ASTM C719-14(2019)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Adhesion and Cohesion of Elastomeric Joint Sealants Under Cyclic Movement (Hockman Cycle)
Standard Test Method for Adhesion and Cohesion of Elastomeric Joint Sealants Under Cyclic Movement (Hockman Cycle)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The failure of a building sealant in an active joint is usually manifested by cohesive failure in the sealant or adhesive failure between the sealant and the substrate, or both. The method described in this test method relates only to the performance of the sealant when properly installed with recommended primers, and does not evaluate sealant failures caused by improper joint design, excessive joint movement, improper application practices, and other factors known to cause sealant failure in buildings and building areas.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is an accelerated laboratory procedure for evaluating the performance of a building sealant in a test configuration that is subjected to water immersion, cyclic movement, and temperature change.3
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C719 − 14 (Reapproved 2019)
Standard Test Method for
Adhesion and Cohesion of Elastomeric Joint Sealants
1,2
Under Cyclic Movement (Hockman Cycle)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C719; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope C109/C109MTest Method for Compressive Strength of
Hydraulic Cement Mortars (Using 2-in. or [50-mm] Cube
1.1 This test method is an accelerated laboratory procedure
Specimens)
for evaluating the performance of a building sealant in a test
C150Specification for Portland Cement
configuration that is subjected to water immersion, cyclic
3 C717Terminology of Building Seals and Sealants
movement, and temperature change.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
3. Terminology
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this test
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
method, refer to Terminology C717.
and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the 4. Summary of Test Method
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4.1 This test method consists of subjecting standard joint
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
specimens to a series of treatments as follows: (a) immersion
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
inwaterforsevendays;(b)exposureinanovenforsevendays
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
while under compression; (c) automatic compression and
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
extension cycling at room temperature at a specified rate and
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
amount of joint movement; and (d) alternate compression and
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
extension of the joint at high and low temperatures,
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
respectively, under specified conditions described herein.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
4.2 The effects of the test shall be evaluated by visual
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
inspection for cohesive and adhesive failures, sealant
2. Referenced Documents
deformation, and bubble formation within the sealant.
4
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4.3 This test method is applicable to any joint movement.
C33Specification for Concrete Aggregates
The most common test movements are 612.5 and 625% as
used in the examples.
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeC24onBuilding
Seals and Sealants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C24.30 on
5. Significance and Use
Adhesion.
5.1 The failure of a building sealant in an active joint is
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2019. Published January 2019. Originally
approved in 1972. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as C719–14. DOI:
usually manifested by cohesive failure in the sealant or
10.1520/C0719-14R19.
adhesive failure between the sealant and the substrate, or both.
2
This test method is also known as the Hockman Cycle in recognition ofArthur
The method described in this test method relates only to the
Hockman who originated the method at the National Bureau of Standards.
3
performance of the sealant when properly installed with
Supporting data are available fromASTM International Headquarters. Request
RR:C24-1013.
recommended primers, and does not evaluate sealant failures
4
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
caused by improper joint design, excessive joint movement,
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
improper application practices, and other factors known to
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. cause sealant failure in buildings and building areas.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C719 − 14 (2019)
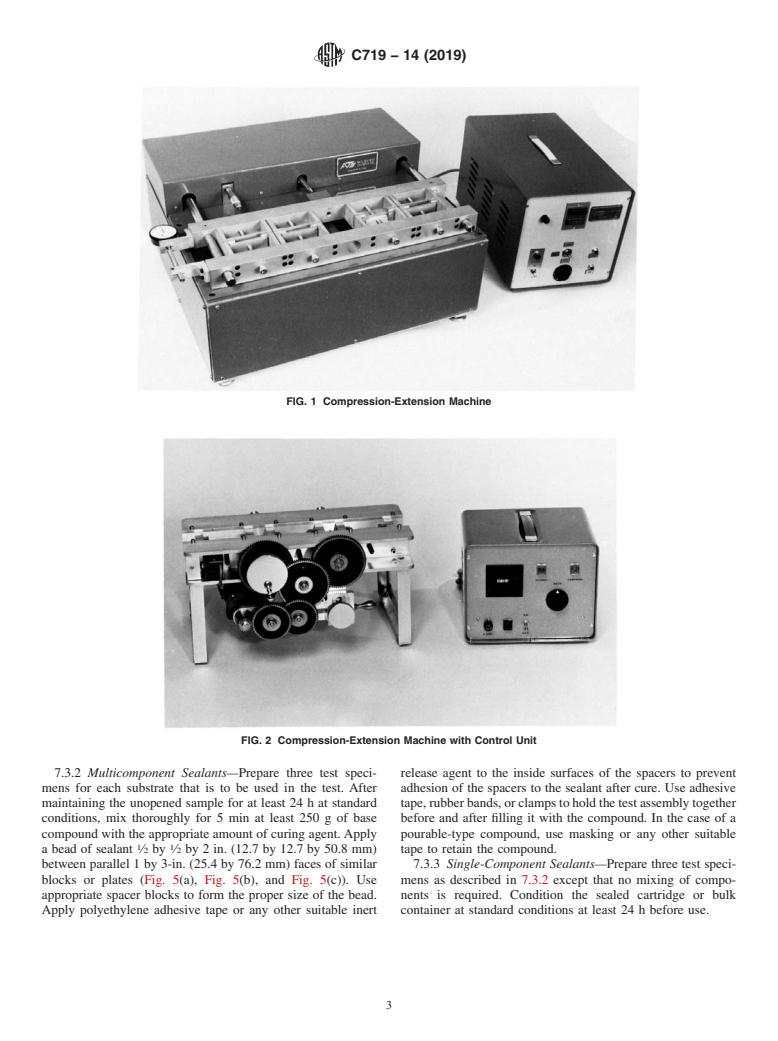
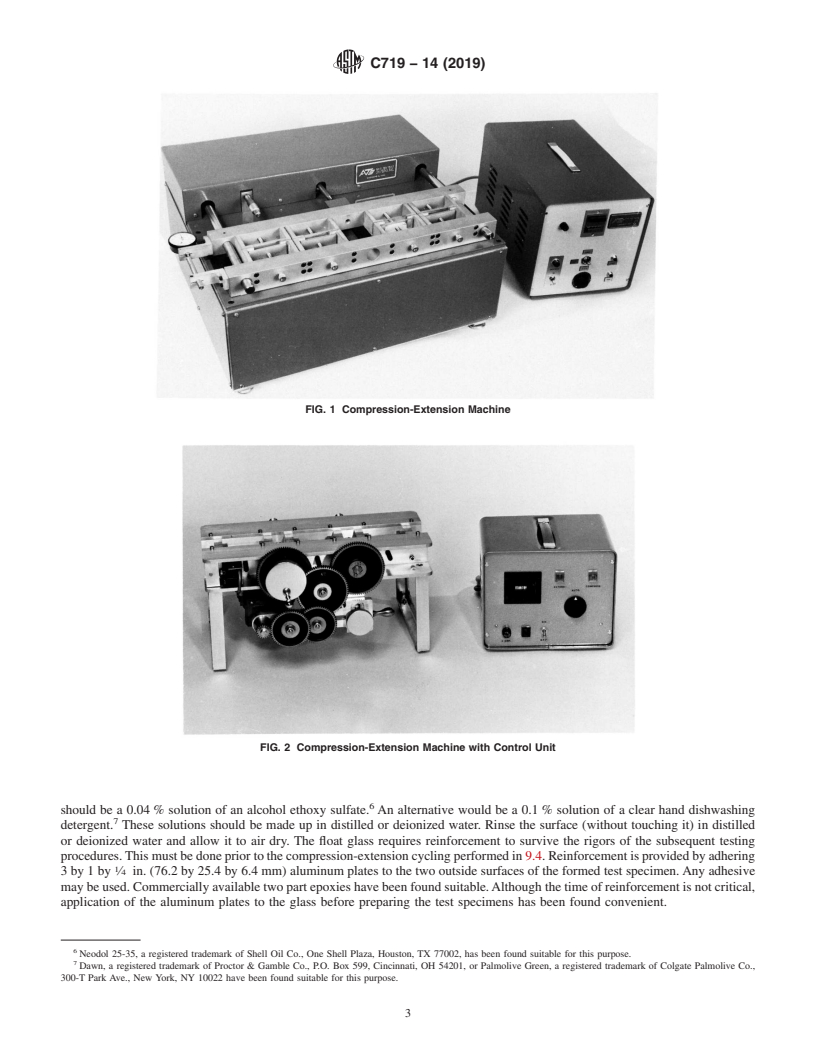
6. Apparatus each block by wet grinding either with a belt sander using No.
5 60aluminumcarbidesandingbeltorusinganironlapwithNo.
6.1 Compression-Extension Machine, designedtoautomati-
60 silicon carbide (or aluminum oxide) grain until the aggre-
cally compress the joint width of the test specimen from 0.500
gate is uniformly exposed. Return blocks to saturated lime
in. (12.7 mm) to the minimum dimension desired (Ta
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C719 − 14 C719 − 14 (Reapproved 2019)
Standard Test Method for
Adhesion and Cohesion of Elastomeric Joint Sealants
1,2
Under Cyclic Movement (Hockman Cycle)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C719; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method is an accelerated laboratory procedure for evaluating the performance of a building sealant in a test
3
configuration that is subjected to water immersion, cyclic movement, and temperature change.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
4
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C33 Specification for Concrete Aggregates
C109/C109M Test Method for Compressive Strength of Hydraulic Cement Mortars (Using 2-in. or [50-mm] Cube Specimens)
C150 Specification for Portland Cement
C717 Terminology of Building Seals and Sealants
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology C717.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 This test method consists of subjecting standard joint specimens to a series of treatments as follows: (a) immersion in water
for seven days; (b) exposure in an oven for seven days while under compression; (c) automatic compression and extension cycling
at room temperature at a specified rate and amount of joint movement; and (d) alternate compression and extension of the joint
at high and low temperatures, respectively, under specified conditions described herein.
4.2 The effects of the test shall be evaluated by visual inspection for cohesive and adhesive failures, sealant deformation, and
bubble formation within the sealant.
4.3 This test method is applicable to any joint movement. The most common test movements are 612.5 and 625 % as used
in the examples.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C24 on Building Seals and Sealants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C24.30 on Adhesion.
Current edition approved July 15, 2014Jan. 1, 2019. Published August 2014January 2019. Originally approved in 1972. Last previous edition approved in 20132014 as
C719 – 13.C719 – 14. DOI: 10.1520/C0719-14.10.1520/C0719-14R19.
2
This test method is also known as the Hockman Cycle in recognition of Arthur Hockman who originated the method at the National Bureau of Standards.
3
Supporting data are available from ASTM International Headquarters. Request RR:C24-1013.
4
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C719 − 14 (2019)
5. Significance and Use
5.1 The failure of a building sealant in an active joint is usually manifested by cohesive failure in the sealant or adhesive failure
between the sealant and the substrate, or both. The method described in this test method relates only to the performance of the
sealant when properly installed with recommended primers, and does not evaluate sealant failures caused by improper joint design,
excessive joint movement, improper application practices, and other factors known to cause sealant failure in buildings and
building areas.
6. Apparatus
5
6.1 Compression-Exten
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.