ASTM B174-10
(Specification)Standard Specification for Bunch-Stranded Copper Conductors for Electrical Conductors
Standard Specification for Bunch-Stranded Copper Conductors for Electrical Conductors
ABSTRACT
This specification covers bare bunch-stranded conductors made from round copper wires, either uncoated or coated with tin, lead, or lead-alloy for use as electrical conductors. Coated wires shall include only those wires with finished diameters and densities substantially equal to the respective diameters and densities of uncoated wires. Bunch-stranded conductors are classified as Class I, Class J, Class K, Class L, Class M, Class O, Class P, and Class Q, according to wire diameter. Requirements for conductor joints, lay length, wires, and strand construction are given. Electrical and elongation tests of wires composing the conductors shall be performed. If a tinning, lead-coating, or lead-alloy-coating test is required, it shall be made on the wires prior to stranding. The methods of determining mass, cross sections, and electrical resistance are detailed. The density of copper to be taken in the calculations is prescribed.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers bare bunch-stranded conductors made from round copper wires, either uncoated or coated with tin, lead, or lead-alloy for use as electrical conductors (Explanatory Note 1 and Explanatory Note 2).
1.2 Coated wires shall include only those wires with finished diameters and densities substantially equal to the respective diameters and densities of uncoated wires.
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.3.1 For conductor sizes designated by AWG or kcmil, the requirements in SI units have been numerically converted from corresponding values, stated or derived, in inch-pound units. For conductor sizes designated by SI units only, the requirements are stated or derived in SI units.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:B174 −10
StandardSpecification for
Bunch-Stranded Copper Conductors for Electrical
1
Conductors
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B174; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope B189 Specification for Lead-Coated and Lead-Alloy-Coated
Soft Copper Wire for Electrical Purposes
1.1 This specification covers bare bunch-stranded conduc-
B193 Test Method for Resistivity of Electrical Conductor
tors made from round copper wires, either uncoated or coated
Materials
with tin, lead, or lead-alloy for use as electrical conductors
B263 Test Method for Determination of Cross-Sectional
(Explanatory Note 1 and Explanatory Note 2).
Area of Stranded Conductors
1.2 Coated wires shall include only those wires with fin-
B354 Terminology Relating to Uninsulated Metallic Electri-
ished diameters and densities substantially equal to the respec-
cal Conductors
tive diameters and densities of uncoated wires.
2.3 American National Standard:
3
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
ANSI C42.35 Definitions of Electrical Terms
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
3. Classification
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
3.1 For the purpose of this specification bunch-stranded
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
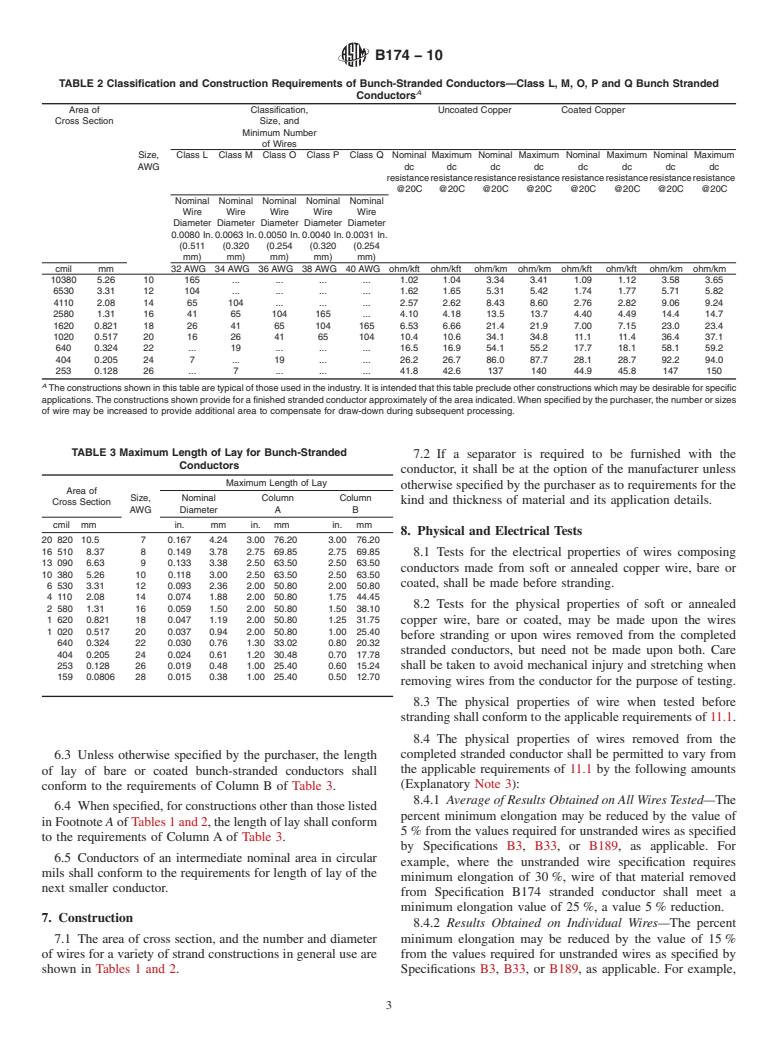
conductors are classified as shown in Tables 1 and 2.
with the standard.
1.3.1 For conductor sizes designated byAWG or kcmil, the
4. Ordering Information
requirements in SI units have been numerically converted from
4.1 Orders for material under this specification shall include
corresponding values, stated or derived, in inch-pound units.
the following information:
For conductor sizes designated by SI units only, the require-
4.1.1 Quantity of each size and class,
ments are stated or derived in SI units.
4.1.2 Conductor size: circular-mil area or AWG (see 7.1),
4.1.3 Class (Section 3 and Table 3),
2. Referenced Documents
4.1.4 Whether coated or uncoated; if coated, designate type
2.1 The following documents of the issue in effect at the
of coating (see 11.1),
time of reference form a part of this specification to the extent
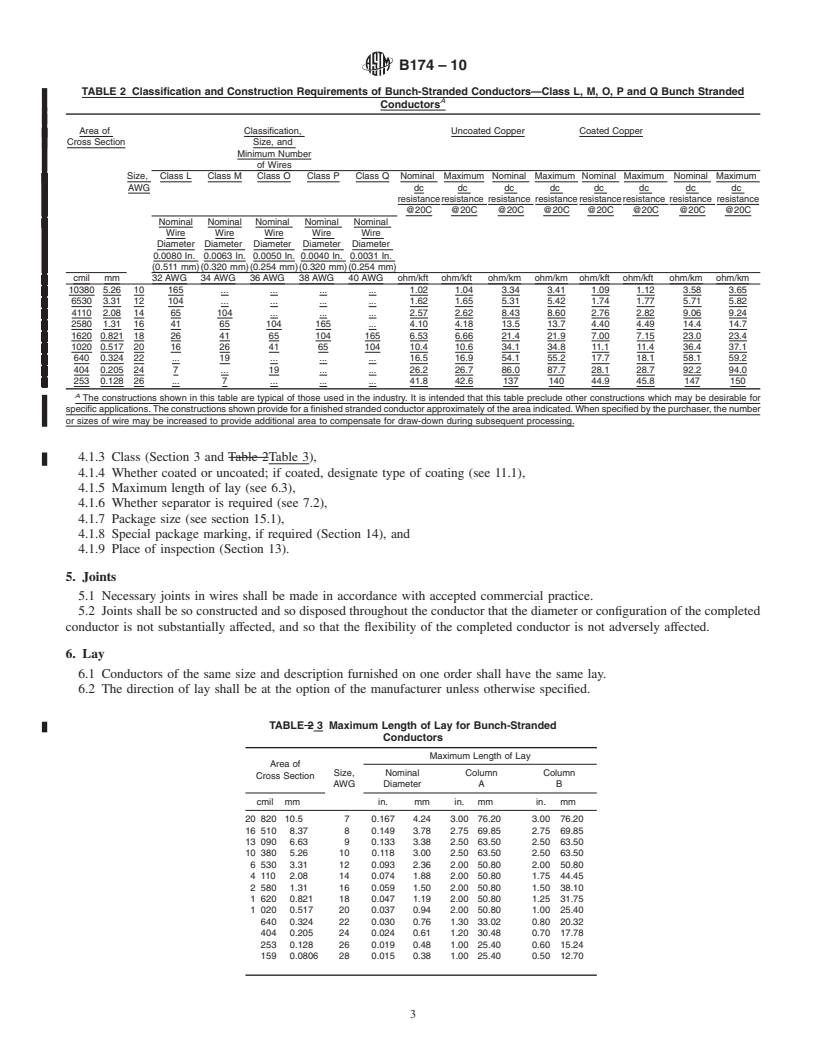
4.1.5 Maximum length of lay (see 6.3),
referenced herein:
4.1.6 Whether separator is required (see 7.2),
2
2.2 ASTM Standards:
4.1.7 Package size (see section 15.1),
B3 Specification for Soft or Annealed Copper Wire
4.1.8 Specialpackagemarking,ifrequired(Section14),and
B33 Specification for Tin-Coated Soft or Annealed Copper
4.1.9 Place of inspection (Section 13).
Wire for Electrical Purposes
B172 Specification for Rope-Lay-Stranded Copper Conduc- 5. Joints
torsHavingBunch-StrandedMembers,forElectricalCon-
5.1 Necessary joints in wires shall be made in accordance
ductors
with accepted commercial practice.
5.2 Joints shall be so constructed and so disposed through-
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B01 on
out the conductor that the diameter or configuration of the
Electrical Conductors and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B01.04 on
completed conductor is not substantially affected, and so that
Conductors of Copper and Copper Alloys.
Current edition approved April 1, 2010. Published May 2010. Originally
the flexibility of the completed conductor is not adversely
ε1
approved in 1941. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as B174 – 02 (2007) .
affected.
DOI: 10.1520/B0174-10.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
the ASTM website. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B174−10
A
TABLE 1 A Classification and Construction Requirements of Bunch-Stranded Conductors —Class I Bunch Stranded Conductors
Area of Classification, Uncoated Copper Coated Copper
Cross Section Size,
and
Minimum
Number
of Wires
Size, Class I Nominal dc Maximum dc Nominal dc Maximum dc Nominal dc Maximum dc Nominal dc Maximum dc
AWG Nominal resistance resistance resistance resistance resistance resistance resistance resistance
Wire @20C @20C @20C @20C @20C @20C @20C @20C
Diameter
0.0201 In.
(0.
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation:B174–02 (Reapproved 2007) Designation: B174 – 10
Standard Specification for
Bunch-Stranded Copper Conductors for Electrical
1
Conductors
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B174; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1
´ NOTE—Table1 was editorially corrected in March 2007.
1. Scope
1.1 Thisspecificationcoversbarebunch-strandedconductorsmadefromroundcopperwires,eitheruncoatedorcoatedwithtin,
lead, or lead-alloy for use as electrical conductors (Explanatory Note 1 and Explanatory Note 2).
1.2 Coated wires shall include only those wires with finished diameters and densities substantially equal to the respective
diameters and densities of uncoated wires.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound either SI units or SIinch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. Each The
values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other.
Combining values formfrom the two systems may result in non-conformance with the specification. Forstandard.
1.3.1 For conductor sizes designated by AWG or kcmil, the requirements in SI units have been numerically converted from
corresponding values, stated or derived, in inch-pound units. For conductor sizes designated by SI units only, the requirements are
stated or derived in SI units.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 The following documents of the issue in effect at the time of reference form a part of this specification to the extent
referenced herein:
2
2.2 ASTM Standards:
B3 Specification for Soft or Annealed Copper Wire
B33 Specification for Tin-Coated Soft or Annealed Copper Wire for Electrical Purposes
B172 Specification for Rope-Lay-Stranded Copper Conductors Having Bunch-Stranded Members, for Electrical Conductors
B189 Specification for Lead-Coated and Lead-Alloy-Coated Soft Copper Wire for Electrical Purposes
B193 Test Method for Resistivity of Electrical Conductor Materials
B263 Test Method for Determination of Cross-Sectional Area of Stranded Conductors
B354 Terminology Relating to Uninsulated Metallic Electrical Conductors
2.3 American National Standard:
3
ANSI C42.35 Definitions of Electrical Terms
3. Classification
3.1 For the purpose of this specification bunch-stranded conductors are classified as shown in Table 1Tables 1 and 2.
4. Ordering Information
4.1 Orders for material under this specification shall include the following information:
4.1.1 Quantity of each size and class,
4.1.2 Conductor size: circular-mil area or AWG (see 7.1),
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B01 on Electrical Conductors and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B01.04 on Conductors
of Copper and Copper Alloys.
Current edition approved March 15, 2007. Published April 2007. Originally approved in 1941. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as B174–02. DOI:
10.1520/B0174-02R07E01.
´1
Current edition approved April 1, 2010. Published May 2010. Originally approved in 1941. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as B174 – 02 (2007) . DOI:
10.1520/B0174-10.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book ofASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B174 – 10
A
TABLE 1 A Classification and Construction Requirements of Bunch-Stranded Conductors —Class I Bunch Stranded Conductors
Area of Size, Classification, Size, and Uncoated Copper Coated Copper
Cross Section AWG Minimum
Number
of Wires
Area of Classification,Cland Uncoated CopperCoated Copper
Cross Section Size, Minimum
AWG Number
of Wires
Size, Class I Class J Class K Class L Class M Class OClass PClass Q
AWG
Size, Class I Nominal dc Maximum dc Nominal dc Maximum dc Nominal dc Maximum dcClass Q
AWG Nominal resistance resistance resistance resistance resistance resistance
Wire Diameter @20C @20C @20C @20C @20C
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.