ASTM A805/A805M-09
(Specification)Standard Specification for Steel, Flat Wire, Carbon, Cold-Rolled
Standard Specification for Steel, Flat Wire, Carbon, Cold-Rolled
ABSTRACT
This specification covers carbon steel flat wire in coils or cut lengths. The steel materials shall be produced from rimmed, capped, semi-killed, hot-rolled or cold-rolled steel. The steel specimens shall undergo cast or heat analysis and product analysis and shall conform to the required chemical compositions of carbon, manganese, phosphorus, sulfur, silicon, and copper. The desired edge shall be classified as follows: prepared edge of a specified contour produced when a very accurate width is required or when the finish of the edge suitable for electroplating is required, or both (Number 1 Edge); not applicable to flat wire products ( Number 2 Edge); approximately square edge produced by slitting (Number 3 Edge); rounded edge produced either by edge rolling or resulting from flat rolling of a round section (Number 4 Edge); square edge produced from slit-edge material on which the burr is eliminated by rolling or filling (Number 5 Edge); and square edge produced by edge rolling when the width tolerance and edge condition are not as exacting as for No. 1 Edge (Number 6 Edge). The dimensional tolerances shall conform to the required values of thickness, width and length. The steel materials shall conform to the required values of temper, Rockwell hardness and tensile strength.
SCOPE
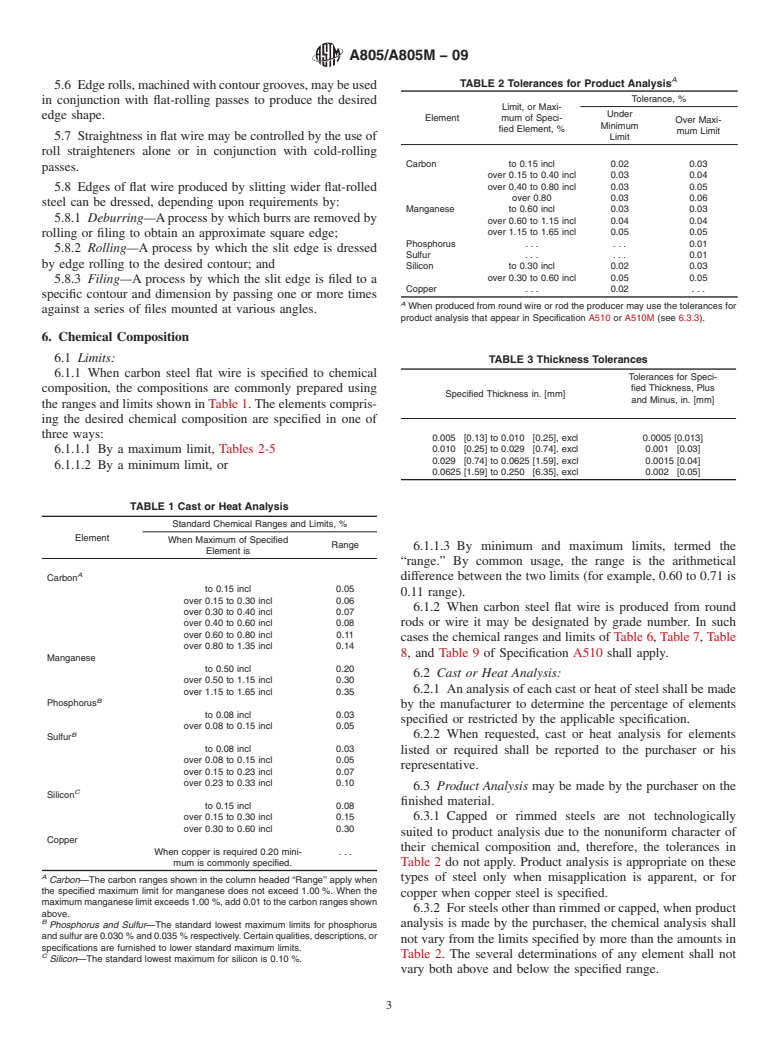
1.1 This specification covers carbon steel flat wire in coils or cut lengths. Flat wire is classified as a cold-rolled section, rectangular in shape, 0.500 in. [12.7 mm] or less in width and under 0.250 in. [6.35 mm] in thickness.
1.2 Low-carbon steel flat wire is produced from steel compositions with a maximum carbon content of 0.25 % by cast or heat analysis.
1.3 Carbon spring steel flat wire is produced to a carbon range in which the specified or required maximum is over 0.25 % by cast or heat analysis.
1.3.1 Two types of carbon spring steel flat wire are produced:
1.3.1.1 Untempered cold-rolled carbon spring steel flat wire, produced to several desirable combinations of properties and
1.3.1.2 Hardened and tempered carbon spring steel wire.
1.4 Definite application flat wire is a product developed for a specific application and may be specified only by size and descriptive name.
1.5 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with this specification.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:A805/A805M −09
StandardSpecification for
1
Steel, Flat Wire, Carbon, Cold-Rolled
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA805/A805M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* A510 Specification for General Requirements forWire Rods
and Coarse Round Wire, Carbon Steel
1.1 This specification covers carbon steel flat wire in coils
A510M Specification for General Requirements for Wire
or cut lengths. Flat wire is classified as a cold-rolled section,
Rods and Coarse Round Wire, Carbon Steel (Metric)
rectangular in shape, 0.500 in. [12.7 mm] or less in width and
3
(Withdrawn 2011)
under 0.250 in. [6.35 mm] in thickness.
A751 Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology for Chemi-
1.2 Low-carbon steel flat wire is produced from steel
cal Analysis of Steel Products
compositions with a maximum carbon content of 0.25 % by
E45 Test Methods for Determining the Inclusion Content of
cast or heat analysis.
Steel
E112 Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size
1.3 Carbon spring steel flat wire is produced to a carbon
range in which the specified or required maximum is over E140 Hardness Conversion Tables for Metals Relationship
Among Brinell Hardness, Vickers Hardness, Rockwell
0.25 % by cast or heat analysis.
1.3.1 Two types of carbon spring steel flat wire are pro- Hardness, Superficial Hardness, Knoop Hardness, Sclero-
scope Hardness, and Leeb Hardness
duced:
4
1.3.1.1 Untempered cold-rolled carbon spring steel flat
2.2 Military Standard:
wire, produced to several desirable combinations of properties MIL-STD-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
4
and
2.3 Federal Standard:
1.3.1.2 Hardened and tempered carbon spring steel wire.
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies)
5
2.4 SAE Standard:
1.4 Definite application flat wire is a product developed for
Recommended Practice SAE J 419 Methods of Measuring
a specific application and may be specified only by size and
Decarburization
descriptive name.
1.5 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units
3. Terminology
are to be regarded as standard. Within the text, the SI units are
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not
3.1.1 annealing—the process of heating to and holding at a
exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used inde-
suitable temperature and then cooling at a suitable rate, for
pendentlyoftheother.Combiningvaluesfromthetwosystems
such purposes as reducing hardness, facilitating cold working,
may result in non-conformance with this specification.
producing a desired microstructure, or obtaining desired
mechanical, physical, or other properties.
2. Referenced Documents
2
3.1.2 batch annealing—annealing that is generally per-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
formed in large cylindrical bell type or large rectangular box or
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
car-type furnaces. The product is protected from scaling and
of Steel Products
decarburization by the use of a controlled atmosphere that
envelops the charge in an inner chamber sealed to prevent the
influx of air or products of combustion. The coils or bundles
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
Stainless Steel and Related Alloysand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.19 on Steel Sheet and Strip.
3
Current edition approved May 1, 2009. Published June 2009. Originally The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
approved in 1982. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as A805 – 08. DOI: www.astm.org.
4
10.1520/A0805_A0805M-09. Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4,
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098, http://
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM www.dodssp.daps.mil.
5
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), 400 Commonwealth
the ASTM website. Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096-0001, http://www.sae.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A805/A805M−09
are heated to a temperature in the vicinity of the lower critical tempers are obtained by the selection and control of c
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:A 805–08 Designation: A 805/A 805M – 09
Standard Specification for
1
Steel, Flat Wire, Carbon, Cold-Rolled
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA 805/A 805M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers carbon steel flat wire in coils or cut lengths. Flat wire is classified as a cold-rolled section,
rectangular in shape, 0.500 in. [12.7 mm] or less in width and under 0.250 in. [6.35 mm] in thickness.
1.2 Low-carbon steel flat wire is produced from steel compositions with a maximum carbon content of 0.25 % by cast or heat
analysis.
1.3 Carbon spring steel flat wire is produced to a carbon range in which the specified or required maximum is over 0.25 % by
cast or heat analysis.
1.3.1 Two types of carbon spring steel flat wire are produced:
1.3.1.1 Untempered cold-rolled carbon spring steel flat wire, produced to several desirable combinations of properties and
1.3.1.2 Hardened and tempered carbon spring steel wire.
1.4 Definite application flat wire is a product developed for a specific application and may be specified only by size and
descriptive name.
1.5 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
only.The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded as standard.Within the text, the SI units are shown
in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used independently of the
other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with this specification.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A 370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing of Steel Products
A 510 Specification for General Requirements for Wire Rods and Coarse Round Wire, Carbon Steel
A 510M Specification for General Requirements for Wire Rods and Coarse Round Wire, Carbon Steel (Metric)
A 751 Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology for Chemical Analysis of Steel Products
E45 Test Methods for Determining the Inclusion Content of Steel
E112 Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size
E 140 Hardness Conversion Tables for Metals Relationship Among Brinell Hardness, Vickers Hardness, Rockwell Hardness,
Superficial Hardness, Knoop Hardness, and Scleroscope Hardness
3
2.2 Military Standard:
MIL-STD-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
3
2.3 Federal Standard:
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies)
4
2.4 SAE Standard:
Recommended Practice SAE J 419 Methods of Measuring Decarburization
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 annealing—the process of heating to and holding at a suitable temperature and then cooling at a suitable rate, for such
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM CommitteeA01 on Steel, Stainless Steel and RelatedAlloys and is the direct responsibility of SubcommitteeA01.19
on Steel Sheet and Strip.
Current edition approved March 1, 2008. Published March 2008. Originally approved in 1982. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as A805–93 (2002).
Current edition approved May 1, 2009. Published June 2009. Originally approved in 1982. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as A 805 – 08.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4, Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098, http://www.dodssp.daps.mil.
4
Available from Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), 400 Commonwealth Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096-0001, http://www.sae.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A 805/A 805M – 09
purposes as reducing hardness, facilitating cold working, producing a desired microstructure, or obtaining desired mechanical,
physical, or other properties.
3.1.2 batch annealing—annealing that is generally pe
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.