ASTM A580/A580M-98
(Specification)Standard Specification for Stainless Steel Wire
Standard Specification for Stainless Steel Wire
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers stainless steel wire, except the free-machining types. It includes round, square, octagon, hexagon, and shape wire in coils only for the more commonly used types of stainless steels for general corrosion resistance and high-temperature service. For bars in straightened and cut lengths, see Specifications A276 or A479/ A479M. Note 1-For free-machining stainless wire, designed especially for optimum machinability, see Specification A581/A581M.
1.2 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI (metric) units are to be regarded separately as standards; within the text and tables, the SI units are shown in [brackets]. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification.
1.3 Unless the order specifies the applicable "M" specification designation, the material shall be furnished to the inch-pound units.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: A 580/A 580M – 98
Standard Specification for
Stainless Steel Wire
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 580/A 580M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope 2.2 Society of Automotive Engineers Standard:
J 1086 Numbering Metals and Alloys
1.1 This specification covers stainless steel wire, except the
free-machining types. It includes round, square, octagon,
3. Ordering Information
hexagon, and shape wire in coils only for the more commonly
3.1 It is the responsibility of the purchaser to specify all
used types of stainless steels for general corrosion resistance
requirements that are necessary for material ordered under this
and high-temperature service. For bars in straightened and cut
specification. Such requirements may include, but are not
lengths, see Specifications A 276 or A 479/A 479M.
limited to, the following:
NOTE 1—For free-machining stainless wire, designed especially for
3.1.1 Quantity (weight),
optimum machinability, see Specification A 581/A 581M.
3.1.2 Name of material (stainless steel),
1.2 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI
3.1.3 Type or UNS designation (Table 1),
(metric) units are to be regarded separately as standards; within
3.1.4 Condition (4.1),
the text and tables, the SI units are shown in [brackets]. The
3.1.5 Finish (4.2),
values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; there-
3.1.6 Cross section (round, square, etc.),
fore, each system must be used independently of the other.
3.1.7 Applicable dimensions including size, thickness and
Combining values from the two systems may result in noncon-
width.
formance with the specification.
3.1.8 ASTM designation A 580/A 580M and date of issue.
1.3 Unless the order specifies the applicable “M” specifica-
3.1.9 Coil diameter (inside or outside diameter, or both) and
tion designation, the material shall be furnished to the inch-
coil weight.
pound units.
3.1.10 Special requirements.
NOTE 2—A typical ordering description is as follows: 5000 lb [2000 kg]
2. Referenced Documents
Type 304, wire, annealed and cold drawn, ⁄2 in. [13 mm] round, ASTM
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Specification A 580/A 580M dated . End use: machined hydraulic
A 276 Specification for Stainless and Heat-Resisting Steel
coupling parts.
Bars and Shapes
4. Manufacture
A 370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
of Steel Products
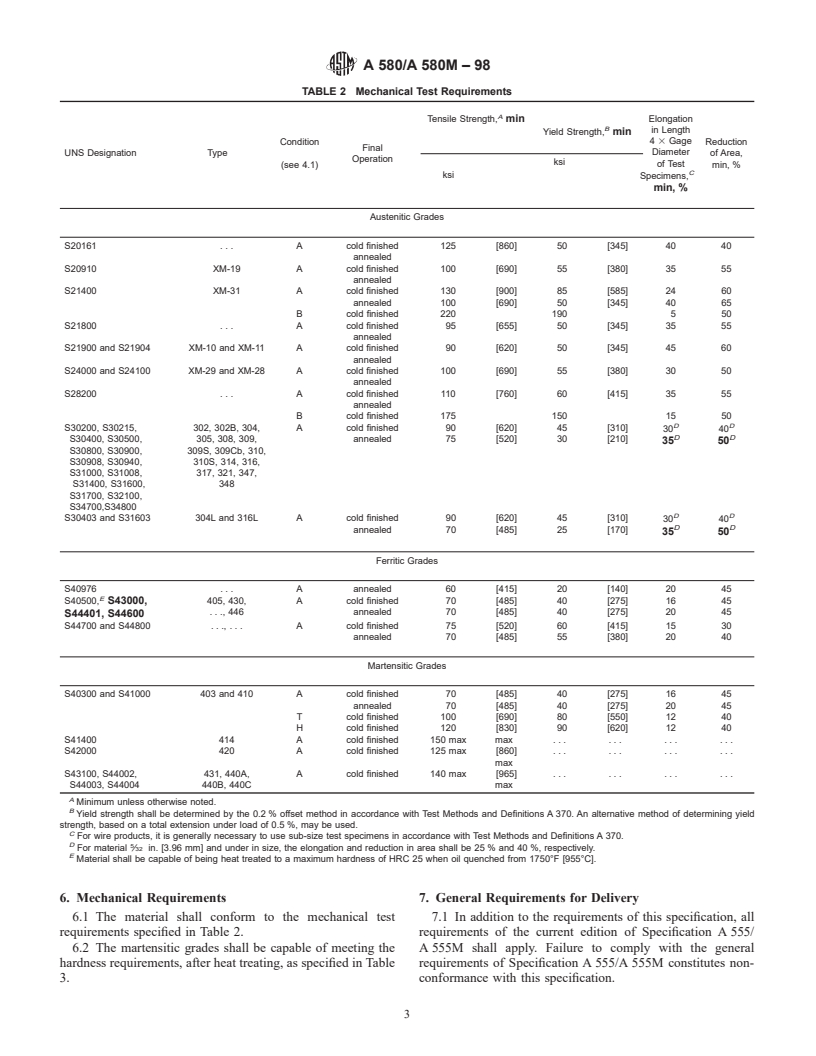
4.1 Condition (Table 2):
A 479/A 479M Specification for Stainless and Heat-
4.1.1 Condition A—Annealed as a final heat treatment.
Resisting Steel Bars, and Shapes for Use in Boilers and
Material in Condition A may be given a final cold drawing for
Other Pressure Vessels
size control or finish, or both, slightly raising tensile strength.
A 555/A 555M Specification for General Requirements for
4.1.2 Condition B—Cold worked to higher strength.
Stainless Steel Wire and Wire Rods
4.1.3 Condition T—Heat treated to an intermediate temper
A 581/A 581M Specification for Free-Machining Stainless
generally by austenitizing, quenching, and tempering at a
Steel Wire and Wire Rods
relatively low temperature.
E 527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys (UNS)
4.1.4 Condition H—Heat treated to a hard temper generally
by austenitizing, quenching, and tempering at a relatively low
temperature.
4.2 Finish:
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
Stainless Steel, and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee 4.2.1 Cold Drawn—A finish resulting from a final cold
A01.17 on Flat Stainless Steel Products.
drawing pass, generally with cold drawing lubricant left on.
Current edition approved June 10, 1998. Published September 1998. Originally
published as A 580 – 67. Last previous edition A 580 – 95a.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.05.
3 5
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.03. Available from Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), 400 Commonwealth
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.01. Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
A 580/A 580M – 98
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
Composition, %
UNS
Manga- Phos- Sul-
Desig- Type
Carbon, Silicon,
A nese, phorus, fur, Chromium Nickel Molybdenum Nitrogen Other Elements
B B
nation
max max
B
max max max
Austenitic Grades
S20161 . 0.15 4.0–6.0 0.040 0.040 3.0–4.0 15.0–18.0 4.0–6.0 0.08–0.20
S20910 XM-19 0.06 4.0–6.0 0.040 0.030 1.00 20.5–23.5 11.5–13.5 1.50–3.00 0.20–0.40 Cb 0.10–0.30
V 0.10–0.30
S21400 XM-31 0.12 14.0–16.0 0.045 0.030 0.30–1.00 17.0–18.5 1.00 0.35 max
max
S21800 . 0.10 7.0–9.0 0.060 0.030 3.5–4.5 16.0–18.0 8.0–9.0 0.08–0.18
S21900 XM-10 0.08 8.0–10.0 0.060 0.030 1.00 19.0–21.5 5.5–7.5 0.15–0.40
S21904 XM-11 0.04 8.0–10.0 0.060 0.030 1.00 19.0–21.5 5.5–7.5 0.15–0.40
S24000 XM-29 0.08 11.5–14.5 0.060 0.030 1.00 17.0–19.0 2.3–3.7 0.20–0.40
S24100 XM-28 0.15 11.0–14.0 0.040 0.030 1.00 16.5–19.0 0.5–2.50 0.20–0.45
S28200 . 0.15 17.0–19.0 0.045 0.030 1.00 17.0–19.0 . 0.75–1.25 0.40–0.60 Cu 0.75–1.25
0.10 max
S30200 302 0.15 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 17.0–19.0 8.0–10.0 0.10 max
S30215 302B 0.15 2.00 0.045 0.030 2.00–3.00 17.0–19.0 8.0–10.0
S30400 304 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 18.0–20.0 8.0–10.5 0.10 max
C
S30403 304L 0.030 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 18.0–20.0 8.0–12.0 0.10 max
S30500 305 0.12 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 17.0–19.0 10.5–13.0
S30800 308 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 19.0–21.0 10.0–12.0
S30900 309 0.20 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 22.0–24.0 12.0–15.0
S30908 309S 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 22.0–24.0 12.0–15.0
S30940 309Cb 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 22.0–24.0 12.0–16.0 0.10 max Cb+Ta 103C min,
1.10 max
S31000 310 0.25 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.50 24.0–26.0 19.0–22.0
S31008 310S 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.50 24.0–26.0 19.0–22.0
S31400 314 0.25 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.50–3.00 23.0–26.0 19.0–22.0
S31600 316 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 16.0–18.0 10.0–14.0 2.00–3.00 0.10 max
C
S31603 316L 0.030 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 16.0–18.0 10.0–14.0 2.00–3.00 0.10 max
S31700 317 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 18.0–20.0 11.0–15.0 3.0–4.0 0.10 max
S32100 321 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 17.0–19.0 9.0–12.0 Ti 53C min
S34700 347 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 17.0–19.0 9.0–13.0 Cb+Ta 103C min
S34800 348 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 17.0–19.0 9.0–13.0 Cb+Ta 103C min
Ta 1.10 max
Co 0.20 max
Ferritic Grades
S40500 405 0.08 1.00 0.040 0.030 1.
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.