ASTM A67-00
(Specification)Standard Specification for Steel Tie Plates, Low-Carbon and High-Carbon Hot-Worked
Standard Specification for Steel Tie Plates, Low-Carbon and High-Carbon Hot-Worked
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers steel tie plates for use in railroad track.
1.2 Two grades of tie plates are described: Grade 1, low carbon, and Grade 2, high-carbon-hot-worked.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
General Information
Relations
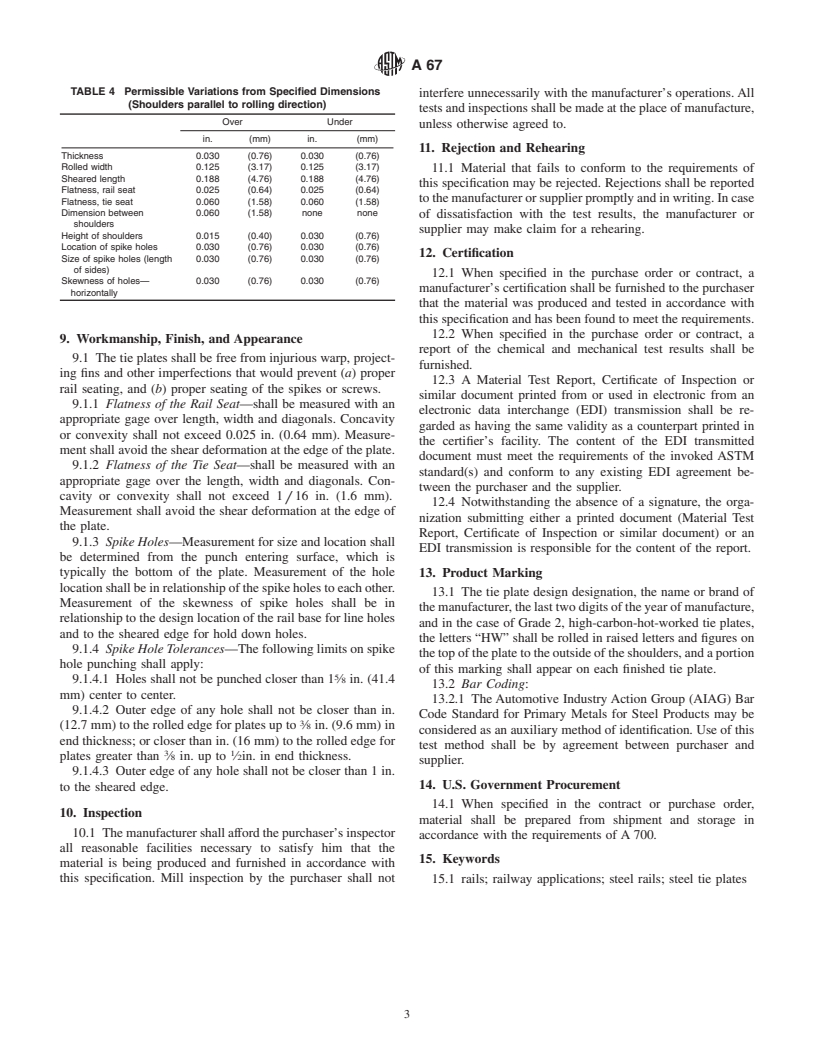
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: A 67 – 00
Standard Specification for
Steel Tie Plates, Low-Carbon and High-Carbon-Hot-Worked
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationA67;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.1.5 length—overall dimension of the plate at right angles
to the rail it supports.
1.1 This specification covers steel tie plates for use in
3.1.6 Discussion—Tie plates of different length can be used
railroad track.
with a given rail section with the length chosen based on the
1.2 Two grades of tie plates are described: Grade 1, low-
traffic density of the track on which it is to be used.
carbon, and Grade 2, high-carbon-hot-worked.
3.1.7 line holes—located at the edge of the rail seat, these
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
holes allow the spikes to contact the edge of the rail base.
as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information
3.1.8 rail seat—the portion of the tie plate that supports the
only.
rail.
2. Referenced Documents 3.1.9 rail seat cant—tie plates are generally rolled with the
rail seat not parallel to the base of the plate so that the rail head
2.1 ASTM Standards:
is tilted toward the centerline of track to help offset lateral
A 700 Practices for Packaging, Marking, and Loading
thrust and provide better wheel bearing on the rail head; the
Methods for Steel Products for Domestic Shipping
AREA recommended cant is a ratio of 1:40.
2.2 American Railway Engineering and Maintenance of
3.1.10 rolled width—the dimension of the finished section
Way Association (AREMA):
as it leaves the rolls and is equal to the length of the tie plate.
Specification for Steel Tie Plates
3.1.11 sheared length—the dimension to which the finished
3. Terminology
section is cut and is equal to the width of the tie plate.
3.1.12 shoulder—a ridge parallel to the rail designed to
3.1 Definitions:
assist in holding the rail in position.
3.1.1 eccentricity—the distance from the shoulder to the
3.1.13 Discussion—The height of the shoulder is about
edge of the tie plate at right angles to the shoulder is larger on
equal to the thickness of the edge of the rail base. If a plate has
the field side than the gage side to compensate for the greater
a single shoulder,theshoulderislocatedonthefieldsideofthe
tendency of the field end to cut into the tie; the horizontal
rail seat to resist the outward thrust of the rail. A double
distance from middle of the rail seat to middle of the tie plate
shoulder plate has an additional shoulder on the gage side of
is the eccentricity.
the rail seat. Single shoulder plates may accommodate a
3.1.2 field side—end of tie plate designed to be located on
desiredrailsectionbyadjustingthepunchingofthespikeholes
the opposite side of the rail from the centerline of track.
on the gage side to match the width of the rail base. Double
3.1.3 gage side—end of tie plate designed to be located
shoulder plates are limited to a single rail base width.
closest to the centerline of track.
3.1.14 tie plate—a part of the track structure placed under
3.1.4 hold down holes—located on the plate away from the
the rail to distribute the wheel load to the tie, cant the rail to the
rail seat, these holes do not allow spikes to contact the edge of
desired angle, assist in maintaining the track to gage and
the rail base. Also called anchor spike holes.
protect the tie.
3.1.15 Discussion—Thetieplatehasarailseat,eitherflator
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
canted, either a single or double shoulder parallel to the rail it
Stainless Steel and RelatedAlloys, and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
supports, and is punched with holes for spikes or other
A01.01 on Steel Rails and Accessories.
fasteners. The bottom of the tie plate is usually flat, but ribbed
Current edition approved September 10, 2000. Published November 2000.
Originally published as A 67 – 16 T. Last previous edition A 67 – 92. or other designs may be used.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.05.
3.1.16 width—overall dimension of the plate parallel to the
Manual of Railway Engineering, Chapter 5, Part 1, and is available from
rail it supports.
American Railway Engineering and Maintenance of Way Assn., 8201 Corporate
Drive, Suite 1125, Landover, MD 20785.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
A67
TABLE 2 Product Analysis Allowance Beyond Limits of
3.1.17 Discussion—Tie plates are generally from 7 to 8 in.
Specified Chemical Analysis
wide.
Under Maximum Over Maximum
Limit, % Limit, %
4. Ordering Information
Carbon 0.04 . . .
4.1 Orders for tie plates under this specification shall
Phosphorus . . . 0.008
Sulfur . . . 0.008
include the following information:
4.1.1 Quantity: number of pieces.
4.1.2 ASTM designation and year of issue.
4.1.3 Grade: 1, low-carbon, or 2, high-carbon-hot-worked
7. Bend Requirements
(see Table 1 and Table 2).
4.1.4 Design: AREMA plan number, or other design in-
7.1 Bend Test:
cluding drawings if required.
7.1.1 Grade 1 or Grade 2 bend test specimens prepared as
4.1.5 Any variation in location and shape of holes, etc.,
required in 7.1.2 shall withstand the respective bend test
from the plan, with dimensional drawing if necessary.
describedinTable3withoutcrackingontheoutsideofthebent
portion.
5. Materials and Manufacture
7.1.2 Thespecimensforbendtestsspecifiedin7.1.1shallbe
taken from finished tie plates, longitudinally with the direction
5.1 Melting Practice—The steel shall be made by any of the
of rolling. They shall be rectangular in section, not less than ⁄2
following processes: basic-oxygen or electric-furnace.
in. (13 mm) in width between machined sides, and shall have
5.2 The steel may be cast by a continuous process, or in
two faces as rolled. Where the tie plate design is such that a
ingots.
specimen cannot be taken between the ribs or projections, the
5.3 Discard—A sufficient discard shall be made to secure
ribs or projections shall be removed to the plane of the plate
freedom from injurious segregation and piping.
surface as part of the specimen preparation.
5.4 Steel accumulated in the form of ingots or blooms,
7.2 Optional Bend Test:
possibly from various heats, that conforms to the requirements
7.2.1 If preferred by the manufacturer, the following full-
of this specification may be used in the manufacture of either
size bend test may be substituted for that described in 7.1.
Grade 1 or Grade 2 tie plates.
7.2.2 Afinished Grade 1 or Grade 2 tie plate shall withstand
5.5 Grade 1 tie plates may be sheared, punched, or slotted
the respective optional bend test described in Table 3 without
either hot or cold, at the option of the manufacturer.
cracking on the outside of the bent portion.
5.6 Grade 2 tie plates shall be sheared, punched, or slotted
7.3 Number of Tests:
hot, at a temperature best suited to the process, and thereafter
7.3.1 One bend test shall be made from each identified heat,
placed into an enclosure to assure proper cooling.
or from each 25 tons (23 Mg) where heats are not identified.
7.3.2 If any test specimen shows defective machining or
6. Chemical Composition
develops flaws, it may be discarded and another specimen
6.1 Thesteelshallconformtotherequirementsforchemical
substituted.
composition specified in Table 1.
7.4 Retest:
6.2 Heat or Cast Analysis:
7.4.1 Highcarbontieplatesrepresentedbybendtestsfailing
6.2.1 An analysis of each heat or cast shall be made by the
to meet the requirements prescribed in 7.1 or 7.2 may be
manufacturer to determi
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.