ASTM F1264-03(2007)
(Specification)Standard Specification and Test Methods for Intramedullary Fixation Devices
Standard Specification and Test Methods for Intramedullary Fixation Devices
SCOPE
1.1 This specification is intended to provide a characterization of the design and mechanical function of intramedullary fixation devices (IMFDs) specify labeling and material requirements, provide test methods for characterization of IMFD mechanical properties and identify needs for further development of test methods and performance criteria. The ultimate goal is to develop a standard which defines performance criteria and methods for measurement of performance-related mechanical characteristics of IMFDs and their fixation to bone. It is not the intention of this specification to define levels of performance or case-specific clinical performance of these devices, as insufficient knowledge is available to predict the consequences of the use of any of these devices in individual patients for specific activities of daily living. It is not the intention of this specification to describe or specify specific designs for IMFDs.
1.2 This specification describes IMFDs for surgical fixation of the skeletal system. It provides basic IFMD geometrical definitions, dimensions, classification, and terminology; labeling and material specifications; performance definitions; test methods and characteristics determined to be important to in-vivo performance of the device.
1.3 This specification includes four standard test methods:
1.3.1 Static Four-Point Bend Test Method- and
1.3.2 Static Torsion Test Method-.
1.3.3 Bending Fatigue Test Method-Annex A1.
1.3.4 Test Method for Bending Fatigue of IMFD Locking Screws-Annex A2.
1.4 A rationale is given in Appendix X1.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F 1264 – 03 (Reapproved 2007)
Standard Specification and Test Methods for
1
Intramedullary Fixation Devices
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 1264; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope A 214/A 214M Specification for Electric-Resistance-
Welded Carbon Steel Heat-Exchanger and Condenser
1.1 This specification is intended to provide a characteriza-
Tubes
tion of the design and mechanical function of intramedullary
A 450/A 450M Specification for General Requirements for
fixationdevices(IMFDs)specifylabelingandmaterialrequire-
Carbon, Ferritic Alloy, and Austenitic Alloy Steel Tubes
ments, provide test methods for characterization of IMFD
D 790 TestMethodsforFlexuralPropertiesofUnreinforced
mechanical properties and identify needs for further develop-
and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials
ment of test methods and performance criteria. The ultimate
E4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
goal is to develop a standard which defines performance
E 691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
criteria and methods for measurement of performance-related
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
mechanicalcharacteristicsofIMFDsandtheirfixationtobone.
F86 Practice for Surface Preparation and Marking of Me-
It is not the intention of this specification to define levels of
tallic Surgical Implants
performance or case-specific clinical performance of these
F 138 Specification for Wrought 18Chromium-14Nickel-
devices, as insufficient knowledge is available to predict the
2.5Molybdenum Stainless Steel Bar and Wire for Surgical
consequences of the use of any of these devices in individual
Implants (UNS S31673)
patients for specific activities of daily living. It is not the
3
F 339 Specification for Cloverleaf Intramedullary Pins
intention of this specification to describe or specify specific
F 383 Practice for Static Bend and Torsion Testing of
designs for IMFDs.
3
Intramedullary Rods
1.2 This specification describes IMFDs for surgical fixation
F 565 Practice for Care and Handling of Orthopedic Im-
of the skeletal system. It provides basic IFMD geometrical
plants and Instruments
definitions, dimensions, classification, and terminology; label-
F 1611 Specification for Intramedullary Reamers
ing and material specifications; performance definitions; test
2.2 AMS Standard:
methods and characteristics determined to be important to
AMS5050 SteelTubing,Seamless,0.15Carbon,Maximum
in-vivo performance of the device.
4
Annealed
1.3 This specification includes four standard test methods:
2.3 SAE Standard:
1.3.1 Static Four-Point Bend Test Method—Annex A1 and
SAEJ524 SeamlessLow-CarbonSteelTubingAnnealedfor
1.3.2 Static Torsion Test Method—Annex A2.
4
Bending and Flaring
1.3.3 Bending Fatigue Test Method—Annex A3.
1.3.4 Test Method for Bending Fatigue of IMFD Locking
3. Terminology
Screws—Annex A4.
3.1 Definitions for Geometric:
1.4 A rationale is given in Appendix X1.
3.1.1 closed section, n—any cross section perpendicular to
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
thelongitudinalaxisofasolidIMFDorhollowIMFDinwhich
standard.
there is no discontinuity of the outer wall. To orient the IMFD
2. Referenced Documents for testing and for insertion, the desired relationship of any
2
irregularities, asymetries, and so forth, to the sagittal and
2.1 ASTM Standards:
coronal planes should be described for the intended applica-
tions.
3.1.2 IMFD curvature, n—dimensions of size and locations
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F04 on
of arcs of the curvature, or mathematical description of the
Medical and Surgical Materials and Devices and is the direct responsibility of
curvature, or other quantitative descriptions to which the
Subcommittee F04.21 on Osteosynthesis.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2007. Published October 2007. Originally
approved in 1989. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as F 1264 – 03.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
3
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Withdrawn.
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), 400 Commonwealth
the ASTM website. Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096-0001, http://www.sae.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F 1264 – 03 (2007)
curvature is manufactured along with tole
...







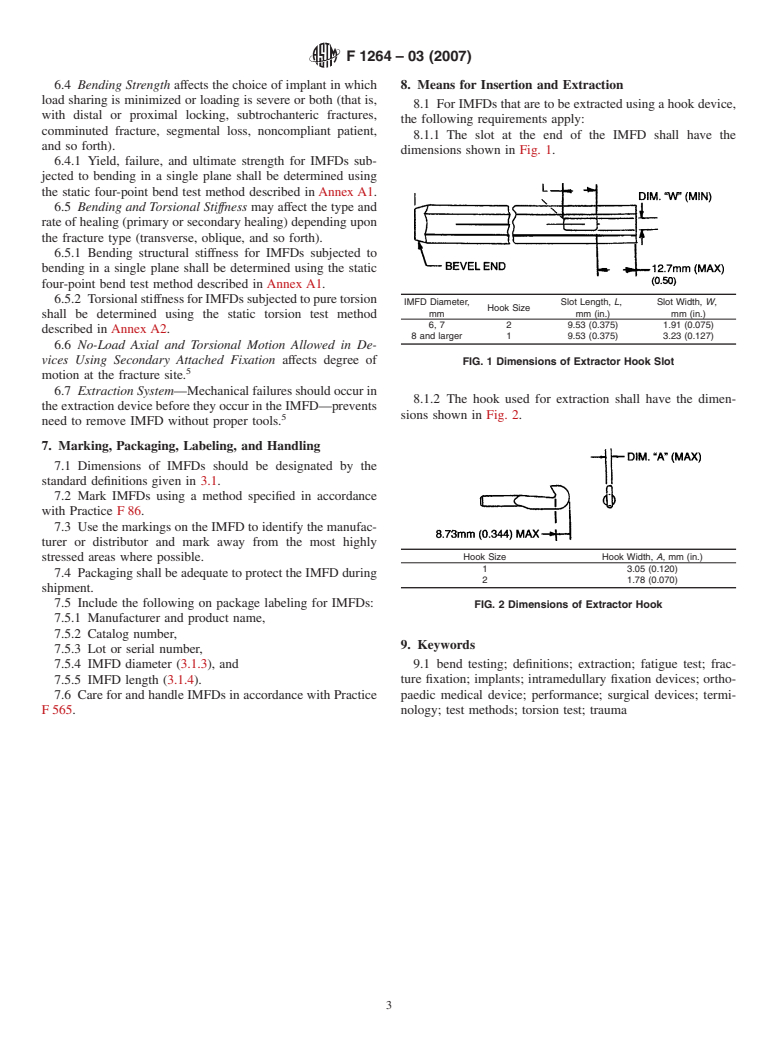
Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.