ASTM D4535-13
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Measurement of Thermal Expansion of Rock Using Dilatometer
Standard Test Methods for Measurement of Thermal Expansion of Rock Using Dilatometer
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Information concerning the thermal expansion characteristics of rocks is important in the design of any underground excavation where the surrounding rock may be heated. Thermal strain causes thermal stresses which ultimately affect excavation stability. Examples of applications where rock thermal strain is important include: nuclear waste repositories, underground power stations, compressed air energy storage facilities, and geothermal energy facilities.
5.2 The coefficient of thermal expansion, α, of rock is known to vary as the temperature changes. These methods provide continuous thermal strain values as a function of temperature, and therefore provide information on how the coefficient of thermal expansion changes with temperature.
5.3 Rocks are also often anisotropic, thus displaying different thermal strains depending on the orientation of strain measurement. These methods allow for measuring strain in one direction only. If anisotropy is expected, specimens with different orientations should be prepared and tested. Note 1—The quality of the result produced by this standard is dependent on the competence of the personnel performing it, and the suitability of the equipment and facilities used. Agencies that meet the criteria of Practice D3740 are generally considered capable of competent and objective testing. Users of this standard are cautioned that compliance with Practice D3740 does not in itself assure reliable results. Reliable results depend on many factors; Practice D3740 provides a means of evaluating some of those factors.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover the laboratory measurement of the one-dimensional linear thermal expansion of rocks using a dilatometer.
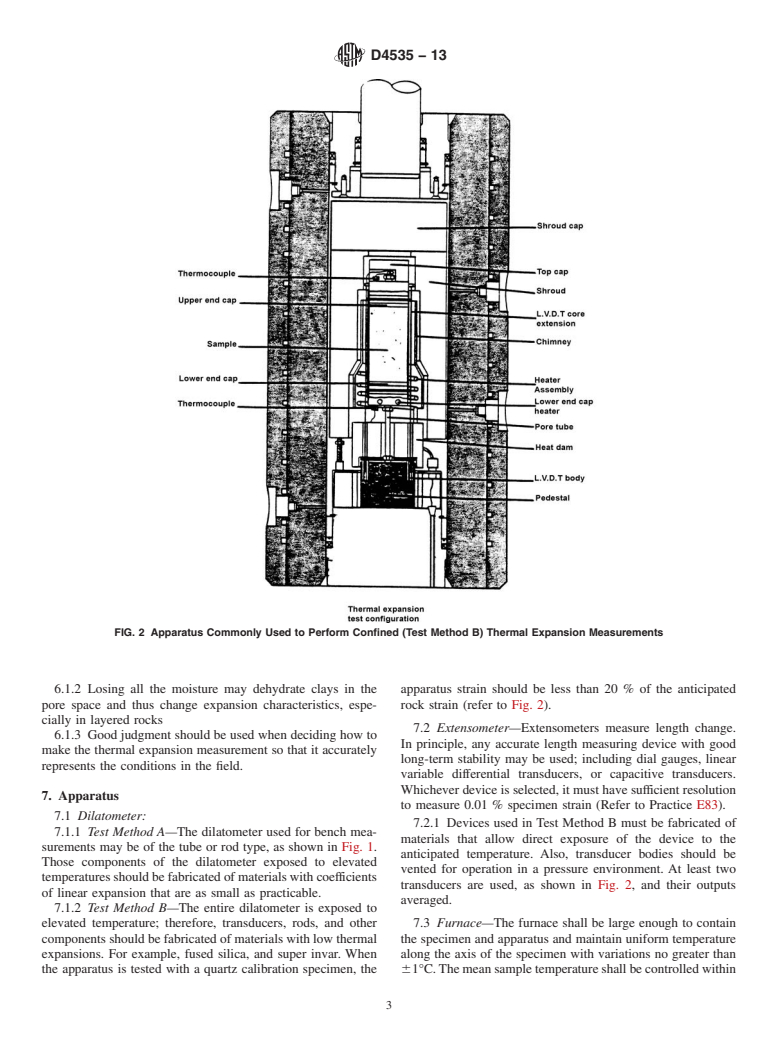
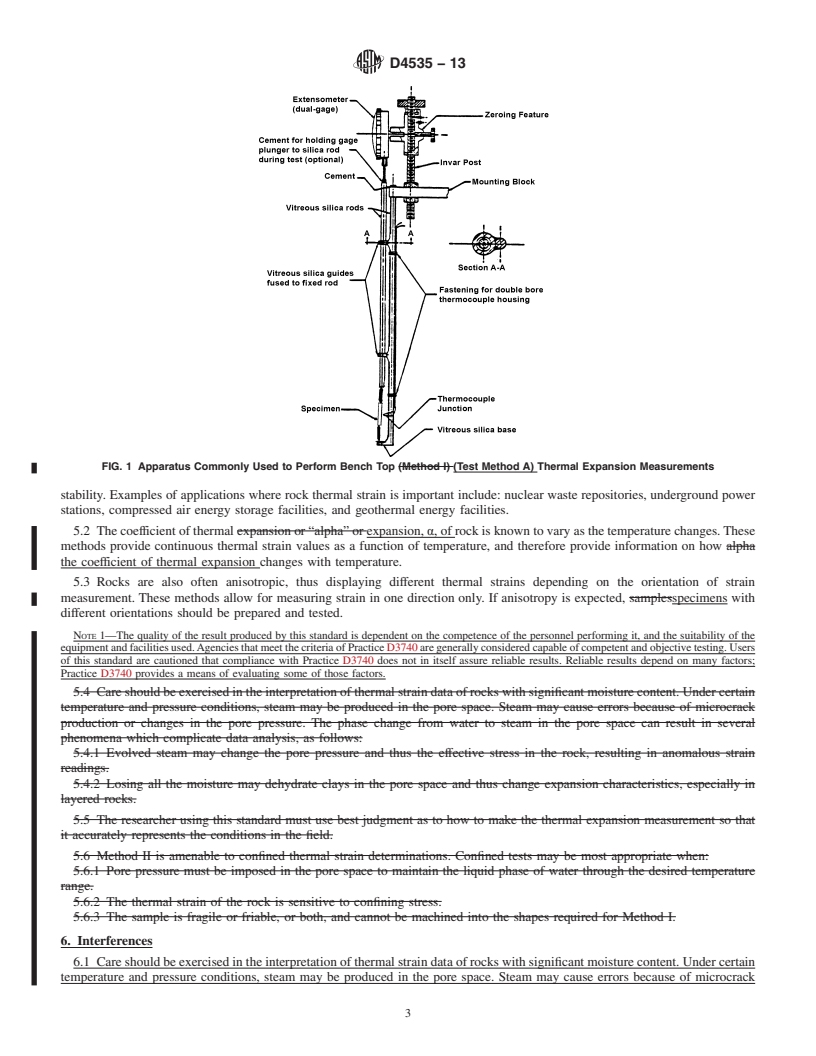
1.2 These test methods are applicable between temperatures of 25°C to 300°C. Both bench top and confined measurement techniques are presented. Test Method A is used for unconfined or bench top measurements and Test Method B is used for confined conditions. Rocks of varying moisture content can be tested.
1.3 For satisfactory results in conformance with these test methods, the principles governing the size, construction, and use of the apparatus described in these test methods should be followed. If the results are to be reported as having been obtained by either test method, then the pertinent requirements prescribed by that test method shall be met.
1.4 These test methods do not establish details of construction and procedures to cover all test situations that might offer difficulties to a person without technical knowledge concerning the theory of heat flow, temperature measurement, and general testing practices. Standardization of these test methods does not reduce the need for such technical knowledge.
1.5 All observed and calculated values shall conform to the guidelines for significant digits and rounding established in Practice D6026.
1.6 The procedures used to specify how data are collected/recorded or calculated, in this standard are regarded as the industry standard. In addition, they are representative of the significant digits that generally should be retained. The procedures used do not consider material variation, purpose for obtaining the data, special purpose studies, or any considerations for the user’s objectives; and it is common practice to increase or reduce significant digits of reported data to be commensurate with these considerations. It is beyond the scope of this standard to consider significant digits used in analytical methods for engineering design.
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to inch-pound units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety an...
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D4535 − 13
StandardTest Methods for
Measurement of Thermal Expansion of Rock Using
1
Dilatometer
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4535; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope of this standard to consider significant digits used in analytical
methods for engineering design.
1.1 Thesetestmethodscoverthelaboratorymeasurementof
the one-dimensional linear thermal expansion of rocks using a 1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
dilatometer. standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to inch-pound units that are provided for informa-
1.2 Thesetestmethodsareapplicablebetweentemperatures
tion only and are not considered standard.
of 25°C to 300°C. Both bench top and confined measurement
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the
techniquesarepresented.TestMethodAisusedforunconfined
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
or bench top measurements and Test Method B is used for
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
confined conditions. Rocks of varying moisture content can be
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
tested.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.3 For satisfactory results in conformance with these test
methods, the principles governing the size, construction, and
2. Referenced Documents
use of the apparatus described in these test methods should be
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
followed. If the results are to be reported as having been
D653Terminology Relating to Soil, Rock, and Contained
obtained by either test method, then the pertinent requirements
Fluids
prescribed by that test method shall be met.
D2216Test Methods for Laboratory Determination ofWater
1.4 These test methods do not establish details of construc-
(Moisture) Content of Soil and Rock by Mass
tion and procedures to cover all test situations that might offer
D3740Practice for Minimum Requirements for Agencies
difficultiestoapersonwithouttechnicalknowledgeconcerning
Engaged in Testing and/or Inspection of Soil and Rock as
the theory of heat flow, temperature measurement, and general
Used in Engineering Design and Construction
testing practices. Standardization of these test methods does
D6026Practice for Using Significant Digits in Geotechnical
not reduce the need for such technical knowledge.
Data
1.5 All observed and calculated values shall conform to the
E122PracticeforCalculatingSampleSizetoEstimate,With
guidelines for significant digits and rounding established in
Specified Precision, the Average for a Characteristic of a
Practice D6026.
Lot or Process
E83Practice for Verification and Classification of Exten-
1.6 The procedures used to specify how data are collected/
someter Systems
recorded or calculated, in this standard are regarded as the
E228Test Method for Linear Thermal Expansion of Solid
industry standard. In addition, they are representative of the
Materials With a Push-Rod Dilatometer
significant digits that generally should be retained. The proce-
dures used do not consider material variation, purpose for
3. Terminology
obtaining the data, special purpose studies, or any consider-
ations for the user’s objectives; and it is common practice to
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
increase or reduce significant digits of reported data to be
3.1.1 For definitions of common technical terms in this
commensuratewiththeseconsiderations.Itisbeyondthescope
standard, refer to Terminology D653.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1
ThesetestmethodsareunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD18onSoil
and Rock and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D18.12 on Rock
2
Mechanics. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2013. Published December 2013. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1985. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as D4535–08. DOI: Standardsvolume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/D4535-13. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4535 − 13
3.2.1 specimen thermal strain, ε—change in length, (L – 4.1.2 Test Method B is most suited for the measurement of
t 2
L ), divided by the original length, L , of the specimen when rock thermal strain under confined conditions and employs a
1 0
the specimen is subjected t
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D4535 − 08 D4535 − 13
Standard Test Methods for
Measurement of Thermal Expansion of Rock Using
1
Dilatometer
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4535; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*Scope
1.1 These test methods cover the laboratory measurement of the one-dimensional linear (one-dimensional) thermal expansion
of rocks using a dilatometer.
1.2 These test methods are applicable between temperatures of 25°C to 300°C. Both bench top and confined measurement
techniques are presented. Test Method A is used for unconfined or bench top measurements and Test Method B is used for confined
conditions. Rocks of varying moisture content can be tested.
1.3 For satisfactory results in conformance with these test methods, the principles governing the size, construction, and use of
the apparatus described in these test methods should be followed. If the results are to be reported as having been obtained by this
either test method, then allthe pertinent requirements prescribed in this by that test method shall be met.
1.4 These test methods do not establish details of construction and procedureprocedures to cover all test situations that might
offer difficulties to a person without technical knowledge concerning the theory of heat flow, temperature measurement, and general
testing practices. Standardization of these test methods does not reduce the need for such technical knowledge. It is recognized also
that it would be unwise, because of the standardization of this method, to resist in any way the further development of improved
or new methods or procedures by research workers.
1.5 All observed and calculated values shall conform to the guidelines for significant digits and rounding established in Practice
D6026.
1.6 The procedures used to specify how data are collected/recorded or calculated, in this standard are regarded as the industry
standard. In addition, they are representative of the significant digits that generally should be retained. The procedures used do not
consider material variation, purpose for obtaining the data, special purpose studies, or any considerations for the user’s objectives;
and it is common practice to increase or reduce significant digits of reported data to be commensurate with these considerations.
It is beyond the scope of this standard to consider significant digits used in analytical methods for engineering design.
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to inch-pound units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D653 Terminology Relating to Soil, Rock, and Contained Fluids
D2216 Test Methods for Laboratory Determination of Water (Moisture) Content of Soil and Rock by Mass
D3740 Practice for Minimum Requirements for Agencies Engaged in Testing and/or Inspection of Soil and Rock as Used in
Engineering Design and Construction
D6026 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Geotechnical Data
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D18 on Soil and Rock and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D18.12 on Rock Mechanics.
Current edition approved July 1, 2008Nov. 1, 2013. Published July 2008December 2013. Originally approved in 1985. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as
D4535 – 85 (2004).D4535 – 08. DOI: 10.1520/D4535-08.10.1520/D4535-13.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standardsvolume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4535 − 13
E122 Practice for Calculating Sample Size to Estimate, Wi
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.