ASTM B395/B395M-18
(Specification)Standard Specification for U-Bend Seamless Copper and Copper Alloy Heat Exchanger and Condenser Tubes
Standard Specification for U-Bend Seamless Copper and Copper Alloy Heat Exchanger and Condenser Tubes
ABSTRACT
This specification establishes the requirements for condenser, evaporator, and heat exchanger U-bends that are manufactured from seamless copper and copper alloy tube. The material of manufacture shall be of such quality and purity that the finished product shall have the properties and characteristics specified. The material shall conform to the chemical composition requirements specified. Tensile test, expansion test, flattening test, mercurous nitrate test or ammonia vapor test, nondestructive examination, hydrostatic test, and pneumatic test shall be made to conform to the requirements specified.
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
18.1 For purpose of determining compliance with the specified limits for requirements of the properties listed in the following table, an observed value or a calculated value shall be rounded as indicated in accordance with the rounding method of Practice E29.
Property
Rounded Unit for Observed or
Calculated Value
Chemical composition
nearest unit in the last
right-hand significant
digit used in expressing
the limiting value
Tensile strength
nearest ksi [nearest 5 MPa]
Elongation
nearest 1 %
Expansion
nearest 1 %
Grain size
nearest multiple of 0.005 mm
SCOPE
1.1 This specification2 establishes the requirements for condenser, evaporator, and heat exchanger U-bend tubes that are manufactured from seamless copper and copper alloy tube.
1.2 Units—The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.3 This specification is applicable to product 2 in. [50 mm] or less, inclusive, in diameter.
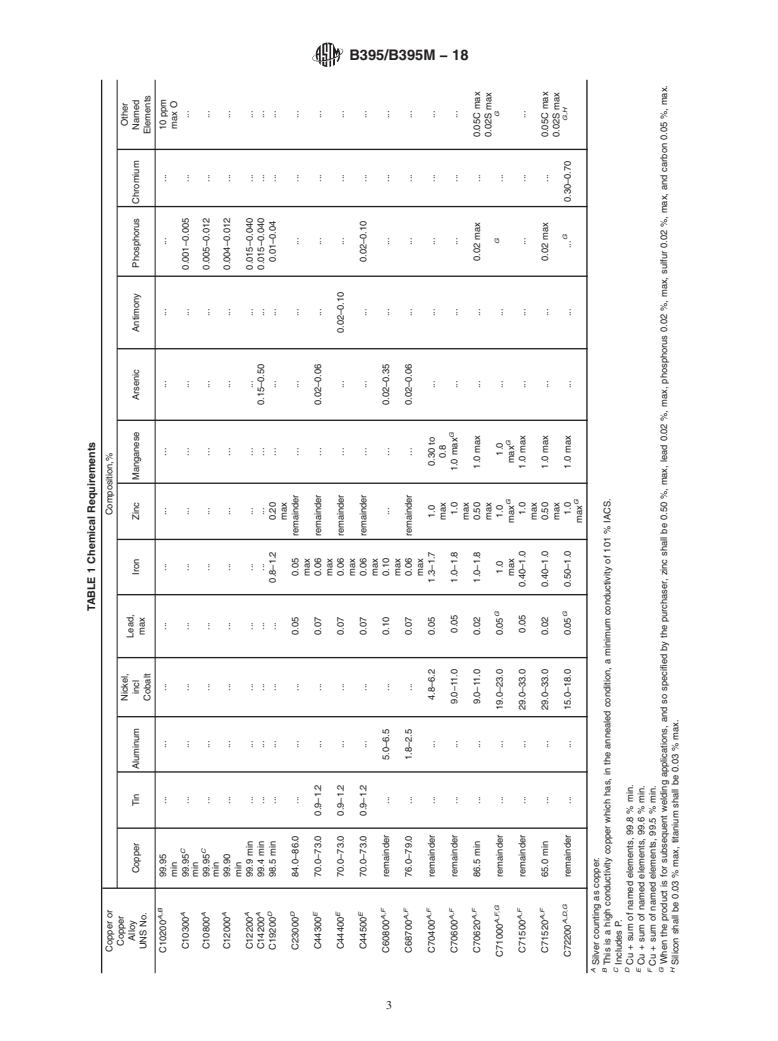
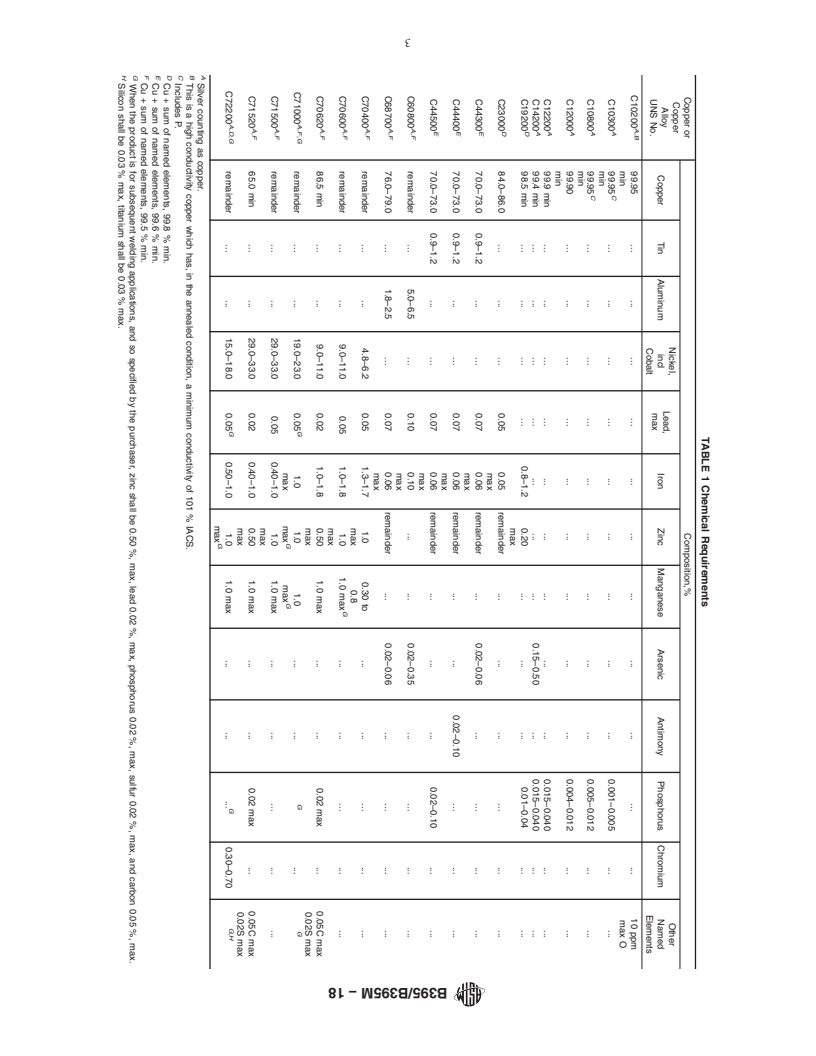
1.4 The product shall be produced from one of the following coppers or copper alloys, as specified in the ordering information:
Copper or
Copper Alloy
UNS No.
Previously Used
Designation
Type of Metal
C10200
OFA
oxygen-free without residual deoxidants
C10300
...
oxygen-free, extra low phosphorus
C10800
...
oxygen-free, low phosphorus
C12000
DLPA
phosphorized, low residual phosphorus
C12200
DHPA
phosphorized, high residual phosphorus
C14200
DPAA
phosphorized, arsenical
C19200
...
phosphorized, 1 % iron
C23000
...
red brass
C44300
Type B
admiralty metal
C44400
Type C
admiralty metal
C44500
Type D
admiralty metal
C60800
...
aluminum bronze
C68700
Type B
aluminum brass
C70400
...
95-5 copper-nickel
C70600
...
90-10 copper-nickel
C70620
...
90-10 copper-nickel-
(modified for welding)
C71000
...
80-20 copper-nickel
C71500
...
70-30 copper-nickel
C71520
...
70-30 copper-nickel-
(modified for welding)
C72200
...
copper-nickel(A) Designations listed in Classification B224.
1.5 The following safety hazard caveat pertains only to the test methods described in this specification.
1.5.1 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. (Warning—Mercury has been designated by many regulatory agencies as a hazardous substance that can cause serious medical issues. Mercury, or its vapor, has been demonstrated to be hazardous to health and corrosive to materials. Caution should be taken when handling mercury and mercury containing products. See the applicable product Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for additional information. Users should be awar...
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:B395/B395M −18
Standard Specification for
U-Bend Seamless Copper and Copper Alloy Heat Exchanger
1
and Condenser Tubes
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B395/B395M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
Copper or
Previously Used
Copper Alloy Type of Metal
2
Designation
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for
UNS No.
condenser, evaporator, and heat exchanger U-bend tubes that
C70400 . 95-5 copper-nickel
are manufactured from seamless copper and copper alloy tube.
C70600 . 90-10 copper-nickel
C70620 . 90-10 copper-nickel-
1.2 Units—The values stated in either SI units or inch-
(modified for welding)
pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within
C71000 . 80-20 copper-nickel
the text, SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in
C71500 . 70-30 copper-nickel
C71520 . 70-30 copper-nickel-
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
(modified for welding)
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
C72200 . copper-nickel
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
A
with the standard.
Designations listed in Classification B224.
1.3 Thisspecificationisapplicabletoproduct2in.[50mm] 1.5 The following safety hazard caveat pertains only to the
test methods described in this specification.
or less, inclusive, in diameter.
1.5.1 This standard does not purport to address all of the
1.4 Theproductshallbeproducedfromoneofthefollowing
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
coppers or copper alloys, as specified in the ordering informa-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
tion:
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
Copper or
Previously Used
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Copper Alloy Type of Metal
Designation
UNS No. (Warning—Mercury has been designated by many regulatory
agencies as a hazardous substance that can cause serious
A
C10200 OF oxygen-free without residual deoxidants
medical issues. Mercury, or its vapor, has been demonstrated to
C10300 . oxygen-free, extra low phosphorus
C10800 . oxygen-free, low phosphorus be hazardous to health and corrosive to materials. Caution
A
C12000 DLP phosphorized, low residual phosphorus
should be taken when handling mercury and mercury contain-
A
C12200 DHP phosphorized, high residual
ing products. See the applicable product Safety Data Sheet
phosphorus
A
C14200 DPA phosphorized, arsenical (SDS) for additional information. Users should be aware that
C19200 . phosphorized, 1 % iron
selling mercury and/or mercury containing products into your
C23000 . red brass
state or country may be prohibited by law.)
C44300 Type B admiralty metal
C44400 Type C admiralty metal
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
C44500 Type D admiralty metal
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
C60800 . aluminum bronze
C68700 Type B aluminum brass
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
1
ThisspecificationisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeB05onCopper
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
and CopperAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.04 on Pipe
and Tube.
2. Referenced Documents
Current edition approved March 1, 2018. Published April 2018. Originally
approved in 1962. Last previous edition approved in 2016 as B395/B395M–16.
2.1 The following documents of the issue in effect on date
DOI: 10.1520/B0395_B0395M-18.
2 of material purchase form a part of this specification to the
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications see related Specifi-
cation SB-395 in Section II of that Code. extent referenced herein:
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B395/B395M−18
3
2.2 ASTM Standards: 3.2.3 u-bend tube, n—atubebent180°inasingleplaneinto
B153Test Method for Expansion (Pin Test) of Copper and a U-shape.
Copper-Alloy Pipe and Tubing
4. Ordering Information
B154Test Method for Mercurous Nitrate Test for Copper
Alloys
4.1 Includ
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: B395/B395M − 16 B395/B395M − 18
Standard Specification for
U-Bend Seamless Copper and Copper Alloy Heat Exchanger
1
and Condenser Tubes
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B395/B395M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
2
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for condenser, evaporator, and heat exchanger U-bend tubes that are
manufactured from seamless copper and copper alloy tube.
1.2 Units—The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text,
SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used
independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.3 This specification is applicable to product 2 in. [50 mm] or less, inclusive, in diameter.
1.4 The product shall be produced from one of the following coppers or copper alloys, as specified in the ordering information:
Copper or
Previously Used
Copper Alloy Type of Metal
Designation
UNS No.
A
C10200 OF oxygen-free without residual deoxidants
C10300 . oxygen-free, extra low phosphorus
C10800 . oxygen-free, low phosphorus
A
C12000 DLP phosphorized, low residual phosphorus
A
C12200 DHP phosphorized, high residual
phosphorus
A
C14200 DPA phosphorized, arsenical
C19200 . phosphorized, 1 % iron
C23000 . red brass
C44300 Type B admiralty metal
C44400 Type C admiralty metal
C44500 Type D admiralty metal
C60800 . aluminum bronze
C68700 Type B aluminum brass
C70400 . 95-5 copper-nickel
C70600 . 90-10 copper-nickel
C70620 . 90-10 copper-nickel-
(modified for welding)
C71000 . 80-20 copper-nickel
C71500 . 70-30 copper-nickel
C71520 . 70-30 copper-nickel-
(modified for welding)
C72200 . copper-nickel
A
Designations listed in Classification B224.
1.5 The following safety hazard caveat pertains only to the test methods described in this specification.
1.5.1 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. (Warning—Mercury has been designated by many regulatory agencies as a
hazardous substance that can cause serious medical issues. Mercury, or its vapor, has been demonstrated to be hazardous to health
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B05 on Copper and Copper Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.04 on Pipe and
Tube.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2016March 1, 2018. Published November 2016April 2018. Originally approved in 1962. Last previous edition approved in 20132016
as B395/B395M – 13.B395/B395M – 16. DOI: 10.1520/B0395_B0395M-16.10.1520/B0395_B0395M-18.
2
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications see related Specification SB-395 in Section II of that Code.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B395/B395M − 18
and corrosive to materials. Caution should be taken when handling mercury and mercury containing products. See the applicable
product Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for additional information. Users should be aware that selling mercury and/or mercury
containing products into your state or country may be prohibited by law.)
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 The following documents of the issue in effect on date of material purchase form a part of this specification to the extent
referenced herein:
3
2.2 ASTM Standards:
B153 Test Method for Expansion (Pin Test) of Copper and Copper-Alloy Pipe a
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.