ASTM E2141-21
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Accelerated Aging of Electrochromic Devices in Sealed Insulating Glass Units
Standard Test Method for Accelerated Aging of Electrochromic Devices in Sealed Insulating Glass Units
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 EC glazings perform a number of important functions in a building envelope including: minimizing the solar energy heat gain; providing for passive solar energy gain; controlling a variable visual connection with the outside world; enhancing human comfort (heat gain), illumination, and glare control; and providing for architectural expression. It is therefore important to understand the relative serviceability of these glazings.
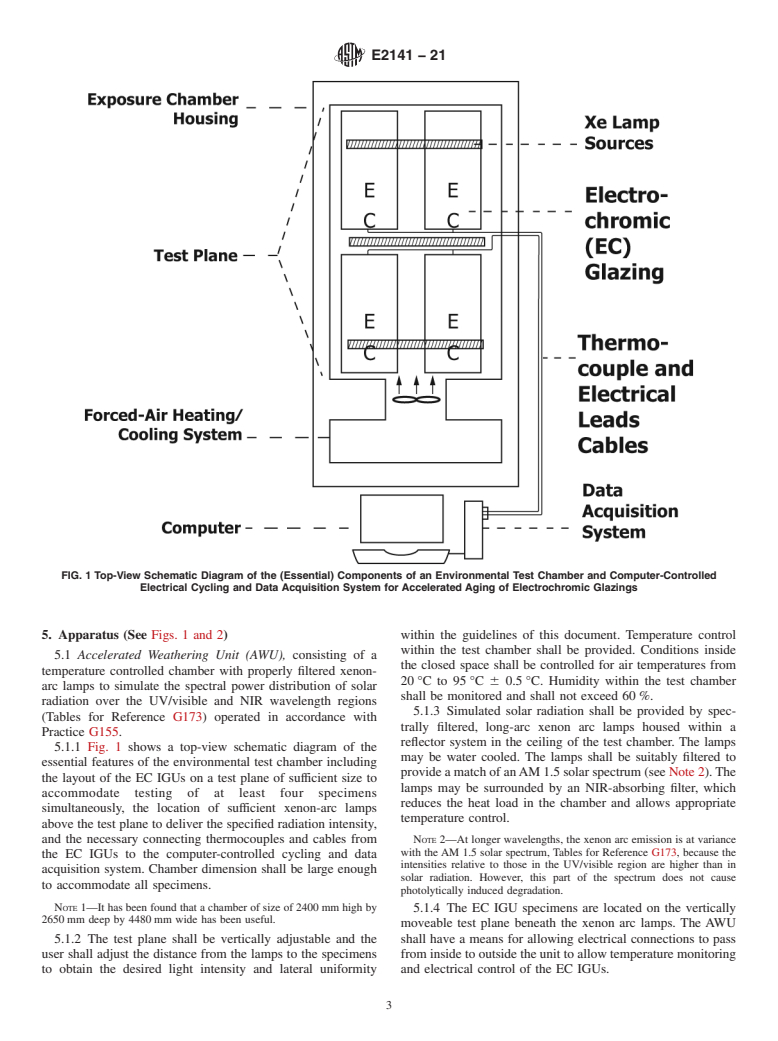
4.2 This test method is intended to provide a means for evaluating the relative serviceability of EC Glazings as described in Section 1.
4.3 The procedures in this test method include (a) rapid but realistic current-voltage cycling tests emphasizing the electrical properties, and (b) environmental test parameters that are typically used in weatherability tests by standards organizations and are realistic for the intended use of large-area EC IGUs.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the accelerated aging of electrochromic devices (ECD) integrated in insulating glass units.
1.2 The test method is applicable for any electrochromic device incorporated into sealed insulating glass units (IGUs) fabricated for vision glass (superstrate and substrate) areas for use in buildings, such as sliding doors, windows, skylights, and exterior wall systems. The layers used for constructing the EC device and electrochromically changing the optical properties may be inorganic or organic materials.
1.3 The electrochromic (EC) glazings used in this test method are exposed to environmental conditions, including solar radiation. They are employed to control the amount of transmitted radiation by absorption and reflection and, thus, limit the solar heat gain and amount of solar radiation that is transmitted into the building.
1.4 The test method is not applicable to other chromogenic devices, such as, photochromic and thermochromic devices which do not respond to electrical stimulus.
1.5 The test method is not applicable to electrochromic (EC) glazings that are constructed from superstrate or substrate materials other than glass.
1.6 The test method referenced herein is a laboratory test conducted under specified conditions. The test is intended to simulate and, in some cases, to also accelerate actual in-service use of the electrochromic glazing. Results from these tests cannot be used to predict the performance with time of in-service units unless actual corresponding in-service tests have been conducted and appropriate analyses have been conducted to show how performance can be predicted from the accelerated aging tests.
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.9 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: E2141 − 21
Standard Test Method for
Accelerated Aging of Electrochromic Devices in Sealed
1
Insulating Glass Units
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2141; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
1.1 This test method covers the accelerated aging of elec-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
trochromic devices (ECD) integrated in insulating glass units.
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
1.2 The test method is applicable for any electrochromic
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
device incorporated into sealed insulating glass units (IGUs)
1.9 This international standard was developed in accor-
fabricated for vision glass (superstrate and substrate) areas for
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
useinbuildings,suchasslidingdoors,windows,skylights,and
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
exterior wall systems. The layers used for constructing the EC
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
device and electrochromically changing the optical properties
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
may be inorganic or organic materials.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
1.3 The electrochromic (EC) glazings used in this test
method are exposed to environmental conditions, including
2. Referenced Documents
solar radiation. They are employed to control the amount of
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
transmitted radiation by absorption and reflection and, thus,
C168Terminology Relating to Thermal Insulation
limit the solar heat gain and amount of solar radiation that is
E177Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
transmitted into the building.
ASTM Test Methods
1.4 The test method is not applicable to other chromogenic
E631Terminology of Building Constructions
devices, such as, photochromic and thermochromic devices
E691Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
which do not respond to electrical stimulus.
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
E2953Specification for Evaluating Accelerated Aging Per-
1.5 Thetestmethodisnotapplicabletoelectrochromic(EC)
formance of Electrochromic Devices in Sealed Insulating
glazings that are constructed from superstrate or substrate
Glass Units
materials other than glass.
G113Terminology Relating to Natural andArtificial Weath-
1.6 The test method referenced herein is a laboratory test
ering Tests of Nonmetallic Materials
conducted under specified conditions. The test is intended to
G155PracticeforOperatingXenonArcLampApparatusfor
simulateand,insomecases,toalsoaccelerateactualin-service
Exposure of Materials
use of the electrochromic glazing. Results from these tests
G173TablesforReferenceSolarSpectralIrradiances:Direct
cannot be used to predict the performance with time of
Normal and Hemispherical on 37° Tilted Surface
in-service units unless actual corresponding in-service tests
3
2.2 ISO Standard:
have been conducted and appropriate analyses have been
ISO 9050 Glass in building - Determination of light
conductedtoshowhowperformancecanbepredictedfromthe
transmittance,solardirecttransmittance,totalsolarenergy
accelerated aging tests.
transmittance, ultraviolet transmittance and related glaz-
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
ing factors
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
standard.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E06 on contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Performance of Buildings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E06.22 Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
on Durability Performance of Building Constructions. the ASTM website.
3
Current edition approved Oct. 15, 2021. Published December 2021. Originally Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), ISO
approved in 2001. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as E2141–14. DOI: Central Secretariat, Chemin de Blandonnet 8, CP 401, 1214 Vernier, Geneva,
10.1520/E2141-21. Switzerland, https://www.iso.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohock
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E2141 − 14 E2141 − 21
Standard Test Method for
Accelerated Aging of Electrochromic Devices in Sealed
1
Insulating Glass Units
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2141; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the accelerated aging of electrochromic devices (ECD) integrated in insulating glass units.
1.2 The test method is applicable for any electrochromic device incorporated into sealed insulating glass units (IGUs) fabricated
for vision glass (superstrate and substrate) areas for use in buildings, such as sliding doors, windows, skylights, and exterior wall
systems. The layers used for constructing the EC device and electrochromically changing the optical properties may be inorganic
or organic materials.
1.3 The electrochromic (EC) glazings used in this test method are exposed under use conditions to solar radiation and are
deployedto environmental conditions, including solar radiation. They are employed to control the amount of transmitted radiation
by absorption and reflection and, thus, limit the solar heat gain and amount of solar radiation that is transmitted into the building.
1.4 The test method is not applicable to other chromogenic devices, such as, photochromic and thermochromic devices which do
not respond to electrical stimulus.
1.5 The test method is not applicable to electrochromic (EC) glazings that are constructed from superstrate or substrate materials
other than glass.
1.6 The test method referenced herein is a laboratory test conducted under specified conditions. The test is intended to simulate
and, in some cases, to also accelerate actual in-service use of the electrochromic windows.glazing. Results from these tests cannot
be used to predict the performance with time of in-service units unless actual corresponding in-service tests have been conducted
and appropriate analyses have been conducted to show how performance can be predicted from the accelerated aging tests.
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.7.1 Exception—Inch-pound units are used 7.6.2.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E06 on Performance of Buildings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E06.22 on Durability
Performance of Building Constructions.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2014Oct. 15, 2021. Published February 2015December 2021. Originally approved in 2001. Last previous edition approved in 20122014
as E2141 – 12.E2141 – 14. DOI: 10.1520/E2141-14.10.1520/E2141-21.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E2141 − 21
1.9 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C168 Terminology Relating to Thermal Insulation
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in ASTM Test Methods
E631 Terminology of Building Constructions
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
E2953 Specification for Evaluating Accelerated Aging Performance of Electrochromic Devices in Sealed Insulating Glass Units
G113 Terminology Relating to Natural and Artificial Weathering Tests of Nonmetallic Materials
G155 Practice for Operating Xenon Arc Lamp Apparatus for Exposure of Materials
G173 Tables for Reference Solar Spectral Irradiances: Direct Normal and Hemispherical on 37° Tilted Surface
3
2.2 ISO Standard:
ISO 9050 Glass in building - Determination of light transmittance, solar direct transmittance, total solar energy transmittance,
ultraviolet tr
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.