 160 [1100] 170 [1170] 15 65
B
75 180 [1240] 190 [1310] 14 60
B
71 200 [1380] 210 [1450] 12 55
B
72 250 [1720] 255 [1760] 10 45
B
73 275 [1895] 280 [1930] 9 40
Miscellaneous
D
81 180 [1240] 190 [1310] 13 45
D
82 200 [1380] 210 [1450] 10 30
D D
83 225 [1550] 260 [1790] 7 20
E D
83 250 [1720] 280 [1930] 4 15
D
84 180 [1240] 185 [1275] 14 45
A
See Note in Table 3.
B
Vacuum melting normally required to achieve list properties.
C
By agreement.
D
Bainitic.
E
Martensitic.
A579/A579M − 04a (2009)
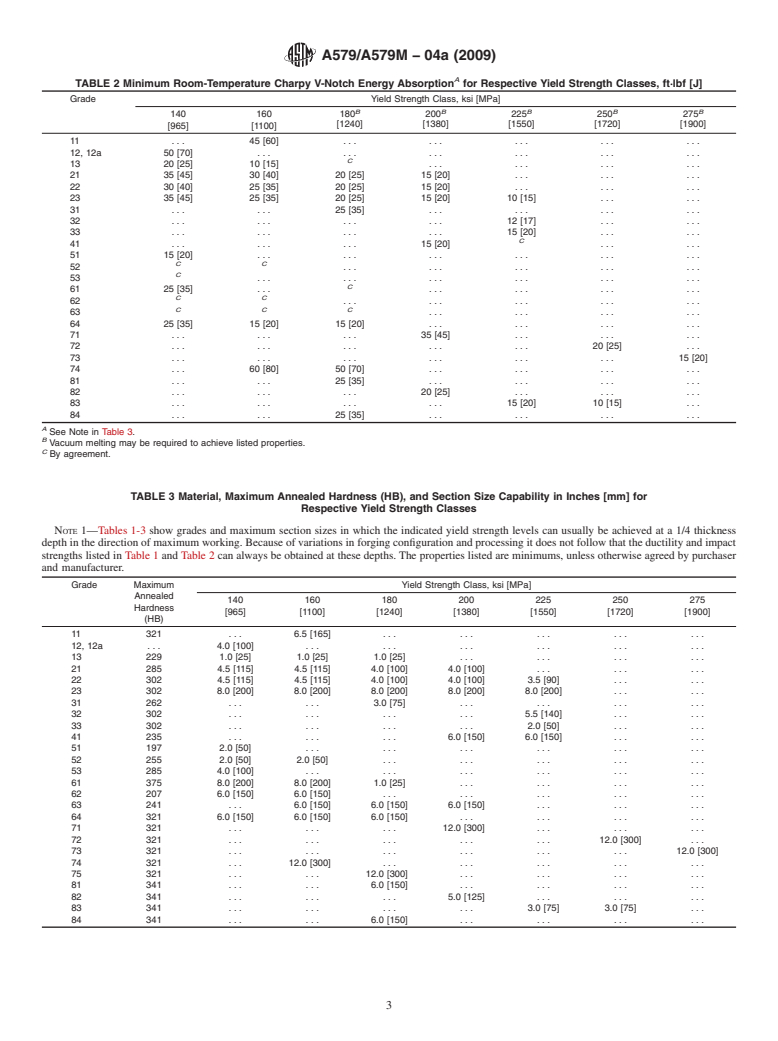
A
TABLE 2 Minimum Room-Temperature Charpy V-Notch Energy Absorption for Respective Yield Strength Classes, ft·lbf [J]
Grade Yield Strength Class, ksi [MPa]
B B B B B
140 160 180 200 225 250 275
[1240] [1380] [1550] [1720] [1900]
[965] [1100]
11 . 45[60] . . . . .
12,12a 50[70] . . . . . .
C
13 20 [25] 10 [15] . . . .
21 35 [45] 30 [40] 20 [25] 15 [20] . . . . . . . . .
22 30 [40] 25 [35] 20 [25] 15 [20] . . . . . . . . .
23 35 [45] 25 [35] 20 [25] 15 [20] 10 [15] . . . . . .
31 . . 25[35] . . . .
32 . . . . 12[17] . .
33 . . . . 15[20] . .
C
41 . . . 15[20] . .
51 15[20] . . . . . .
CC
52 . . . . .
C
53 . . . . . .
C
61 25 [35] . . . . . . .
CC
62 . . . . .
CCC
63 . . . .
64 25 [35] 15 [20] 15 [20] . . . . . . . . . . . .
71 . . . 35[45] . . .
72 . . . . . 20[25] .
73 . . . . . . 15[20]
74 . 60[80] 50[70] . . . .
81 . . 25[35] . . . .
82 . . . 20[25] . . .
83 . . . . 15[20] 10[15] .
84 . . 25[35] . . . .
A
See Note in Table 3.
B
Vacuum melting may be required to achieve listed properties.
C
By agreement.
TABLE 3 Material, Maximum Annealed Hardness (HB), and Section Size Capability in Inches [mm] for
Respective Yield Strength Classes
NOTE 1—Tables 1-3 show grades and maximum section sizes in which the indicated yield strength levels can usually be achieved at a 1/4 thickness
depth in the direction of maximum working. Because of variations in forging configuration and processing it does not follow that the ductility and impact
strengths listed in Table 1 and Table 2 can always be obtained at these depths. The properties listed are minimums, unless otherwise agreed by purchaser
and manufacturer.
Grade Maximum Yield Strength Class, ksi [MPa]
Annealed
140 160 180 200 225 250 275
Hardness
[965] [1100] [1240] [1380] [1550] [1720] [1900]
(HB)
11 321 . . . 6.5 [165] . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
12, 12a . . . 4.0 [100] . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
13 229 1.0 [25] 1.0 [25] 1.0 [25] . . . . . . . . . . . .
21 285 4.5 [115] 4.5 [115] 4.0 [100] 4.0 [100] . . . . . . . . .
22 302 4.5 [115] 4.5 [115] 4.0 [100] 4.0 [100] 3.5 [90] . . . . . .
23 302 8.0 [200] 8.0 [200] 8.0 [200] 8.0 [200] 8.0 [200] . . . . . .
31 262 . . 3.0[75] . . . .
32 302 . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.5 [140] . . . . . .
33 302 . . . . 2.0[50] . .
41 235 . . . . . . . . . 6.0 [150] 6.0 [150] . . . . . .
51 197 2.0[50] . . . . . .
52 255 2.0 [50] 2.0 [50] . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
53 285 4.0 [100] . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
61 375 8.0 [200] 8.0 [200] 1.0 [25] . . . . . . . . . . . .
62 207 6.0 [150] 6.0 [150] . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
63 241 . . . 6.0 [150] 6.0 [150] 6.0 [150] . . . . . . . . .
64 321 6.0 [150] 6.0 [150] 6.0 [150] . . . . . . . . . . . .
71 321 . . . . . . . . . 12.0 [300] . . . . . . . . .
72 321 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12.0 [300] . . .
73 321 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12.0 [300]
74 321 . . . 12.0 [300] . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
75 321 . . . . . . 12.0 [300] . . . . . . . . . . . .
81 341 . . . . . . 6.0 [150] . . . . . . . . . . . .
82 341 . . . . . . . . . 5.0 [125] . . . . . . . . .
83 341 . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.0 [75] 3.0 [75] . . .
84 341 . . . . . . 6.0 [150] . . . . . . . . . . . .
A579/A579M − 04a (2009)
TABLE 4 Chemical Requirements
Elements Composition, %
min max min max min max min max min max min max min max
Grade 11 12 12a 13 21 22 23
Carbon 0.23 0.28 . . . 0.12 . . . 0.20 0.27 0.33 0.31 0.38 0.38 0.43 0.45 0.50
Manganese . . . 0.20 0.60 0.90 0.60 0.90 0.40 0.60 0.60 0.90 0.60 0.90 0.60 0.90
Phosphorus . . . 0.01 . . . 0.010 . . . 0.015 . . . 0.025 . . . 0.025 . . . 0.025 . . . 0.015
Sulfur . . . 0.01 . . . 0.010 . . . 0.015 . . . 0.025 . . . 0.025 . . . 0.025 . . . 0.015
Silicon . . . 0.10 0.20 0.35 0.20 0.35 0.20 0.35 0.20 0.35 0.20 0.35 0.15 0.30
Nickel 2.75 3.25 4.75 5.25 4.75 5.25 . . . . . . 1.65 2.00 1.65 2.00 0.40 0.70
Chromium 1.40 1.65 0.40 0.70 0.40 0.70 0.80 1.10 0.65 0.90 0.70 0.90 0.90 1.20
Molybdenum 0.8 1.0 0.30 0.65 0.30 0.65 0.15 0.25 0.30 0.60 0.30 0.60 0.90 1.10
Vanadium . . . . . . 0.05 0.10 0.05 0.10 0.05 0.10 0.17 0.23 0.05 0.10 0.08 0.15
Columbium 0.03 0.07 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A
Grade 31 32 33 41 51 52 53
Carbon 0.23 0.28 0.40 0.45 0.41 0.46 0.38 0.43 . . . 0.15 0.20 0.25 . . . 0.20
Manganese 1.20 1.50 0.65 0.90 0.75 1.00 0.20 0.40 . . . 1.00 0.50 1.00 . . . 1.00
Phosphorus . . . 0.025 . . . 0.025 . . . 0.025 . . . 0.015 . . . 0.025 . . . 0.025 . . . 0.025
Sulfur . . . 0.025 . . . 0.025 . . . 0.025 . . . 0.015 . . . 0.025 . . . 0.025 . . . 0.025
Silicon 1.30 1.70 1.45 1.80 1.40 1.75 0.80 1.00 . . . 1.00 . . . 0.50 . . . 1.00
Nickel 1.65 2.00 1.65 2.00 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.75 0.50 1.00 1.25 2.50
Chromium 0.20 0.40 0.65 0.90 1.90 2.25 4.75 5.25 11.5 13.5 11.0 12.5 15.0 17.0
Molybdenum 0.35 0.45 0.30 0.45 0.45 0.60 1.20 1.40 . . . 0.50 0.90 1.25 . . . . . .
Copper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.50 . . . . . . . . . . . .
Titanium . . . . . . . . . . . 0.05 . .
Vanadium . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.03 0.08 0.40 0.60 . . . . . . 0.20 0.30 . . . . . .
Cobalt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.25 . . . . . .
Aluminum . . . . . . . . . 0.05 . 0.05 . .
Tungsten . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.90 1.25 . . . . . .
Tin . . . . . . . . . 0.05 . 0.04 . .
A,B A,B A,B A,B A,B A,B A,B
Grade 61 62 63 64 71 72 73
Carbon . . . 0.07 . . . 0.09 . . . 0.09 0.10 0.15 . . . 0.03 . . . 0.03 . . . 0.03
Manganese . . . 1.00 . . . 1.00 . . . 1.00 0.50 1.25 . . . 0.10 . . . 0.10 . . . 0.10
Phosphorus . . . 0.025 . . . 0.025 . . . 0.025 . . . 0.025 . . . 0.01 . . . 0.01 . . . 0.01
Sulfur . . . 0.025 . . . 0.025 . . . 0.025 . . . 0.025 . . . 0.01 . . . 0.01 . . . 0.01
Silicon . . . 1.00 . . . 1.00 . . . 0.50 . . . 0.50 . . . 0.10 . . . 0.10 . . . 0.10
Nickel 3.0 5.0 6.5 7.75 6.5 7.75 4.0 5.0 17.0 19.0 17.0 19.0 18.0 19.0
Chromium 15.5 17.5 16.0 18.0 14.0 15.25 15.0 16.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Molybdenum . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 2.75 2.50 3.25 3.0 3.5 4.6 5.2 4.6 5.2
Copper 3.0 5.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Titanium . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.15 0.25 0.30 0.50 0.50 0.80
Columbium 0.15 0.45 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cobalt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8.0 9.0 7.0 8.5 8.5 9.5
Aluminum . . . . . . 0.75 1.50 0.75 1.25 . . . . . . 0.05 0.15 0.05 0.15 0.05 0.15
Nitrogen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.07 0.13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A,B A,B A,B A,B A,B A,B
Grade 74 75 81 82 83 84
Carbon . . . 0.03 . . . 0.03 0.24 0.30 0.28 0.34 0.42 0.
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.