ASTM B393-99
(Specification)Standard Specification for Niobium and Niobium Alloy Strip, Sheet, and Plate
Standard Specification for Niobium and Niobium Alloy Strip, Sheet, and Plate
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers four grades of wrought niobium and niobium alloy strip, sheet, and plate as follows: Note-Committee B-10 has adopted "niobium" as the designation for Element No. 41, formerly named "columbium."
1.1.1 R04200-Type 1 -Reactor grade unalloyed niobium,
1.1.2 R04210-Type 2 -Commercial grade unalloyed niobium,
1.1.3 R04251-Type 3 -Reactor grade niobium alloy containing 1% zirconium, and
1.1.4 R04261-Type 4 -Commercial grade niobium alloy containing 1% zirconium.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the test methods portion of this specification. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: B 393 – 99
Standard Specification for
Niobium and Niobium Alloy Strip, Sheet, and Plate
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B 393; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.1.2 plate—a flat product 6 in. (152.4 mm) or more in
width and greater than ⁄16in. (4.76 mm) in thickness.
1.1 This specification covers four grades of wrought nio-
3.1.3 sheet—a flat product 6 in. (152.4 mm) or more in
bium and niobium alloy strip, sheet, and plate as follows:
width and from 0.005 in. (0.13 mm) to ⁄16 in. (4.76 mm) in
NOTE 1—Committee B-10 has adopted “niobium” as the designation
thickness.
for Element No. 41, formerly named “columbium.”
3.1.4 strip—a flat product, which may be supplied in coil,
1.1.1 R04200-Type 1— Reactor grade unalloyed niobium,
less than 6 in. (152.4 mm) in width and from 0.005 in. (0.13
1.1.2 R04210-Type 2— Commercial grade unalloyed nio-
mm) to ⁄16 in. (4.76 mm) in thickness.
bium,
4. Ordering Information
1.1.3 R04251-Type 3— Reactor grade niobium alloy con-
taining 1 % zirconium, and
4.1 Orders for materials under this specification shall in-
1.1.4 R04261-Type 4— Commercial grade niobium alloy
clude the following information as applicable:
containing 1 % zirconium.
4.1.1 Type and grade (Section 1),
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
4.1.2 ASTM designation and year of issue,
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for
4.1.3 Method of manufacture (Section 5),
information only.
4.1.4 Temper designation (Section 8),
1.3 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the
4.1.5 Quantity in weight, number of pieces, and dimensions,
test methods portion of this specification. This standard does
4.1.6 Chemistry (Section 6),
not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any,
4.1.7 Mechanical properties (Section 7),
associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
4.1.8 Quality and finish (Section 10),
standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices
4.1.9 Sampling (Section 11),
and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior
4.1.10 Marking (Section 18),
to use.
4.1.11 Packaging (Section 19),
4.1.12 Required reports (Section 17),
2. Referenced Documents
4.1.13 Disposition of rejected material (Section 16), and
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4.1.14 Additions to the specification and supplementary
B 391 Specification for Niobium and Niobium Alloy In-
requirements, as required.
gots
5. Materials and Manufacture
E 8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
E 29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
5.1 Material covered by this specification shall be made
Determine Conformance with Specifications
from ingots that conform to Specification B 391 and that are
produced by vacuum or plasma arc melting, vacuum electron-
3. Terminology
beam melting, or a combination of these three methods.
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
5.2 The various niobium mill products covered by this
3.1.1 lot—a lot shall consist of all material produced from
specification are formed with the conventional extrusion,
the same ingot at one time, with the same cross section,
forging, swaging, rolling, and drawing equipment normally
processed with the same nominal metallurgical parameters and
available in metal working plants.
heat treated at the same conditions.
6. Chemical Requirements
6.1 The niobium and niobium alloy ingots and billets for
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B-10 on conversion to finished products covered by this specification
Reactive and Refractory Metals and Alloysand is the direct responsibility of
shall conform to the requirements for chemical composition
Subcommittee B10.03on Niobium and Tantalum.
and hardness as prescribed in Table 1 and Table 2.
Current edition approved Dec. 10, 1999. Published January 2000.
6.2 The manufacturer’s ingot analysis shall be considered
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 02.04.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
Copyright © ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
B 393
A
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements TABLE 4 Mechanical Properties for Material, Annealed
Condition (90 % Minimum Recrystallized)
Type 1 Type 2 Type 3 Type 4
(Reactor (Commercial (Reactor (Commercial
Elongation in 1-in. (25.4-
Ultimate Tensile Yield Strength
Grade Grade Grade Grade
mm) gage length, min, %
Grade Strength, min, (0.2 % offset),
Element Unalloyed Unalloyed Niobium- Niobium-
0.010 or Less Than
psi (MPa) min, psi (MPa)
Niobium) Niobium) 1% 1%
Greater 0.010
R04200 R04210 Zirconium) Zirconium)
Types 1 and 2 18 000 (125) 10 500 (73) 20 15
R04251 R04261
Types 3 and 4 28 000 (195) 18 000 (125) 20 15
A
Max Weight % (Except Where Otherwise Specified)
Refer to Section 14 for conditions of mechanical tests.
Each ingot:
Carbon 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01
that is, at least 90 % recrystallized.
Nitrogen 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01
8.2 Other temper designations, such as cold-worked temper
Oxygen 0.015 0.025 0.015 0.025
or stress-relieved temper, can be specified as agreed upon
Hydrogen 0.0015 0.0015 0.0015 0.0015
Zirconium 0.02 0.02 0.8 to 1.2 0.8 to 1.2
between the purchaser and the manufacturer at the time of
(range) (range)
purchase.
Tantalum 0.1 0.3 0.1 0.5
Iron 0.005 0.01 0.005 0.01
9. Permissible Variations in Dimensions and Weight
Silicon 0.005 0.005 0.005 0.005
Tungsten 0.03 0.05 0.03 0.05
9.1 Tolerances for thickness, width, and length for flat-
Nickel 0.005 0.005 0.005 0.005
rolled products covered by this specification shall be as
Molybdenum 0.010 0.020 0.010 0.050
Hafnium 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 prescribed in Table 5.
Titanium 0.02 0.03 0.02 0.03
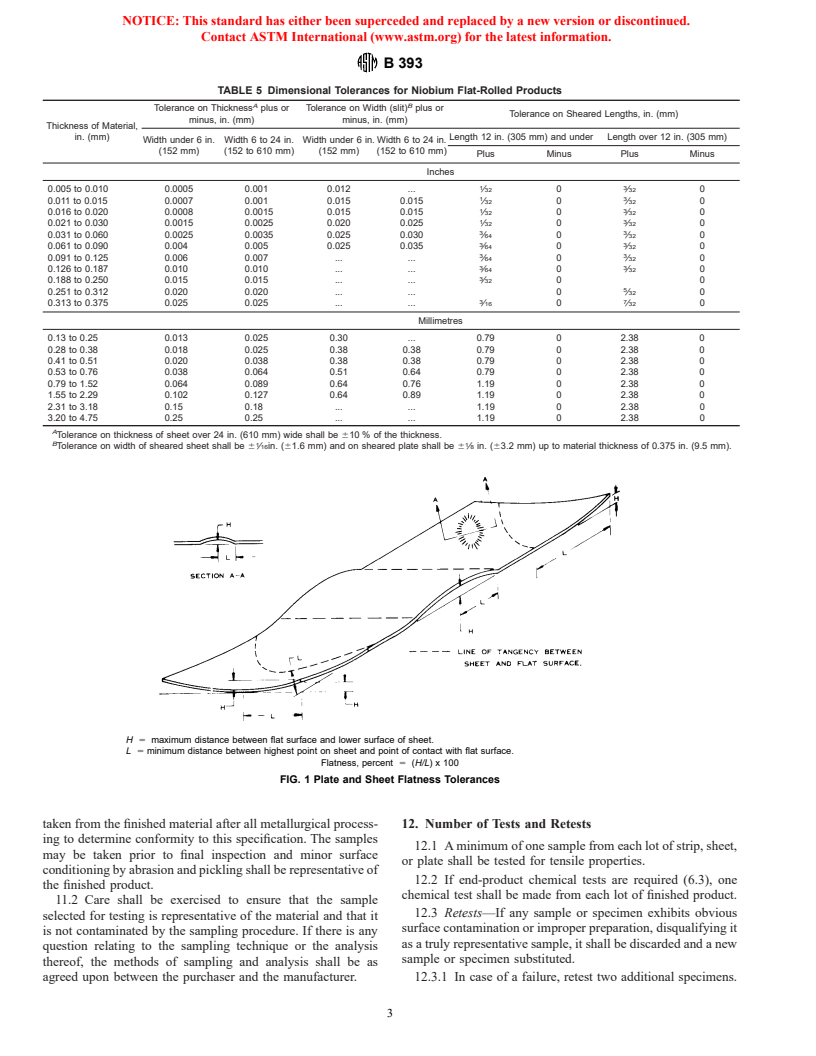
9.2 Flatness tolerance for sheet and plate products supplied
When specified:
under this specification shall be a maximum of 6 % as
Boron 2 ppm . 2 ppm .
Aluminum 0.002 0.005 0.002 0.005
determined by the following equation (see Fig. 1):
Beryllium 0.005 . 0.005 .
Flatness, % 5 ~H/L! 3 100
Chromium 0.002 . 0.002 .
Cobalt 0.002 . 0.002 . (1)
where:
H 5 maximum vertical distance between a flat reference
TABLE 2 Brinell Hardness
and the lower surface of the sheet, and
L 5 minimum horizontal distance between the highest
Type 1 Type 2 Type 3 Type 4
Maximum average 90 125 125 135
point on a sheet and the point of contact with a flat
Maximum per individual impression 105 150 140 150
reference surface. (Fig. 1 is included to illustrate the
method for taking measurements for calculation of
sheet flatness. However, a value of H less than ⁄32 in.
the chemical analysis for products supplied under this specifi-
(0.070 mm) shall not be cause for rejection.)
cation, except for interstitials as specified in 6.3.
9.3 Quantity or Weight—For orders requiring up to 100 lb
6.3 When requested by the purchaser at the time of pur-
(45.4 kg) of finished product, the manufacturer may overship
chase, the manufacturer shall furnish a report certifying the
by 20 %. When the order is for quantities up to 1000 lb (453.6
values of the interstitial elements (C, O, N, H) as prescribed in
kg), the manufacturer may overship by 10 %. The permissible
Table 3 for each lot of material supplied.
overshipment shall be negotiated for orders larger than this
7. Mechanical Requirements
quantity.
7.1 The annealed materials supplied under this specification
10. Quality and Finish
shall conform to the requirements for mechanical properties as
10.1 Finished niobium and niobium alloy strip, sheet, and
specified in Table 4.
plate shall be free of injurious internal and external imperfec-
8. Temper Designations
tions of a nature that will interfere with the purpose for which
it was intended. Material may be finished as rolled, as cleaned,
8.1 Unless otherwise stated, the materials supplied under
or as ground. If shipped as hot-worked, cold-worked, cleaned,
these specifications shall be in the fully annealed condition,
or ground, the manufacturer shall be permitted to remove
TABLE 3 Additional Chemical Requirements for Finished
minor surface imperfections, if such removal does not reduce
Product (When Specified by Purchaser)
the dimensions below the minimum permitted by the tolerances
Type 2 Type 3 Type 4
specified in Table 5.
Type 1
(Commercial (Reactor (Commercial
(Reactor Grade 10.2 The finished strip, sheet, or plate shall be visibly free of
Grade Grade Grade
Element Unalloyed
oxide, grease, oil, residual lubricants, and other extraneous
Unalloyed Niobium—1 % Niobium—1 %
Niobium)
Niobium) Zirconium) Zirconium)
materials.
R04200
R04210 R04251 R04261
10.3 Methods of testing for these defects and standards of
Max Weight %
acceptability shall be as agreed upon between the manufacturer
Oxygen 0.0250 0.0400 0.0250 0.0400
and the purchaser.
Carbon 0.0100 0.0150 0.0100 0.0150
Nitrogen 0.0100 0.0100 0.0100 0.0100
11. Sampling
Hydrogen 0.0015 0.0015 0.0015 0.0015
11.1 Samples fo
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.