ASTM E454-12(2016)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Industrial Perforated Plate and Screens (Square Opening Series)
Standard Specification for Industrial Perforated Plate and Screens (Square Opening Series)
ABSTRACT
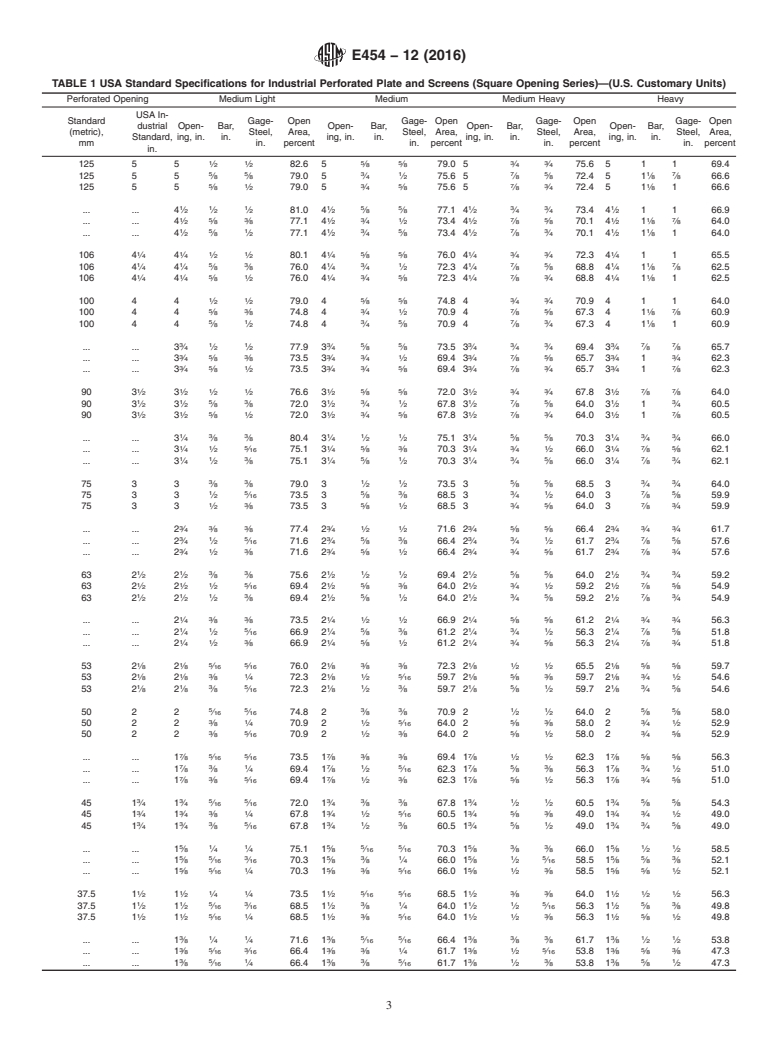
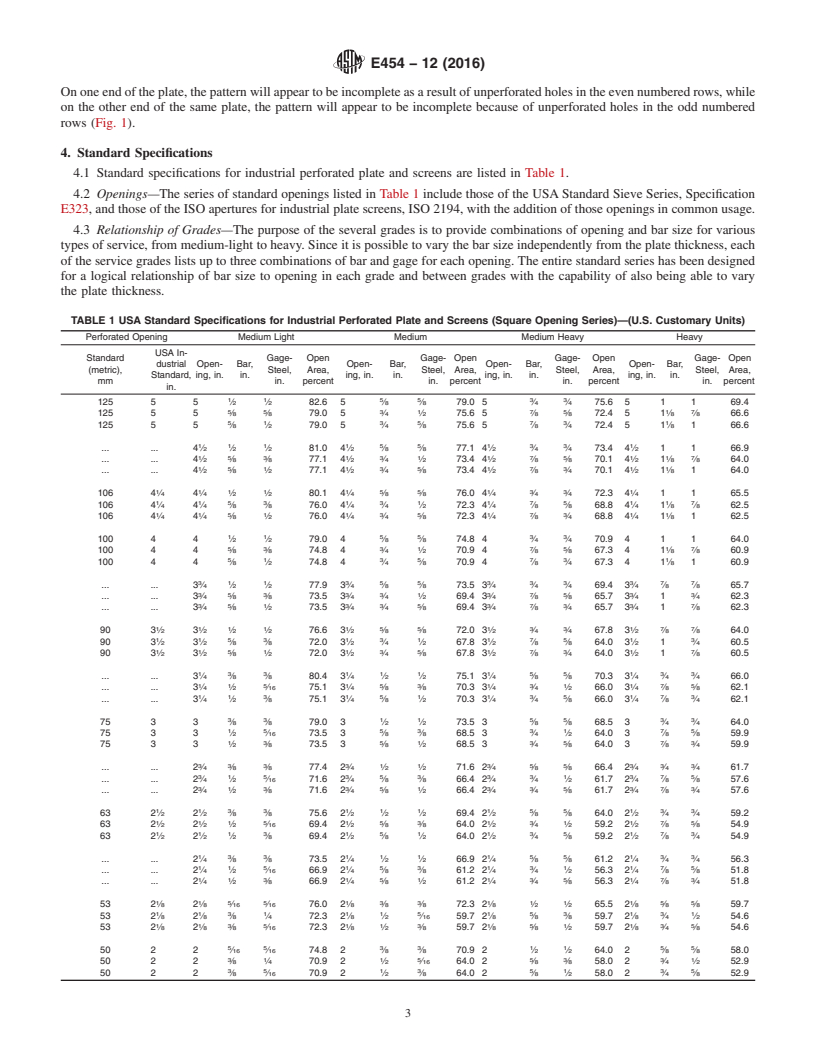
This specification covers the various sizes of square opening perforated plates and screens for general industrial uses, including the separating or grading of materials according to designated nominal particle size, and lists standards for openings punched with various bar sizes and thicknesses of plate for various grades of service. This specification does not apply to perforated plate or screens with round, hexagon, slotted, or other shaped openings.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers the sizes of square opening perforated plate and screens for general industrial uses, including the separating or grading of materials according to designated nominal particle size, and lists standards for openings from 5 in. (125 mm) to 0.127 (1/8 ) in. (3.35 mm) punched with bar sizes and thicknesses of plate for various grades of service. Methods of checking industrial perforated plate and screens are included as information in Annex A3.
1.2 This specification does not apply to perforated plate or screens with round, hexagon, slotted, or other shaped openings.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:E454 −12 (Reapproved 2016)
Standard Specification for
Industrial Perforated Plate and Screens (Square Opening
1
Series)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E454; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
Industrial perforated plate can be produced in many thousands of combinations of size and shape
of opening, bar size, thickness of material, and type of metal. Such variety is often confusing and, to
the vast majority of perforated plate users, unnecessary, since each usually requires only a very few
specifications.
The purpose of this specification is to simplify this problem by a condensed table of recommended
specifications covering a wide range of openings in which industrial perforated plate is made, with
several recommended bar sizes and thicknesses of plate for each opening, for use in various grades of
service.
By making selections from this standard, the user will be guided to specifications that are being
regularly produced, thus avoiding inadvertent selection of specifications that, because of little or no
demand,areunobtainable,exceptonspecialorder(usuallyquiteexpensiveunlessthequantityordered
is sufficient to justify the cost of special tooling).
Ifauserhasaspecificapplicationforindustrialperforatedplatethatcannotbesolvedbyaselection
from this standard, it is recommended that he consult his perforated plate supplier on the availability
of an acceptable alternative specification.
1. Scope responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
1.1 This specification covers the sizes of square opening
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
perforated plate and screens for general industrial uses, includ-
ing the separating or grading of materials according to desig-
2. Referenced Documents
nated nominal particle size, and lists standards for openings
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1
from 5 in. (125 mm) to 0.127 ( ⁄8) in. (3.35 mm) punched with
E323 Specification for Perforated-Plate Sieves for Testing
bar sizes and thicknesses of plate for various grades of service.
Purposes
Methodsofcheckingindustrialperforatedplateandscreensare
E1638 Terminology Relating to Sieves, Sieving Methods,
included as information in Annex A3.
and Screening Media
1.2 This specification does not apply to perforated plate or 3
2.2 ISO Standards:
screenswithround,hexagon,slotted,orothershapedopenings.
ISO 2194 Industrial screens —Woven wire cloth, perforated
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded plate and electroformed sheet — Designation and nominal
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical sizes of openings
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
1
ThisspecificationisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeE29onParticle contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
and Spray Characterization and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E29.01 Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
on Sieves, Sieving Methods, and Screening Media. the ASTM website.
3
Current edition approved July 1, 2016. Published July 2016. Originally approved Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 1, ch. de
in 1972. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as E454 – 12. DOI: 10.1520/ la Voie-Creuse, Case postale 56, CH-1211, Geneva 20, Switzerland, http://
E0454-12R16. www.iso.ch.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E454−12 (2016)
FIG. 1Unfinished End Pattern Finished End Pattern
2.3 Other Documents: 3.2.11 perforated pattern, n—the patterns that the perfora-
4
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies) tions are arranged in, usually in a staggered pattern with
4
Mil-Std-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage midpoints nominally at the vertices of isosceles triangles or
square patterns arranged in line with their midpoints nominally
3. Terminology
at the vertices of squares.
3.2.12 screen, n—(1) surface provided with apertures of
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 For general terms related to sieves, sieving methods, uniform size and shape; (2) another term used interchangeably
for woven wire cloth; (3) machine provided with one
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E454 − 12 E454 − 12 (Reapproved 2016)
Standard Specification for
Industrial Perforated Plate and Screens (Square Opening
1
Series)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E454; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
Industrial perforated plate can be produced in many thousands of combinations of size and shape
of opening, bar size, thickness of material, and type of metal. Such variety is often confusing and, to
the vast majority of perforated plate users, unnecessary, since each usually requires only a very few
specifications.
The purpose of this specification is to simplify this problem by a condensed table of recommended
specifications covering a wide range of openings in which industrial perforated plate is made, with
several recommended bar sizes and thicknesses of plate for each opening, for use in various grades of
service.
By making selections from this standard, the user will be guided to specifications that are being
regularly produced, thus avoiding inadvertent selection of specifications that, because of little or no
demand, are unobtainable, except on special order (usually quite expensive unless the quantity ordered
is sufficient to justify the cost of special tooling).
If a user has a specific application for industrial perforated plate that can not be solved by a selection
from this standard, it is recommended that he consult his perforated plate supplier on the availability
of an acceptable alternative specification.
1. Scope*Scope
1.1 This specification covers the sizes of square opening perforated plate and screens for general industrial uses, including the
separating or grading of materials according to designated nominal particle size, and lists standards for openings from 5 in. (125
1
mm) to 0.127 ( ⁄8) in. (3.35 mm) punched with bar sizes and thicknesses of plate for various grades of service. Methods of checking
industrial perforated plate and screens are included as information in Annex A3.
1.2 This specification does not apply to perforated plate or screens with round, hexagon, slotted, or other shaped openings.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E323 Specification for Perforated-Plate Sieves for Testing Purposes
E1638 Terminology Relating to Sieves, Sieving Methods, and Screening Media
3
2.2 ISO Standards:
ISO 2194 Industrial screens — Woven wire cloth, perforated plate and electroformed sheet — Designation and nominal sizes
of openings
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E29 on Particle and Spray Characterization and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E29.01 on
Sieves, Sieving Methods, and Screening Media.
Current edition approved June 15, 2012July 1, 2016. Published June 2012 July 2016. Originally approved in 1972. Last previous edition approved in 20112012 as
E454 – 11.E454 – 12. DOI: 10.1520/E0454-12.10.1520/E0454-12R16.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 1, ch. de la Voie-Creuse, Case postale 56, CH-1211, Geneva 20, Switzerland, http://www.iso.ch.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E454 − 12 (2016)
FIG. 1 UnfinishedUnfinished End Pattern Finished Pattern Finished End Pat-
tern
2.3 Other Documents:
4
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies)
4
Mil-Std-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.