ASTM D1305-99(2004)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Electrical Insulating Paper and Paperboard-Sulfate (Kraft) Layer Type
Standard Specification for Electrical Insulating Paper and Paperboard-Sulfate (Kraft) Layer Type
ABSTRACT
This specification covers electrically insulating, unbleached sulfate paper and paperboard used as layer insulation in coils, transformers, and other similar apparatus. The materials may also be used as turn insulation, slot liners, wedges, phase insulation, and separator papers in stranded wire/cable constructions. This specification does not include tissue for manufacture of capacitors. Other commonly used terms for the materials include soft coil wrap, dense coil wrap, kraft coil insulation, dry-finished kraft, and water-finished kraft. The materials covered in this specification are classified into four types according to density range and nominal thickness and should conform to the required values of ash content, alcohol-soluble material content, aqueous extract conductivity, water-soluble chloride content, fiber composition, moisture content, hydrogen ion concentration, pH, tensile strength, dielectric breakdown voltage, and conducting paths.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers electrical grade unsized, unbleached sulfate paper and paperboard for use as layer insulation in coils, transformers, and similar apparatus. Tissue for the manufacture of capacitors is not included in this specification. Other commonly used designations include:
1.1.1 Soft Coil Wrap,
1.1.2 Dense Coil Wrap,
1.1.3 Kraft Coil Insulation,
1.1.4 Dry-Finished Kraft, and
1.1.5 Water-Finished Kraft.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
An American National Standard
Designation: D1305 – 99 (Reapproved 2004)
Standard Specification for
Electrical Insulating Paper and Paperboard—Sulfate (Kraft)
Layer Type
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1305; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
TABLE 1 Types of Untreated Kraft Insulating Tissue, Paper, and
1. Scope
Paperboard
1.1 This specification covers electrical grade unsized, un-
Type Density Range, Nominal Thickness,
bleached sulfate paper and paperboard for use as layer insula-
g/cm mil (µm)
tion in coils, transformers, and similar apparatus. Other appli-
I less than 0.77 1 (25) to 30 (760)
cations may include, but are not limited to, turn insulation, slot
II 0.77 to 0.86 0.5 (12) to 30 (760)
liners, wedges, phase insulation, and separator papers in III 0.86 to 0.95 0.4 (10) to 30 (760)
IV over 0.95 0.2 (5) to 30 (760)
stranded wire/cable constructions. Tissue for the manufacture
of capacitors is not included in this specification. Other
commonly used designations include:
5. Ordering Information
1.1.1 Soft Coil Wrap,
5.1 Orders shall specify the type, including whether water
1.1.2 Dense Coil Wrap,
finish or not (see Note 1), nominal thickness, form, width,
1.1.3 Kraft Coil Insulation,
length (for sheets), nominal outside diameter, and core inside
1.1.4 Dry-Finished Kraft, and
diameter (for rolls).
1.1.5 Water-Finished Kraft.
NOTE 1—Water finish is not available with certain combinations of
2. Referenced Documents
Kraft type and thickness. In general, water finish is restricted to paper and
paperboard in the higher density ranges, that is, Types III and IV.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D202 Test Methods for Sampling and Testing Untreated
6. Materials
Paper Used for Electrical Insulation
6.1 Thematerialshallbenaturalunbleachedsulfatepaperor
D1711 Terminology Relating to Electrical Insulation
paperboard, free of dyes, pigments, fillers, or sizing. It may be
3. Terminology
furnished either with water-finish or without.
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this stan-
7. Detail Requirements
dard, refer to Terminology D1711.
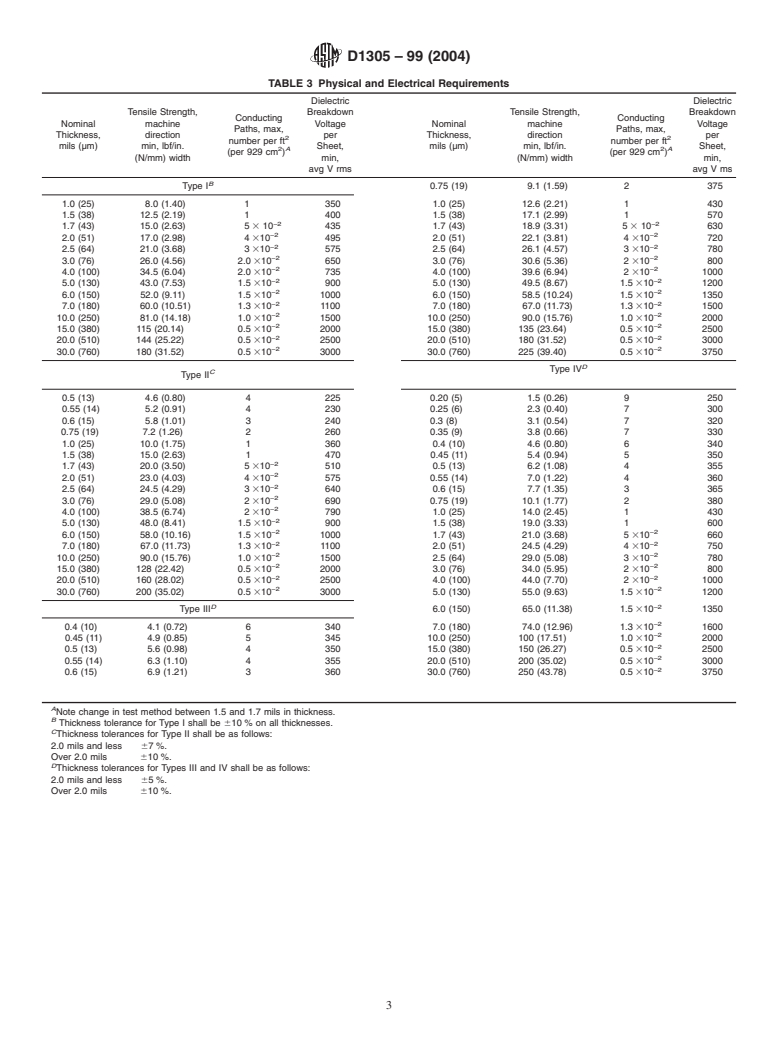
7.1 The material shall conform to the chemical, physical,
4. Classification
and electrical requirements specified inTables 1-4, when tested
in accordance with the methods prescribed in Section 11.
4.1 Four types of paper and paperboard are covered by this
specification, as shown in Table 1. The material is available in
8. Interpretation of Numerical Requirements
sheets, pads, or rolls.
8.1 Unless otherwise stated, all specified limits in this
specification apply to the average of determinations applicable
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D09 on
to a sample as defined.
Electrical and Electronic Insulating Materials and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D09.19 on Dielectric Sheet and Roll Products.
9. Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance
Current edition approved March 10, 1999. Published June 1999. Originally
9.1 The material shall be uniform in thickness, density,
approved in 1954. Last previous edition approved in 1998 as D1305 – 87 (1998).
DOI: 10.1520/D1305-99R04.
formation, and texture. The material shall be as free of welts,
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
wrinkles,creases,holes,slimespots,stains,shives,weakspots,
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
blisters, tears, cuts, and other defects; and from resin, dirt,
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. carbon, rubber, metal particles, corrosive substances, or other
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D1305 – 99 (2004)
TABLE 2 Chemical Requirements
carriers for safe transportation at the lowest rate to the point of
Property min max delivery, unless otherwise specified in the contract or order.
12.2 Package Marking—Each container shall be marked on
Ash, % . 0.5
Alcohol-soluble material, % . 1.0
the side or on one end of the package, or on both the side and
A
Aqueous extract conductivity, mS/m . 1.0
end, with the name and type of material, specification number,
Water-soluble chlorides, ppm . 32
purchase order number, manufacturer’s name or trade mark, or
Fiber composition: unbleached sulfate, % 100 .
Moisture, as received, % 4 7
both, manufacturer’s roll number, lot number, and the date of
Moisture, as received, for water finished paper, % 4 9
manufacture. Each roll or pad shall be marked on one side with
Hydrogen ion concentration, pH 6.5 8.0
the manufacturer’s name and lot number and the customer’s
A
1 mS/m = 10 µV/cm.
purchase order number.
foreign material, as consistent with good manufacturing pro-
13. Retest and Rejection
cesses and in keeping with the requirements of this specifica-
13.1 If the results of any test do not conform to the
tion.Rollsandpadsshallbecompactlywound.Splicesshallbe
requirements prescribed in this specification, at the option of
kept to a minimum. Splicing compounds shall be noncorrosive
the manufacturer that test shall be repeated on two additional
and shall have no deleterious effect on the insulating or
sets of specimens from the same batch or shipment, each of
dielectric values of the paper.
which shall conform to the requirements specified. If either of
these two additional sets of specimens fails, the material may
10. Sampling
be rejected at the option of the purchaser.
10.1 Sample the paper in accordance with Test Methods
13.2 Notice of failure of material based on tests made in
D202.
accordance with this specification shall be reported to the
11. Test Methods manufacturer within 3 weeks from receipt of the material by
the purchaser.Any portion of an accepted shipment of material
11.1 Th
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.