ASTM F739-12e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Permeation of Liquids and Gases through Protective Clothing Materials under Conditions of Continuous Contact
Standard Test Method for Permeation of Liquids and Gases through Protective Clothing Materials under Conditions of Continuous Contact
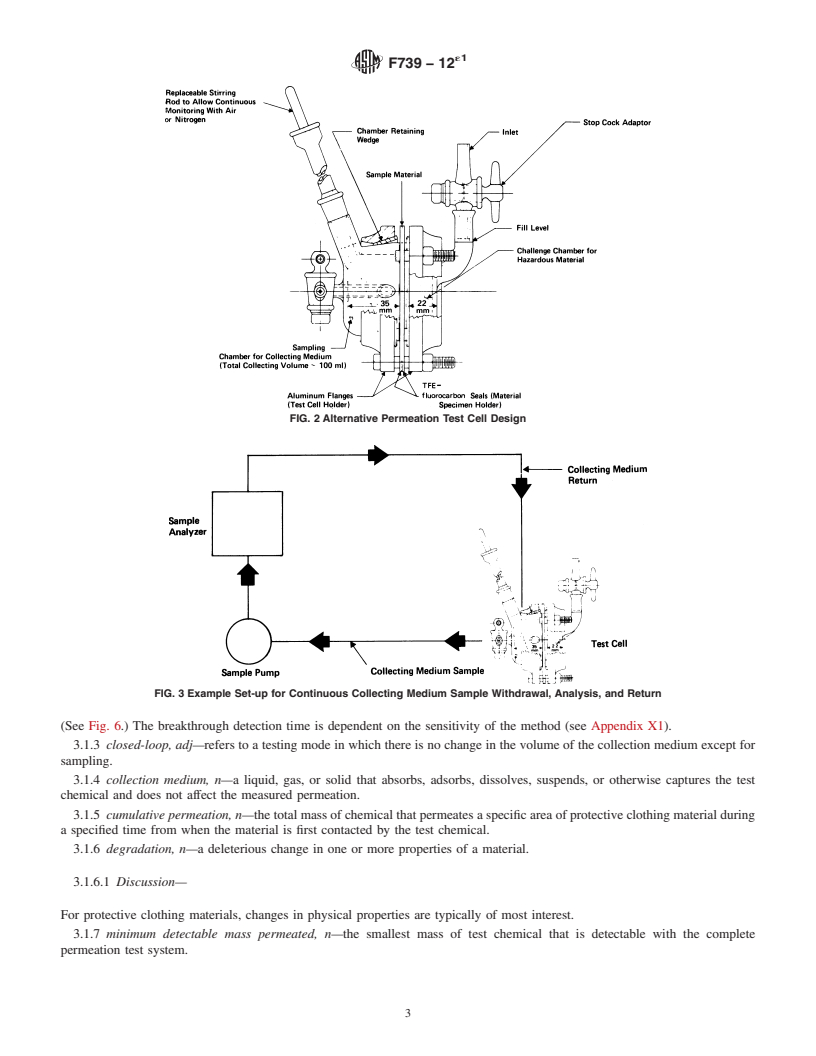
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is normally used to evaluate flat specimens from finished items of protective clothing and from materials that are candidates for items of protective clothing.
5.1.1 Finished items of protective clothing include gloves, arm shields, aprons, suits, hats, boots, respirators, and the like.
5.1.2 The phrase “specimens from finished items” encompasses seamed or other discontinuous regions as well as the usual continuous regions of protective clothing items.
5.2 The breakthrough detection time, standardized breakthrough time, permeation rate, and cumulative permeation are key measures of the effectiveness of a clothing material as a barrier to the test chemical. Such information is used in the comparison of clothing materials during the process of selecting clothing for protection from hazardous chemicals. Long breakthrough detection times, long standardized breakthrough detection times, low amounts of cumulative permeation, and low permeation rates are characteristics of better barriers.
Note 1: At present, only limited quantitative information exists about acceptable levels of dermal contact with most chemicals. Therefore, the data obtained using this test method cannot be used to infer safe exposure levels.
5.2.1 The reporting of a standardized breakthrough time greater than a specific time period means that the test chemical has not permeated the specimen at a rate exceeding 0.1 μg/cm2/min in the designated time. Permeation may or may not have occurred at a lower rate during this time interval.
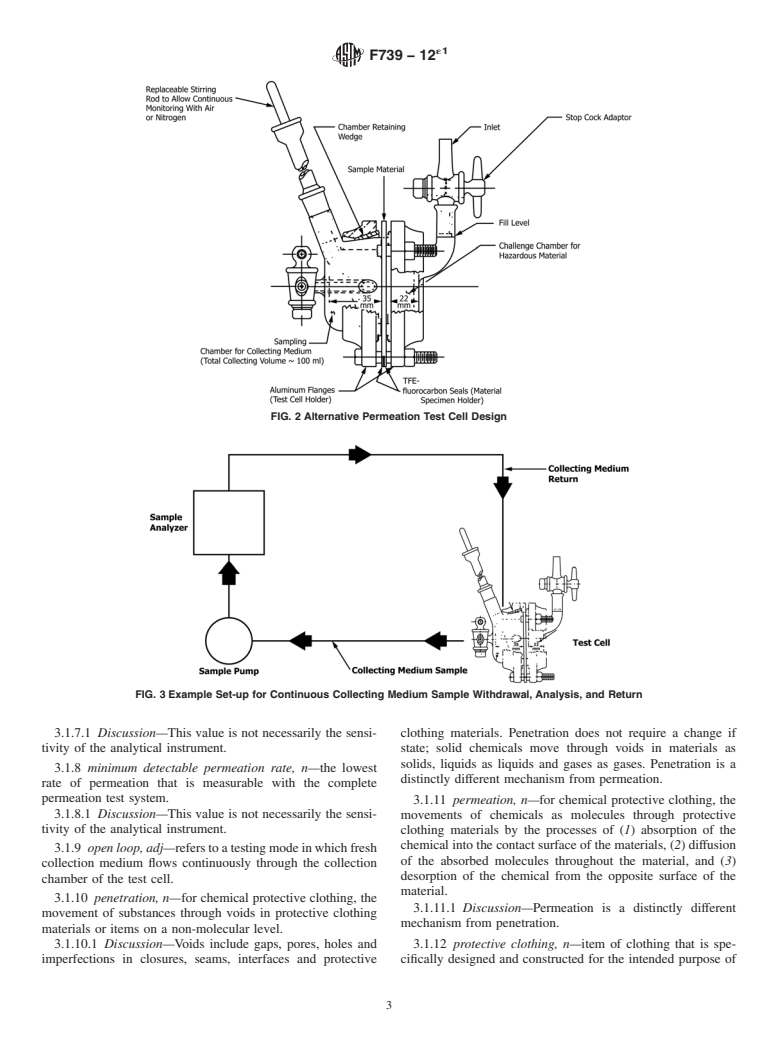
5.3 The sensitivity of the test method in detecting low permeation rates or amounts of the test chemical that permeate is determined by the combination of the analytical technique and collection system selected, and the ratio of material specimen area to collection medium volume or flow rate.
5.3.1 The analytical technique employed should be capable of measuring the concentration of the test chemical in the collection medium at, or below...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method measures the permeation of liquids and gases through protective clothing materials under the condition of continuous contact.
1.2 This test method is designed for use when the test chemical is a gas or a liquid, where the liquid is either volatile (that is, having a vapor pressure greater than 1 mm Hg at 25°C) or soluble in water or another liquid that does not interact with the clothing material.
1.3 Values states in SI units are to be regarded as standard. Values given in parentheses are not exact equivalents and are given for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in Section 7.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
´1
Designation: F739 − 12
Standard Test Method for
Permeation of Liquids and Gases Through Protective
1
Clothing Materials Under Conditions of Continuous Contact
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF739;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Editorially corrected 8.8.1 in February 2015.
INTRODUCTION
Workersinvolvedintheproduction,use,andtransportationofliquidandgaseouschemicalscanbe
exposed to numerous compounds capable of causing harm upon contact with the human body. The
deleterious effects of these chemicals can range from acute trauma such as skin irritation and burn, to
chronicdegenerativediseasesuchascancer.Sinceengineeringcontrolsmaynoteliminateallpossible
exposures, attention is often placed on reducing the potential for direct skin contact through the use
of protective clothing that resists permeation, penetration, and degradation.
Thistestmethodisusedtomeasurethepermeationofliquidsandgasesthroughprotectiveclothing
materials under the conditions of continuous contact of the clothing material by the test chemical.
Resistance to permeation under the condition of intermittent contact with the test chemical should be
determined by Test Method F1383. In certain situations, the permeation of liquids through protective
clothingmaterialscanbemeasuredusingapermeationcupfollowingTestMethodF1407.Penetration
of liquids should be determined by Test Method F903. An undesirable change in the physical
properties of protective clothing materials is called degradation. Procedures for measuring the
degradation of rubbers, plastics, and coated fabrics are found in Test Method D471, Test Method
D543, and Test Method D751, respectively.Astarting point for selecting the chemicals to be used in
assessing the chemical resistance of clothing materials is Guide F1001.
1. Scope responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
1.1 Thistestmethodmeasuresthepermeationofliquidsand
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precau-
gasesthroughprotectiveclothingmaterialsunderthecondition
tionary statements are given in Section 7.
of continuous contact.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
1.2 This test method is designed for use when the test
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
chemical is a gas or a liquid, where the liquid is either volatile
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
(thatis,havingavaporpressuregreaterthan1mmHgat25°C)
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
or soluble in water or another liquid that does not interact with
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
the clothing material.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
1.3 Values states in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
2. Referenced Documents
Values given in parentheses are not exact equivalents and are
2
given for information only.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D471Test Method for Rubber Property—Effect of Liquids
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the D543Practices for Evaluating the Resistance of Plastics to
Chemical Reagents
D751Test Methods for Coated Fabrics
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeF23onPersonal
ProtectiveClothingandEquipmentandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommittee
2
F23.30 on Chemicals. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2012. Published October 2012. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1981. Last previous edition approved in 2007 as F739–07. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/F0739-12E01. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
´1
F739 − 12
FIG. 1 ASTM Permeation Test Cell
D1777Test Method for Thickness of Textile Materials 3.1.1 analytical technique, n—a procedure whereby the
E105Practice for Probability Sampling of Materials concentration of the test chemical in a collection medium is
E171Practice for Conditioning and Testing Flexible Barrier quantitatively determined.
Packaging
3.1.1.1 Discussion—These techniques are often specific to
E177Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in individual chemical and collection medium combinations.
ASTM Test Methods
Applicable techniques include, but are not limited to, flame
E6
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: F739 − 12 F739 − 12
Standard Test Method for
Permeation of Liquids and Gases through Protective
1
Clothing Materials under Conditions of Continuous Contact
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F739; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A superscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Editorially corrected 8.8.1 in February 2015.
INTRODUCTION
Workers involved in the production, use, and transportation of liquid and gaseous chemicals can be
exposed to numerous compounds capable of causing harm upon contact with the human body. The
deleterious effects of these chemicals can range from acute trauma such as skin irritation and burn, to
chronic degenerative disease such as cancer. Since engineering controls may not eliminate all possible
exposures, attention is often placed on reducing the potential for direct skin contact through the use
of protective clothing that resists permeation, penetration, and degradation.
This test method is used to measure the permeation of liquids and gases through protective clothing
materials under the conditions of continuous contact of the clothing material by the test chemical.
Resistance to permeation under the condition of intermittent contact with the test chemical should be
determined by Test Method F1383. In certain situations, the permeation of liquids through protective
clothing materials can be measured using a permeation cup following Test Method F1407. Penetration
of liquids should be determined by Test Method F903. An undesirable change in the physical
properties of protective clothing materials is called degradation. Procedures for measuring the
degradation of rubbers, plastics, and coated fabrics are found in Test Method D471, Test Method
D543, and Test Method D751, respectively. A starting point for selecting the chemicals to be used in
assessing the chemical resistance of clothing materials is Guide F1001.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method measures the permeation of liquids and gases through protective clothing materials under the condition of
continuous contact.
1.2 This test method is designed for use when the test chemical is a gas or a liquid, where the liquid is either volatile (that is,
having a vapor pressure greater than 1 mm Hg at 25°C) or soluble in water or another liquid that does not interact with the clothing
material.
1.3 Values states in SI units are to be regarded as standard. Values given in parentheses are not exact equivalents and are given
for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in Section 7.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D471 Test Method for Rubber Property—Effect of Liquids
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F23 on Personal Protective Clothing and Equipment and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
F23.30 on Chemicals.
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2012. Published October 2012. Originally approved in 1981. Last previous edition approved in 2007 as F739 – 07. DOI:
10.1520/F0739-12.10.1520/F0739-12E01.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
´1
F739 − 12
FIG. 1 ASTM Permeation Test Cell
D543 Practices for Evaluating the Resistance of Plastics to Chemical Reagents
D751 Test Methods for Coated Fabrics
D1777 Test Method for Thickness of Textile Materials
E105 Practice for Probability Sampling of Materials
E171 Practice for Conditioning and Testing Flexible Barrier Packaging
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in ASTM Test Methods
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
F903 Test Method for Resistance of Materials Used in Protective Clothing to Penetration by
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.