ASTM C1817-15
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for The Determination of the Oxygen to Metal (O/M) Ratio in Sintered Mixed Oxide ((U, Pu)O2) Pellets by Gravimetry
Standard Test Method for The Determination of the Oxygen to Metal (O/M) Ratio in Sintered Mixed Oxide ((U, Pu)O<inf>2</inf>) Pellets by Gravimetry
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 MOX is used as a nuclear-reactor fuel. This test method is designed to determine whether the O/M ratio meets the requirements of the fuel specification. Examples for establishing a fuel specification are given in Specification C833.
5.2 This method is suitable for all sintered MOX pellets containing up to 10 weight % PuO2 when the UO2 and PuO2 meet the requirements of Specifications C753 and C757.
SCOPE
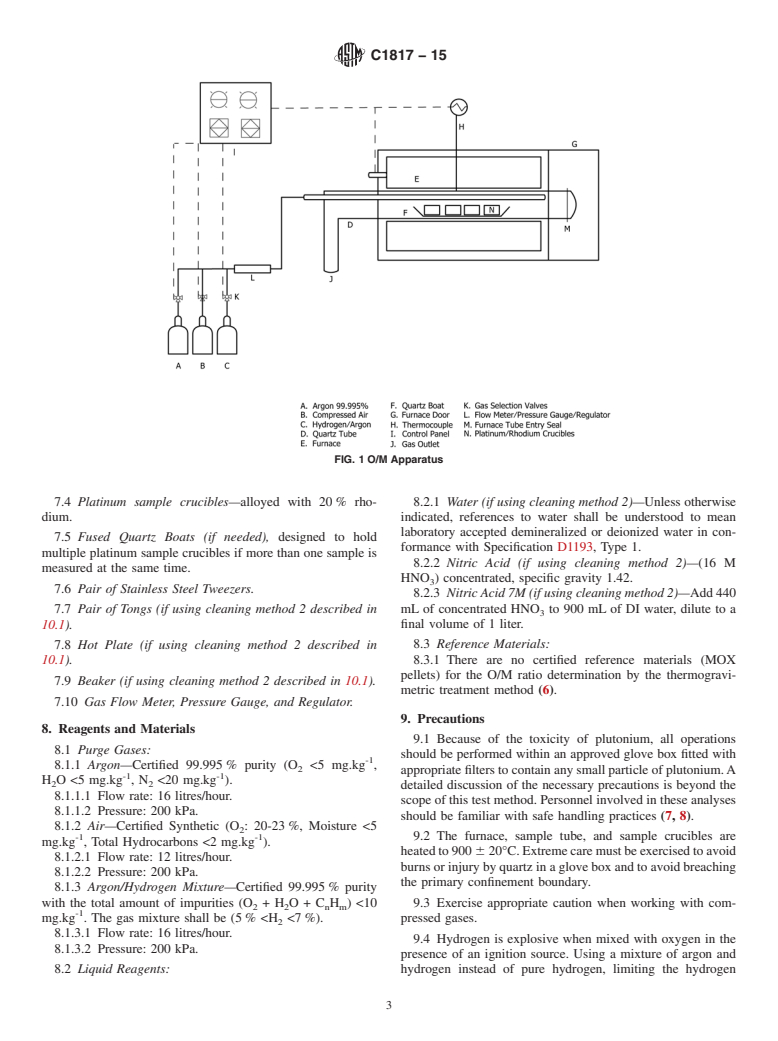
1.1 This practice is an alternative method to Test Method C698 for the determination of the oxygen-to-metal atom ratio (O/M) in sintered mixed oxide fuel (MOX) pellets. The method presented in Test Method C698 is a one-step thermogravimetric method for determining O/M ratio in sintered MOX powders and pellets. As stated in Test Method C698, thermogravimetric methods using a two-step heating cycle are also satisfactory (1, 2).2 The method presented in this test method is a two-step heating cycle method. This test method is applicable to sintered MOX pellets containing up to 10 weight percent PuO2.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C1817 − 15
StandardTest Method for
The Determination of the Oxygen to Metal (O/M) Ratio in
1
Sintered Mixed Oxide ((U, Pu)O ) Pellets by Gravimetry
2
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1817; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope C859 Terminology Relating to Nuclear Materials
C1068 Guide for Qualification of Measurement Methods by
1.1 This practice is an alternative method to Test Method
a Laboratory Within the Nuclear Industry
C698 for the determination of the oxygen-to-metal atom ratio
C1672 Test Method for Determination of Uranium or Pluto-
(O/M)insinteredmixedoxidefuel(MOX)pellets.Themethod
nium Isotopic Composition or Concentration by the Total
presented in Test Method C698 is a one-step thermogravimet-
Evaporation Method Using a Thermal Ionization Mass
ric method for determining O/M ratio in sintered MOX
Spectrometer
powders and pellets. As stated in Test Method C698, thermo-
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
gravimetric methods using a two-step heating cycle are also
2 D1356 Terminology Relating to Sampling and Analysis of
satisfactory (1, 2). The method presented in this test method is
Atmospheres
atwo-stepheatingcyclemethod.Thistestmethodisapplicable
4
2.2 ISO Standards:
to sintered MOX pellets containing up to 10 weight percent
ISO 21484 Nuclear Fuel Technology – Determination of the
PuO .
2
O/M Ratio in MOX Pellets – Gravimetric Method – First
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
Edition
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
3. Terminology
standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method but not
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the defined herein, refer to Terminology C859.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
3.2.1 average of the relative atomic mass—the weighted
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
average of the relative atomic mass of an element calculated as
a function of its isotopic composition.
2. Referenced Documents
3 3.2.2 mole fraction—the ratio of the number of molecules
2.1 ASTM Standards:
(or moles) of a compound or element to the total number of
C698 Test Methods for Chemical, Mass Spectrometric, and
molecules (or moles) present (Terminology D1356).
Spectrochemical Analysis of Nuclear-Grade Mixed Ox-
ides ((U, Pu)O ) 3.2.3 MOX—nuclearfuelcomposedofamixtureofuranium
2
and plutonium oxides ((U, Pu)O ).
C753 Specification for Nuclear-Grade, Sinterable Uranium
2
Dioxide Powder
3.2.4 O/M—ratio of the oxygen atoms divided by the metal
C757 Specification for Nuclear-Grade Plutonium Dioxide
atoms in the sample.
Powder, Sinterable
3.2.5 relative atomic mass—a dimensionless physical
C833 Specification for Sintered (Uranium-Plutonium) Diox-
quantity, the ratio of the average mass of atoms of an element
ide Pellets
1
(from a single given sample or source) to ⁄12 of the mass of an
atom of carbon-12 (known as the unified atomic mass unit).
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee C26 on Nuclear
3.2.6 scavenging—the process of pushing a gas out by
Fuel Cycle and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C26.05 on Methods of
Test. introducing a fresh flow in.
Current edition approved June 1, 2015. Published July 2015. DOI: 10.1520/
3.2.7 sintering—the process of forming a solid mass of
C1817-15.
2
material by heat or pressure, or both, without melting it to the
The boldface numbers in parentheses refer to a list of references at the end of
this standard.
point of liquefaction.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 1, ch. de
the ASTM website. la Voie-Creuse, CP 56, CH-1211 Geneva 20, Switzerland, http://www.iso.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1817 − 15
4. Summary of Test Method gain due to redox reactions. Even inert impurities present in
sufficiently high amounts compromise the accuracy of O/M
4.1 The purpose of the analysis is to test the stoichiometry
ratios because the true mass of the ((U, Pu)O ) subjected to the
2
of the MOX pellet
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.