ASTM E2555-21e1
(Practice)Standard Practice for Factors and Procedures for Applying the MIL-STD-105 Plans in Life and Reliability Inspection
Standard Practice for Factors and Procedures for Applying the MIL-STD-105 Plans in Life and Reliability Inspection
ABSTRACT
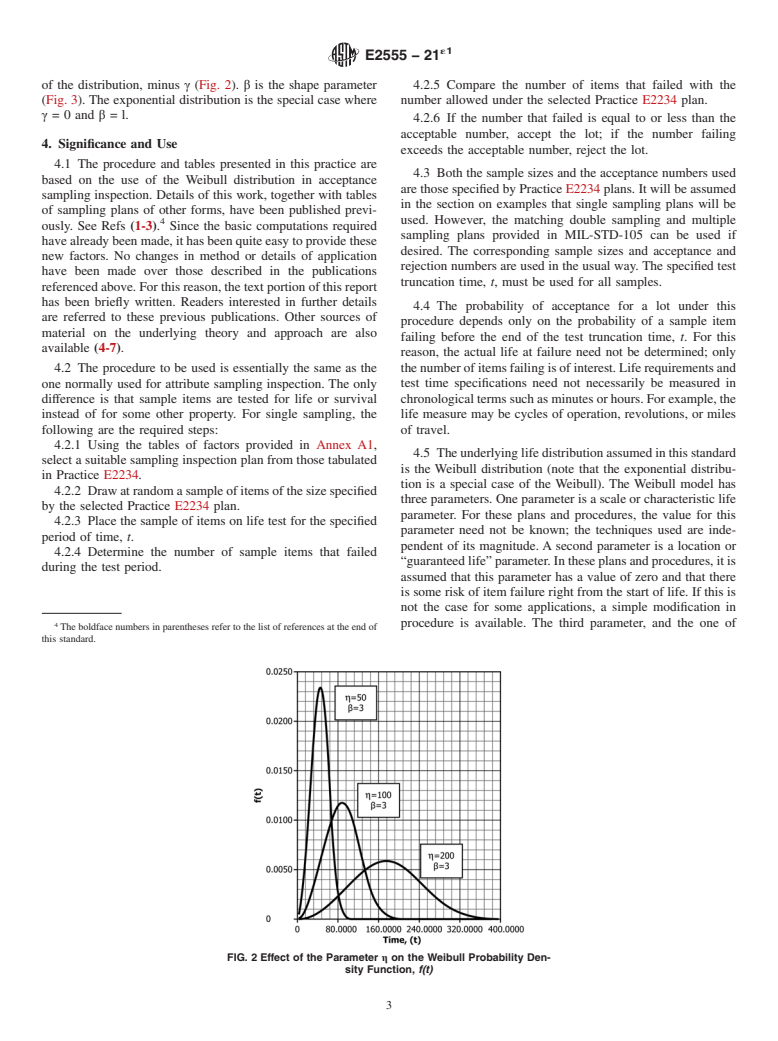
This practice presents a procedure and related tables of factors for adapting Practice E2234 (equivalent to MIL-STD105) sampling plans to acceptance sampling inspection when the item quality of interest is life length or reliability. Factors are provided for three alternative criteria for lot evaluation: mean life, hazard rate, and reliable life. Inspection of the sample is by attributes with testing truncated at the end of some prearranged period of time. The Weibull distribution, together with the exponential distribution as a special case, is used as the underlying statistical model. The procedure and tables presented in this practice are based on the use of the Weibull distribution in acceptance sampling inspection.
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 The procedure and tables presented in this practice are based on the use of the Weibull distribution in acceptance sampling inspection. Details of this work, together with tables of sampling plans of other forms, have been published previously. See Refs (1-3).4 Since the basic computations required have already been made, it has been quite easy to provide these new factors. No changes in method or details of application have been made over those described in the publications referenced above. For this reason, the text portion of this report has been briefly written. Readers interested in further details are referred to these previous publications. Other sources of material on the underlying theory and approach are also available (4-7).
4.2 The procedure to be used is essentially the same as the one normally used for attribute sampling inspection. The only difference is that sample items are tested for life or survival instead of for some other property. For single sampling, the following are the required steps:
4.2.1 Using the tables of factors provided in Annex A1, select a suitable sampling inspection plan from those tabulated in Practice E2234.
4.2.2 Draw at random a sample of items of the size specified by the selected Practice E2234 plan.
4.2.3 Place the sample of items on life test for the specified period of time, t.
4.2.4 Determine the number of sample items that failed during the test period.
4.2.5 Compare the number of items that failed with the number allowed under the selected Practice E2234 plan.
4.2.6 If the number that failed is equal to or less than the acceptable number, accept the lot; if the number failing exceeds the acceptable number, reject the lot.
4.3 Both the sample sizes and the acceptance numbers used are those specified by Practice E2234 plans. It will be assumed in the section on examples that single sampling plans will be used. However, the matching double sampling and multiple sampling plans provided in MIL-...
SCOPE
1.1 This practice presents a procedure and related tables of factors for adapting Practice E2234 (equivalent to MIL-STD-105) sampling plans to acceptance sampling inspection when the item quality of interest is life length or reliability. Factors are provided for three alternative criteria for lot evaluation: mean life, hazard rate, and reliable life. Inspection of the sample is by attributes with testing truncated at the end of some prearranged period of time. The Weibull distribution, together with the exponential distribution as a special case, is used as the underlying statistical model.
1.2 A system of units is not specified by this practice.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issue...
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
´1
Designation: E2555 − 21 An American National Standard
Standard Practice for
Factors and Procedures for Applying the MIL-STD-105 Plans
1
in Life and Reliability Inspection
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2555; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Editorial corrections were made to the Terminology section in January 2022.
1. Scope 2.2 Other Documents:
MIL-STD-105ESampling Procedures and Tables for In-
1.1 This practice presents a procedure and related tables of
3
spection by Attributes
factors for adapting Practice E2234 (equivalent to MIL-STD-
105) sampling plans to acceptance sampling inspection when
3. Terminology
the item quality of interest is life length or reliability. Factors
are provided for three alternative criteria for lot evaluation: 3.1 Definitions:
mean life, hazard rate, and reliable life. Inspection of the
3.1.1 TheterminologydefinedinTerminologyE456applies
sampleisbyattributeswithtestingtruncatedattheendofsome
to this practice unless modified herein.
prearranged period of time. The Weibull distribution, together
3.1.2 acceptance quality limit (AQL), n—qualitylimitthatis
with the exponential distribution as a special case, is used as
theworsttolerableprocessaveragewhenacontinuingseriesof
the underlying statistical model.
lots is submitted for acceptance sampling. E2234
1.2 A system of units is not specified by this practice. 3.1.2.1 Discussion—Thisdefinitionsupersedesthatgivenin
MIL-STD-105E.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.2.2 Discussion—A sampling plan and an AQL are cho-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
sen in accordance with the risk assumed. Use of a value of
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
AQL for a certain defect or group of defects indicates that the
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
sampling plan will accept the great majority of the lots or
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
batchesprovidedtheprocessaveragelevelofpercentdefective
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
(or defects per hundred units) in these lots or batches are no
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
greater than the designated value ofAQL. Thus, theAQL is a
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
designated value of percent defective (or defects per hundred
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
units) for which lots will be accepted most of the time by the
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
sampling procedure being used. The sampling plans provided
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
herein are so arranged that the probability of acceptance at the
designated AQL value depends upon the sample size, being
2. Referenced Documents
generally higher for large samples than for small ones, for a
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
given AQL. The AQL alone does not identify the chances of
E456Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
accepting or rejecting individual lots or batches but more
E2234Practice for Sampling a Stream of Product by Attri-
directly relates to what might be expected from a series of lots
butes Indexed by AQL
or batches, provided the steps indicated in this refer to the
E2586Practice for Calculating and Using Basic Statistics
operating characteristic curve of the plan to determine the
relative risks.
3.1.3 consumer’s risk, n—probability that a lot having
1
ThispracticeisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeE11onQualityand
specified rejectable quality level will be accepted under a
Statistics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E11.40 on Reliability.
defined sampling plan.
Current edition approved May 1, 2021. Published June 2021. Originally
ɛ1
approved in 2007. Last previous version approved in 2018 as E2555–07 (2018) .
DOI: 10.1520/E2555-21E01.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
3
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM MIL-STD-105Eisalsocommonlyreferredtoas“MIL-STD-105.”Itisvirtually
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on identical in content to its predecessor, MIL-STD-105D.These documents are out of
the ASTM website. print.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
--
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.