ASTM F1138-98
(Specification)Standard Specification for Spray Shields for Mechanical Joints
Standard Specification for Spray Shields for Mechanical Joints
SCOPE
1.1 This specification describes the manufacturing requirements for spray shield stock and the fabrication and installation requirements for spray shields made from that stock.
1.1.1 Sections 2 through 14 address the manufacturing requirements for the spray shield stock. Annex A1 addresses the fabrication and installation requirements for the spray shields.
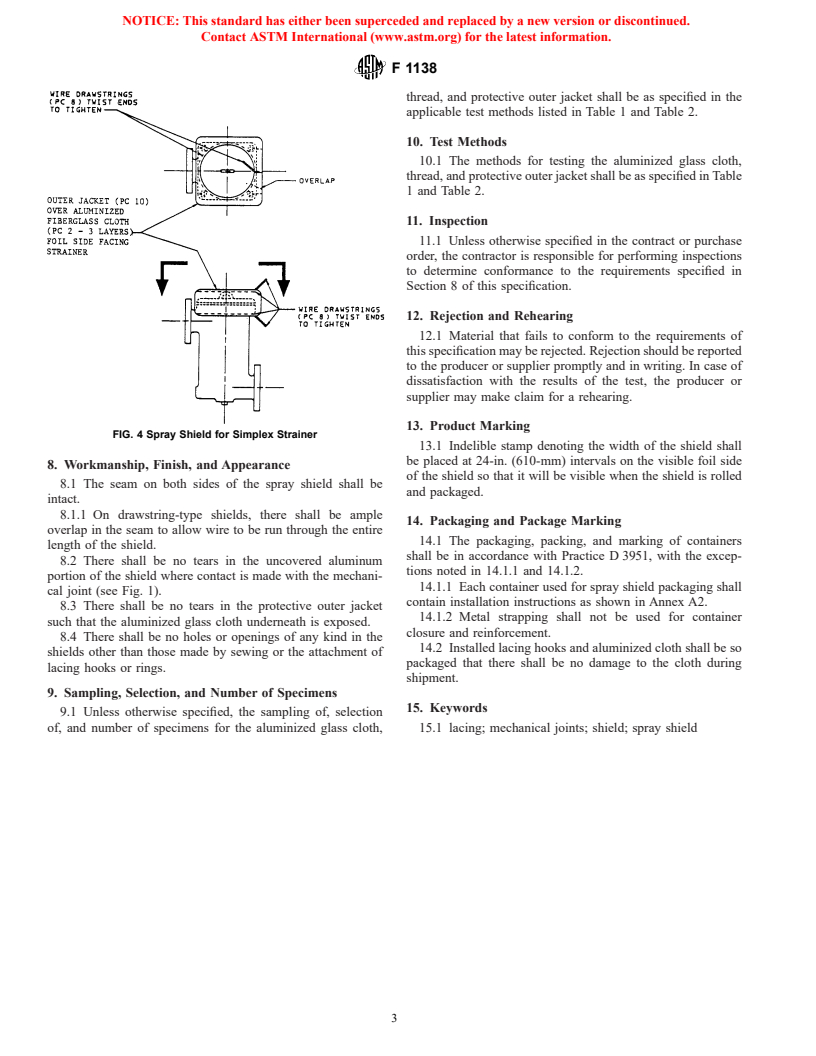
1.1.2 Fig. 1 shows the typical construction of a spray shield. Figs. 2 through 6 show methods of installation of a spray shield on various mechanical joints.
1.2 The shields are intended for use around mechanical joints (flanged, bolted unions, etc.) in liquid piping systems to prevent the impingement of flammable liquid on hot surfaces or fluids onto electrical switchboards and components resulting from a leak in the mechanical joint.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
An American National Standard
Designation: F 1138 – 98
Standard Specification for
Spray Shields for Mechanical Joints
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 1138; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope Falling-Pendulum Type (Elmendorf) Apparatus
D 1682 Test Methods for Breaking Load and Elongation of
1.1 This specification describes the manufacturing require-
Textile Fabrics
ments for spray shield stock and the fabrication and installation
D 1777 Method for Measuring Thickness of Textile Mate-
requirements for spray shields made from that stock.
rials
1.1.1 Sections 2-14 address the manufacturing requirements
D 3389 Test Method for Coated Fabrics Abrasion Resis-
for the spray shield stock. Annex A1 addresses the fabrication
tance (Rotary Platform, Double-Head Abrader)
and installation requirements for the spray shields.
D 3776 Test Methods for Mass Per Unit Area (Weight) of
1.1.2 Fig. 1 shows the typical construction of a spray shield.
Fabric
Figs. 2-6 show methods of installation of a spray shield on
D 3786 Test Method for Hydraulic Bursting Strength of
various mechanical joints.
Knitted Goods and Nonwoven Fabrics: Diaphragm Burst-
1.2 The shields are intended for use around mechanical
ing Strength Tester Method
joints (flanged, bolted unions, and so forth) in liquid piping
D 3951 Practice for Commercial Packaging
systems to prevent the impingement of flammable liquid on hot
F 501 Test Method for Aerospace Materials Response to
surfaces or fluids onto electrical switchboards and components
Flame, With Vertical Test Specimen (For Aerospace Ve-
resulting from a leak in the mechanical joint.
hicles Standard Conditions)
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
2.2 American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for
Standards:
information only.
AATCC-22 Water Repellency, Spray Test
2. Referenced Documents
AATCC-35 Water Resistance, Rain Test
AATCC-127 Water Resistance, Hydrostatic Pressure Test
2.1 ASTM Standards:
2.3 Military Standards:
A 176 Specification for Stainless and Heat-Resisting Chro-
MIL-C-20079 Cloth, Glass, Tape, Textile Glass and Thread,
mium Steel Plate, Sheet, and Strip
Glass
A 276 Specification for Stainless Steel Bars and Shapes
MIL-C-20696 Cloth, Coated, Nylon Waterproof
A 580 Specification for Stainless Steel Wire
2.4 Federal Standard:
B 134 Specification for Brass Wire
WW-C-440 Clamps, Hose (Low Pressure)
B 164 Specification for Nickel-Copper Alloy Rod, Bar, and
Wire
3. Ordering Information
B 166 Specification for Nickel-Chromium-Iron Alloys
3.1 ASTM designation and year of issue,
(UNS N 06600, N 06601, and N 06690) and Nickel–Chro-
3.2 Length and width required (see 7.1), and
mium–Cobalt–Molybdenum Alloy (UNS N 06617) Rod,
3.3 Type of stainless steel (see 4.1).
Bar, and Wire
6 3.4 Type of lacing hardware required (see 4.1.1).
D 1388 Test Method for Stiffness of Fabrics
D 1424 Test Method for Tearing Strength of Fabrics by
1 7
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F25 on Ships Discontinued—Replaced by D 5034 and D 5035, Annual Book of ASTM
and Marine Technology and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F25.07 on Standards, Vol 07.02.
General Requirements. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 09.02.
Current edition approved April 10, 1998. Published October 1998. Originally Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 07.02.
published as F 1138 – 88. Last previous edition F 1138 – 92 (1997). Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.09.
2 11
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.03. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.03.
3 12
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.05. Available from American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists, PO
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 02.01. Box 12215, Research Triangle Park, NC 27709.
5 13
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 02.04. Available from Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 07.01. Office, Washington, DC 20402.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
F 1138
FIG. 1 Spray Shield Construction (Typical)
FIG. 3 Spray Shield for Pump Inlet Head
FIG. 2 Installation of Butterfly Valve Shield
5. Physical and Mechanical Properties
5.1 The physical and mechanical properties for the alumi-
nized glass cloth, thread, and protective outer jacket shall be as
4. Materials and Manufacture
specified in Table 1 and Table 2.
4.1 Lacing hooks, lacing rings, and lacing washers (see Fig.
7) shall be constructed of stainless steel in accordance with
6. Requirements
Specifications A 176, A 276, or A 580.
6.1 If lacing hooks or rings are of the type that fasten by
4.1.1 Lacing rings may be used instead of lacing hooks
stitching, the hooks or rings shall be attached to the backup
where practicable or preferable (see 3.3).
washers using a wire stitch machine and wire (Pieces 5 or 8 in
4.1.2 Lacing washers for fastening hooks or rings shall be
Table 1).
two-hole washers.
6.2 Lacing anchor/self-locking washer-type systems shall
4.2 Stitch wire (Piece 5 in Table 1) shall be constructed of
not be used on spray shields.
stainless steel in accordance with Specification A 580.
7. Dimensions and Permissible Variations
4.3 The aluminized glass cloth, thread, and the protective
outer jacket shall be constructed of material as specified in 7.1 The material for shields shall be standardized as given in
Table 1 and Table 2. Table 3 tolerances to be + ⁄4 in. (6 mm) and −0 in. for width.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
F 1138
thread, and protective outer jacket shall be as specified in the
applicable test methods listed in Table 1 and Table 2.
10. Test Methods
10.1 The methods for testing the aluminized glass cloth,
thread, and protective outer jacket shall be as specified in Table
1 and Table 2.
11. Inspection
11.1 Unless otherwise specified in the contract or purchase
order, the contractor is responsible for performing inspections
to determine conformance to the requirements specified in
Section 8 of this specification.
12. Rejection and Rehearing
12.1 Material that fails to conform to the requirements of
this specification may be rejected. Rejection should be reported
to the producer or supplier promptly and in writing. In case of
dissatisfaction with the results of the test, the producer or
supplier may make claim for a rehearing.
13. Product Marking
FIG. 4 Spray Shield for Simplex Strainer
13.1 Indelible stamp denoting the width of the shield shall
be placed at 24-in. (610-mm) intervals on the visible foil side
8. Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance
of the shield so that it will be visible when the shield is rolled
8.1 The seam on both sides of the spray shield shall be
and packaged.
intact.
8.1.1 On drawstring-type shields, there shall be ample
14. Packaging and Package Marking
overlap in the seam to allow wire to be run through the entire
14.1 The packaging, packing, and marking of containers
length of the shield.
shall be in accordance with Practice D 3951, with the excep-
8.2 There shall be no tears in the uncovered aluminum
tions noted in 14.1.1 and 14.1.2.
portion of the shield where contact is
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.