ASTM F488-95
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for On-site Screening of Heterotrophic Bacteria in Water (Withdrawn 2004)
Standard Test Method for On-site Screening of Heterotrophic Bacteria in Water (Withdrawn 2004)
SCOPE
1.1 This screening test method covers the detection and enumeration of bacteria contained in a water sample employing a commercial device specifically designed for that purpose. This test method applies only to the enumeration of those viable bacteria that will grow under the test conditions specified (for example, medium, temperature, time, etc.). It is not applicable to the detection of anaerobic bacteria.
1.2 No bacterial culture technique can enumerate all the viable bacteria in a sample, since bacteria occur singly, in pairs, chains, or clusters and no single set of growth conditions or media can satisfy the physiological requirements of all bacteria in a sample. Therefore, this test method cannot provide a total bacterial count, but can only strive to achieve a relative count of viable aerobic and facultative anaerobic bacteria present in a sample.
1.3 The test method applies to samples in which the number of culturable bacteria per millilitre exceeds at least 10 and no more than 160 bacteria/mL in the sample or sample dilution.
1.4 This test method is intended to be used as a simplified field method where bacteriological laboratory facilities are not readily available.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact ASTM
International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
An American National Standard
Designation:F 488–95
Standard Test Method for
1
On-Site Screening of Heterotrophic Bacteria in Water
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 488; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer
to Terminology D 1129.
1.1 This screening test method covers the detection and
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
enumerationofbacteriacontainedinawatersampleemploying
3.2.1 dynamic system—a system or container in which the
a commercial device specifically designed for that purpose.
water contained is in motion.
This test method applies only to the enumeration of those
3.2.2 estimated bacterial count—the number of bacteria
viable bacteria that will grow under the test conditions speci-
present in a 1.0-mLsample that can be cultured into individual,
fied (for example, medium, temperature, time, etc.). It is not
countable colonies by the technique described in this test
applicable to the detection of anaerobic bacteria.
method.
1.2 No bacterial culture technique can enumerate all the
3.2.3 static system—a system or container in which the
viablebacteriainasample,sincebacteriaoccursingly,inpairs,
water is not in motion. Water held in a bottle or storage tank is
chains, or clusters and no single set of growth conditions or
an example of a static system.
media can satisfy the physiological requirements of all bacteria
3.2.4 CFU—colony forming units.
in a sample. Therefore, this test method cannot provide a total
3.2.4.1 Discussion—Examples are a pump-driven water
bacterial count, but can only strive to achieve a relative count
circulating system and a flowing-water purification line.
of viable aerobic and facultative anaerobic bacteria present in
a sample.
4. Summary of Test Method
1.3 The test method applies to samples in which the number
3
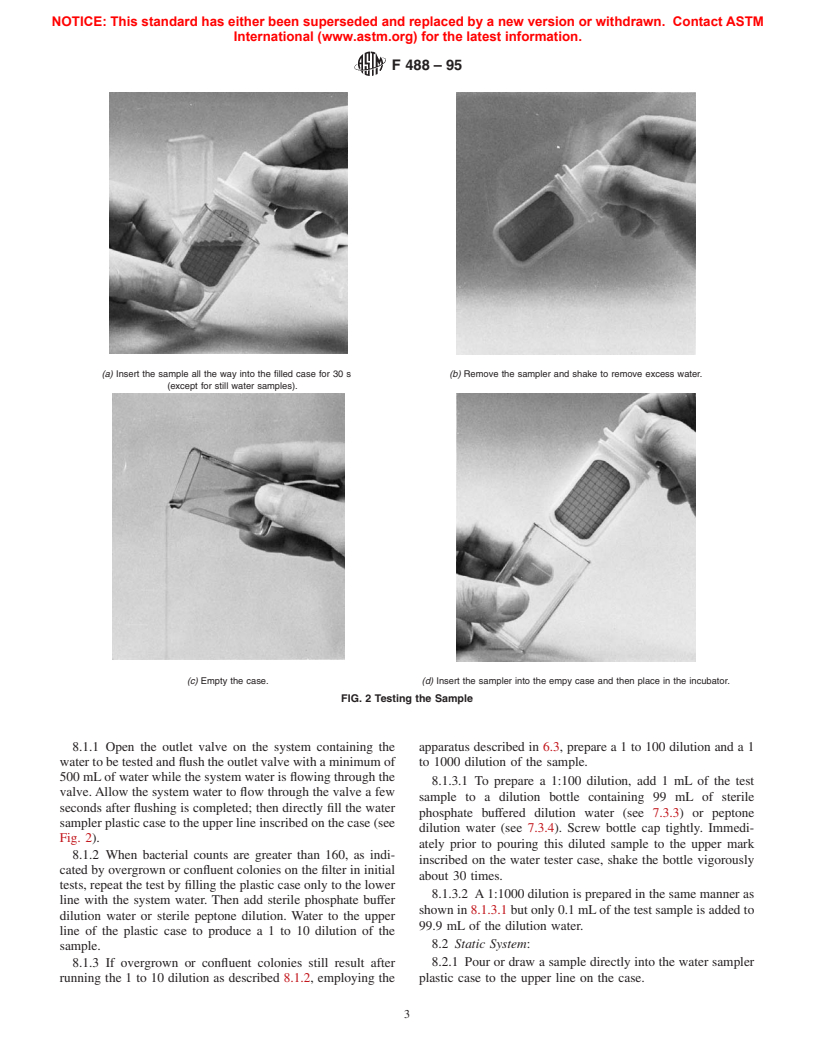
4.1 A commercially available water sampler device (SPC
of culturable bacteria per millilitre exceeds at least 10 and no
Sampler) is immersed in a water sample. A1.0-mL volume is
more than 160 bacteria/mL in the sample or sample dilution.
automatically drawn through a 0.45-um pore size bacteria
1.4 This test method is intended to be used as a simplified
retentive membrane filter into a backing pad of absorbent
field method where bacteriological laboratory facilities are not
material. The absorbent pad, sealed to the back of the filter
readily available.
contains a dehydrated nutrient medium which hydrates and
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
diffuses through the filter.The water sampler is then incubated,
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
and the bacteria trapped on the filter surface grow into visible
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
colonies. The colonies may be counted directly or preferably
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
with low-power magnification.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
4.2 With high bacterial count samples, a suitable dilution is
2. Referenced Documents prepared prior to conducting the test described in 4.1.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5. Significance and Use
2
D 1129 Terminology Relating to Water
2 5.1 This test method provides a means for locating the
D 1193 Specification for Reagent Water
source of bacterial contaminations in a system.
D 3370 Practices for Sampling Water from Closed Con-
2
5.2 This is a screening test method that should be limited to
duits
use in estimating levels of bacterial contamination in a system.
3. Terminology Thistestmethodisintendedtoprovideasimplefieldtechnique
toward estimating the bacteria count in samples of water. Since
3.1 Definitions:
the method employs a 1-mL sample, it is not statistically
significant unless the culturable bacteria are present in greater
than 10 cfu/mL.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D-19 on Water
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D19.24 on Water Microbiology.
Current edition approved April 15, 1995. Published August 1995. Originally
e1 3
published as F 488 – 76 T. Last previous edition F 488 – 79 . A SPC Sampler, available from Millipore Corp., Bedford, MA 01730, or its
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol. 11.01. equivalent, has been found suitable for this purpose.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdraw
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.